Abstract
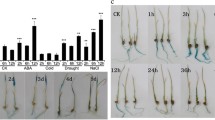
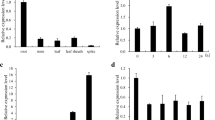
High salinity causes remarkable losses in rice productivity worldwide mainly because it inhibits growth and reduces grain yield. To cope with environmental changes, plants evolved several adaptive mechanisms, which involve the regulation of many stress-responsive genes. Among these, we have chosen OsRMC to study its transcriptional regulation in rice seedlings subjected to high salinity. Its transcription was highly induced by salt treatment and showed a stress-dose-dependent pattern. OsRMC encodes a receptor-like kinase described as a negative regulator of salt stress responses in rice. To investigate how OsRMC is regulated in response to high salinity, a salt-induced rice cDNA expression library was constructed and subsequently screened using the yeast one-hybrid system and the OsRMC promoter as bait. Thereby, two transcription factors (TFs), OsEREBP1 and OsEREBP2, belonging to the AP2/ERF family were identified. Both TFs were shown to bind to the same GCC-like DNA motif in OsRMC promoter and to negatively regulate its gene expression. The identified TFs were characterized regarding their gene expression under different abiotic stress conditions. This study revealed that OsEREBP1 transcript level is not significantly affected by salt, ABA or severe cold (5 °C) and is only slightly regulated by drought and moderate cold. On the other hand, the OsEREBP2 transcript level increased after cold, ABA, drought and high salinity treatments, indicating that OsEREBP2 may play a central role mediating the response to different abiotic stresses. Gene expression analysis in rice varieties with contrasting salt tolerance further suggests that OsEREBP2 is involved in salt stress response in rice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal PK, Jha B (2010) Transcription factors in plants and ABA dependent and independent abiotic stress signalling. Biol Plant 54(2):201–212. doi:10.1007/s10535-010-0038-7
Allen MD, Yamasaki K, Ohme-Takagi M, Tateno M, Suzuki M (1998) A novel mode of DNA recognition by a beta-sheet revealed by the solution structure of the GCC-box binding domain in complex with DNA. EMBO J 17(18):5484–5496. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.18.5484
Anthony RG, Henriques R, Helfer A, Meszaros T, Rios G, Testerink C, Munnik T, Deak M, Koncz C, Bogre L (2004) A protein kinase target of a PDK1 signalling pathway is involved in root hair growth in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 23(3):572–581. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600068
Bossi F, Cordoba E, Dupre P, Mendoza MS, Roman CS, Leon P (2009) The Arabidopsis ABA-INSENSITIVE (ABI) 4 factor acts as a central transcription activator of the expression of its own gene, and for the induction of ABI5 and SBE2.2 genes during sugar signaling. Plant J 59(3):359–374. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03877.x
Cao YF, Wu YF, Zheng Z, Song FM (2005) Overexpression of the rice EREBP-like gene OsBIERF3 enhances disease resistance and salt tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Physiol Mol Plant P 67(3–5):202–211. doi:10.1016/j.pmpp.2006.01.004
Cao Y, Song F, Goodman RM, Zheng Z (2006) Molecular characterization of four rice genes encoding ethylene-responsive transcriptional factors and their expressions in response to biotic and abiotic stress. J Plant Physiol 163(11):1167–1178. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2005.11.004
Chao DY, Luo YH, Shi M, Luo D, Lin HX (2005) Salt-responsive genes in rice revealed by cDNA microarray analysis. Cell Res 15(10):796–810. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290349
Chen Z (2001) A superfamily of proteins with novel cysteine-rich repeats. Plant Physiol 126(2):473–476. doi:10.1104/pp.126.2.473
Cheng C, Yun KY, Ressom HW, Mohanty B, Bajic VB, Jia Y, Yun SJ, de los Reyes BG (2007) An early response regulatory cluster induced by low temperature and hydrogen peroxide in seedlings of chilling-tolerant japonica rice. BMC Genomics 8:175. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-175
Cheong YH, Moon BC, Kim JK, Kim CY, Kim MC, Kim IH, Park CY, Kim JC, Park BO, Koo SC, Yoon HW, Chung WS, Lim CO, Lee SY, Cho MJ (2003) BWMK1, a rice mitogen-activated protein kinase, locates in the nucleus and mediates pathogenesis-related gene expression by activation of a transcription factor. Plant Physiol 132(4):1961–1972. doi:10.1104/pp.103.023176
Chung S, Parish RW (2008) Combinatorial interactions of multiple cis-elements regulating the induction of the Arabidopsis XERO2 dehydrin gene by abscisic acid and cold. Plant J 54(1):15–29. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03399.x
Contreras-Moreira B (2010) 3D-footprint: a database for the structural analysis of protein-DNA complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 38(Database issue):D91–D97. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp781
Cotsaftis O, Plett D, Johnson AA, Walia H, Wilson C, Ismail AM, Close TJ, Tester M, Baumann U (2011) Root-specific transcript profiling of contrasting rice genotypes in response to salinity stress. Mol Plant 4(1):25–41. doi:10.1093/mp/ssq056ssq056
Cotsaftis O, Plett D, Shirley N, Tester M, Hrmova M (2012) A two-staged model of Na+ exclusion in rice explained by 3D modeling of HKT transporters and alternative splicing. PLoS ONE 7(7):e39865. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039865
Cutcliffe JW, Hellmann E, Heyl A, Rashotte AM (2011) CRFs form protein–protein interactions with each other and with members of the cytokinin signalling pathway in Arabidopsis via the CRF domain. J Exp Bot 62(14):4995–5002. doi:10.1093/jxb/err199
Dietz KJ, Vogel MO, Viehhauser A (2010) AP2/EREBP transcription factors are part of gene regulatory networks and integrate metabolic, hormonal and environmental signals in stress acclimation and retrograde signalling. Protoplasma 245(1–4):3–14. doi:10.1007/s00709-010-0142-8
Dixit R, Nasrallah ME, Nasrallah JB (2000) Post-transcriptional maturation of the S receptor kinase of Brassica correlates with co-expression of the S-locus glycoprotein in the stigmas of two Brassica strains and in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 124(1):297–311. doi:10.1104/pp.124.1.297
Dubos C, Stracke R, Grotewold E, Weisshaar B, Martin C, Lepiniec L (2010) MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 15(10):573–581. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2010.06.005
Figueiredo DD, Barros PM, Cordeiro AM, Serra TS, Lourenco T, Chander S, Oliveira MM, Saibo NJ (2012) Seven zinc-finger transcription factors are novel regulators of the stress responsive gene OsDREB1B. J Exp Bot 63(10):3643–3656. doi:10.1093/jxb/ers035
Fujimoto SY, Ohta M, Usui A, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2000) Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors act as transcriptional activators or repressors of GCC box-mediated gene expression. Plant Cell 12(3):393–404. doi:10.2307/3870944
Garvie CW, Wolberger C (2001) Recognition of specific DNA sequences. Mol Cell 8(5):937–946. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00392-6
Gutterson N, Reuber TL (2004) Regulation of disease resistance pathways by AP2/ERF transcription factors. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7(4):465–471. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2004.04.007
Ham BK, Park JM, Lee SB, Kim MJ, Lee IJ, Kim KJ, Kwon CS, Paek KH (2006) Tobacco Tsip1, a DnaJ-type Zn finger protein, is recruited to and potentiates Tsi1-mediated transcriptional activation. Plant Cell 18(8):2005–2020. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.043158
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.51.1.463
Hauser F, Horie T (2010) A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K(+)/Na(+) ratio in leaves during salinity stress. Plant, Cell Environ 33(4):552–565. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02056.x
Hu XJ, Zhang ZB, Xu P, Fu ZY, Hu SB, Song WY (2010) Multifunctional genes: the cross-talk among the regulation networks of abiotic stress responses. Biol Plant 54(2):213–223. doi:10.1007/s10535-010-0039-6
Huang Z, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Zhang H, Huang D, Huang R (2004) Tomato TERF1 modulates ethylene response and enhances osmotic stress tolerance by activating expression of downstream genes. FEBS Lett 573(1–3):110–116. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.07.064
Jeong S, Trotochaud AE, Clark SE (1999) The Arabidopsis CLAVATA2 gene encodes a receptor-like protein required for the stability of the CLAVATA1 receptor-like kinase. Plant Cell 11(10):1925–1934. doi:10.2307/3871087
Jiang J, Li J, Xu Y, Han Y, Bai Y, Zhou G, Lou Y, Xu Z, Chong K (2007) RNAi knockdown of Oryza sativa root meander curling gene led to altered root development and coiling which were mediated by jasmonic acid signalling in rice. Plant, Cell Environ 30(6):690–699. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01663.x
Kachroo A, Nasrallah ME, Nasrallah JB (2002) Self-incompatibility in the Brassicaceae: receptor-ligand signaling and cell-to-cell communication. Plant Cell 14:S227–S238. doi:10.1105/tpc.010440
Kader MA, Lindberg S (2005) Uptake of sodium in protoplasts of salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant cultivars of rice, Oryza sativa L. determined by the fluorescent dye SBFI. J Exp Bot 56(422):3149–3158. doi:10.1093/jxb/eri312
Kader MA, Seidel T, Golldack D, Lindberg S (2006) Expressions of OsHKT1, OsHKT2, and OsVHA are differentially regulated under NaCl stress in salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J Exp Bot 57(15):4257–4268. doi:10.1093/jxb/erl199
Kazan K (2006) Negative regulation of defence and stress genes by EAR-motif-containing repressors. Trends Plant Sci 11(3):109–112. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2006.01.004
Kumari S, Sabharwal VP, Kushwaha HR, Sopory SK, Singla-Pareek SL, Pareek A (2009) Transcriptome map for seedling stage specific salinity stress response indicates a specific set of genes as candidate for saline tolerance in Oryza sativa L. Funct Integr Genomics 9(1):109–123. doi:10.1007/s10142-008-0088-5
Lee KS, Choi WY, Ko JC, Kim TS, Gregorio GB (2003) Salinity tolerance of japonica and indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) at the seedling stage. Planta 216(6):1043–1046. doi:10.1007/s00425-002-0958-3
Liu F, Xu W, Wei Q, Zhang Z, Xing Z, Tan L, Di C, Yao D, Wang C, Tan Y, Yan H, Ling Y, Sun C, Xue Y, Su Z (2010) Gene expression profiles deciphering rice phenotypic variation between Nipponbare (Japonica) and 93–11 (Indica) during oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 5(1):e8632. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008632
Mena M, Cejudo FJ, Isabel-Lamoneda I, Carbonero P (2002) A role for the DOF transcription factor BPBF in the regulation of gibberellin-responsive genes in barley aleurone. Plant Physiol 130(1):111–119. doi:10.1104/pp.005561
Mito T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Ohme-Takagi M, Matsui K (2011) Generation of chimeric repressors that confer salt tolerance in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Biotechnol J 9(7):736–746. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2010.00578.x
Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012) AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819(2):86–96. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.08.004
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Nakano T, Suzuki K, Fujimura T, Shinshi H (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 140(2):411–432. doi:10.1104/pp.105.073783
Negrão S, Courtois B, Ahmadi N, Abreu I, Saibo N, Oliveira MM (2011) Recent updates on salinity stress in rice: from physiological to molecular responses. Crit Rev Plant Sci 30(4):329–377. doi:10.1080/07352689.2011.587725
Negrão S, Almadanim MC, Pires IS, Abreu IA, Maroco J, Courtois B, Gregorio GB, McNally KL, Oliveira MM (2013) New allelic variants found in key rice salt-tolerance genes: an association study. Plant Biotechnol J 11(1):87–100. doi:10.1111/pbi.12010
Okamuro JK, Caster B, Villarroel R, Van Montagu M, Jofuku KD (1997) The AP2 domain of APETALA2 defines a large new family of DNA binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(13):7076–7081. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.13.7076
Ouwerkerk PBF, Meijer AH (2001) Yeast One-Hybrid screening for DNA-protein interactions. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 12.12.11–12.12.22. doi:10.1002/0471142727.mb1212s55
Pardo JM (2010) Biotechnology of water and salinity stress tolerance. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21(2):185–196. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2010.02.005
Park JM, Park CJ, Lee SB, Ham BK, Shin R, Paek KH (2001) Overexpression of the tobacco Tsi1 gene encoding an EREBP/AP2-type transcription factor enhances resistance against pathogen attack and osmotic stress in tobacco. Plant Cell 13(5):1035–1046. doi:10.2307/3871362
Rabbani MA, Maruyama K, Abe H, Khan MA, Katsura K, Ito Y, Yoshiwara K, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2003) Monitoring expression profiles of rice genes under cold, drought, and high-salinity stresses and abscisic acid application using cDNA microarray and RNA gel-blot analyses. Plant Physiol 133(4):1755–1767. doi:10.1104/pp.103.025742
Rojo E, Sharma VK, Kovaleva V, Raikhel NV, Fletcher JC (2002) CLV3 is localized to the extracellular space, where it activates the Arabidopsis CLAVATA stem cell signaling pathway. Plant Cell 14(5):969–977. doi:10.1105/tpc.002196
RoyChoudhury A, Gupta B, Sengupta DN (2008) Trans-acting factor designated OSBZ8 interacts with both typical abscisic acid responsive elements as well as abscisic acid responsive element-like sequences in the vegetative tissues of indica rice cultivars. Plant Cell Rep 27(4):779–794. doi:10.1007/s00299-007-0498-1
Sahi C, Singh A, Blumwald E, Grover A (2006) Beyond osmolytes and transporters: novel plant salt-stress tolerance-related genes from transcriptional profiling data. Physiol Plant 127(1):1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2005.00610.x
Saibo NJ, Lourenco T, Oliveira MM (2009) Transcription factors and regulation of photosynthetic and related metabolism under environmental stresses. Ann Bot 103(4):609–623. doi:10.1093/aob/mcn227
Sattelmacher B (2001) The apoplast and its significance for plant mineral nutrition. New Phytol 149(2):167–192. doi:10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00034.x
Shao HB, Guo QJ, Chu LY, Zhao XN, Su ZL, Hu YC, Cheng JF (2007) Understanding molecular mechanism of higher plant plasticity under abiotic stress. Colloids Surf B 54(1):37–45. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.07.002
Steffens NO, Galuschka C, Schindler M, Bulow L, Hehl R (2004) AthaMap: an online resource for in silico transcription factor binding sites in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32(Database issue):D368–D372. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh017
Takasaki H, Maruyama K, Kidokoro S, Ito Y, Fujita Y, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Nakashima K (2010) The abiotic stress-responsive NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC5 regulates stress-inducible genes and stress tolerance in rice. Mol Genet Genomics 284(3):173–183. doi:10.1007/s00438-010-0557-0
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24(8):1596–1599. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm092
Tang W, Ezcurra I, Muschietti J, McCormick S (2002) A cysteine-rich extracellular protein, LAT52, interacts with the extracellular domain of the pollen receptor kinase LePRK2. Plant Cell 14(9):2277–2287. doi:10.1105/tpc.003103
Tester M, Davenport R (2003) Na+ tolerance and Na+ transport in higher plants. Ann Bot 91(5):503–527. doi:10.1093/aob/mcg058
Tieman DM, Taylor MG, Ciardi JA, Klee HJ (2000) The tomato ethylene receptors NR and LeETR4 are negative regulators of ethylene response and exhibit functional compensation within a multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(10):5663–5668. doi:10.1073/pnas.090550597
Tran LS, Urao T, Qin F, Maruyama K, Kakimoto T, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2007) Functional analysis of AHK1/ATHK1 and cytokinin receptor histidine kinases in response to abscisic acid, drought, and salt stress in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(51):20623–20628. doi:10.1073/pnas.0706547105
Turatsinze JV, Thomas-Chollier M, Defrance M, van Helden J (2008) Using RSAT to scan genome sequences for transcription factor binding sites and cis-regulatory modules. Nat Protoc 3(10):1578–1588. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.97
Walia H, Wilson C, Condamine P, Liu X, Ismail AM, Zeng L, Wanamaker SI, Mandal J, Xu J, Cui X, Close TJ (2005) Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage. Plant Physiol 139(2):822–835. doi:10.1104/pp.105.065961
Walia H, Wilson C, Zeng L, Ismail AM, Condamine P, Close TJ (2007) Genome-wide transcriptional analysis of salinity stressed japonica and indica rice genotypes during panicle initiation stage. Plant Mol Biol 63(5):609–623. doi:10.1007/s11103-006-9112-0
Wang H, Huang Z, Chen Q, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Wu Y, Huang D, Huang R (2004) Ectopic overexpression of tomato JERF3 in tobacco activates downstream gene expression and enhances salt tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 55(2):183–192. doi:10.1007/s11103-004-0113-6
Wang D, Pan Y, Zhao X, Zhu L, Fu B, Li Z (2011) Genome-wide temporal-spatial gene expression profiling of drought responsiveness in rice. BMC Genomics 12:149. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-12-149
Wankhade SD, Bahaji A, Mateu-Andres I, Cornejo MJ (2010) Phenotypic indicators of NaCl tolerance levels in rice seedlings: variations in development and leaf anatomy. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 32(6):1161–1169. doi:10.1007/s11738-010-0511-0
Wen JQ, Oono K, Imai R (2002) Two novel mitogen-activated protein signaling components, OsMEK1 and OsMAP1, are involved in a moderate low-temperature signaling pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 129(4):1880–1891. doi:10.1104/pp.006072
Wu L, Chen X, Ren H, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Wang J, Wang XC, Huang R (2007) ERF protein JERF1 that transcriptionally modulates the expression of abscisic acid biosynthesis-related gene enhances the tolerance under salinity and cold in tobacco. Planta 226(4):815–825. doi:10.1007/s00425-007-0528-9
Xiong L, Lee H, Ishitani M, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of osmotic stress-responsive gene expression by the LOS6/ABA1 locus in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277(10):8588–8596. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109275200
Xu ZS, Xia LQ, Chen M, Cheng XG, Zhang RY, Li LC, Zhao YX, Lu Y, Ni ZY, Liu L, Qiu ZG, Ma YZ (2007) Isolation and molecular characterization of the Triticum aestivum L. ethylene-responsive factor 1 (TaERF1) that increases multiple stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 65(6):719–732. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9237-9
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2005) Organization of cis-acting regulatory elements in osmotic- and cold-stress-responsive promoters. Trends Plant Sci 10(2):88–94. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.012
Yoshida S, Foorno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA (eds) (1976) Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice, 3rd edn. International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos
Zarei A, Korbes AP, Younessi P, Montiel G, Champion A, Memelink J (2011) Two GCC boxes and AP2/ERF-domain transcription factor ORA59 in jasmonate/ethylene-mediated activation of the PDF1.2 promoter in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 75(4–5):321–331. doi:10.1007/s11103-010-9728-y
Zhang H, Huang Z, Xie B, Chen Q, Tian X, Zhang X, Lu X, Huang D, Huang R (2004) The ethylene-, jasmonate-, abscisic acid- and NaCl-responsive tomato transcription factor JERF1 modulates expression of GCC box-containing genes and salt tolerance in tobacco. Planta 220(2):262–270. doi:10.1007/s00425-004-1347-x
Zhang L, Tian LH, Zhao JF, Song Y, Zhang CJ, Guo Y (2009a) Identification of an apoplastic protein involved in the initial phase of salt stress response in rice root by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Plant Physiol 149(2):916–928. doi:10.1104/pp.108.131144
Zhang Y, Chen C, Jin XF, Xiong AS, Peng RH, Hong YH, Yao QH, Chen JM (2009b) Expression of a rice DREB1 gene, OsDREB1D, enhances cold and high-salt tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Bmb Rep 42(8):486–492. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2009.42.8.486
Zhao LF, Xu SB, Chai TY, Wang T (2006) OsAP2–1, an AP2-like gene from Oryza sativa, is required for flower development and male fertility. Sex Plant Reprod 19(4):197–206. doi:10.1007/s00497-006-0036-2
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. Dorothea Bartels for her critical reading of the manuscript and Dr. Pieter B. F. Ouwerkerk for his helpful advices regarding the yeast one-hybrid system. This work was supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) through national funds allocated to research projects [POCI/BIA-BCM/56063/2004 and PTDC/BIA-BCM/099836/2008] and PhD scholarships [SFRH/BD/31011/2006 to TS, SFRH/BD/29258/2006 to DF, SFRH/BD/74946/2010 to AC, SFRH/BD/65229/2009 to DA, SFRH/BPD/34943/2007 to TL]. NS and IA were supported by Programa Ciência 2007, financed by POPH (QREN). AS and BCM work was supported by funding from Programa Euroinvestigación 2008 [EUI2008-03612].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serra, T.S., Figueiredo, D.D., Cordeiro, A.M. et al. OsRMC, a negative regulator of salt stress response in rice, is regulated by two AP2/ERF transcription factors. Plant Mol Biol 82, 439–455 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0073-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-013-0073-9