Abstract
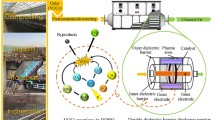
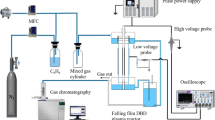
The degradation of perfluorosurfactants (PFS), particularly of PFOS, has been studied in dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) and nano-pulse corona discharge (PCD) reactors. DBD-plasma is generated in two different types of reactors. First, in a suitable falling film reactor with a planar configuration for the treatment of ca. 0.4 L PFS solution, and second, in a horizontal trough reactor for the treatment of ca. 8 L PFS contaminated water. For the comparison, the efficiency of PFS degradation by ozonation and photocatalytic ozonation processes were also examined using a similar falling film reactor, and it was found that these methods are not as efficient as the DBD plasma. The degradation of PFSs by non-thermal plasma was investigated in dependence on PFS concentration and gas atmosphere by HPLC/MS and ion chromatography. Concerning the energy yield, the nano-pulse corona is significantly more efficient than the DBD plasma. For an initial PFOS concentration of 10 mg/L the G50 of the PCD is about 200 mg/kWh, while it is less than 100 mg/kWh for the DBD reactor. Compared to the plasma in He atmosphere, in all reactors the decomposition of PFS under Ar atmosphere results in a deeper mineralization, which is expressed by fluoride recovery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Houde M, Martin JW, Letcher RJ, Solomon KR, Muir DC (2006) Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: a review. Environ Sci Technol 40(11):3463–3473
Merino N, Qu Y, Deeb RA, Hawley EL, Hoffmann MR, Mahendra S (2016) Degradation and removal methods for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water. Environ Eng Sci 33:615–649
Wang S, Yang Q, Chen F, Sun J, Luo K, Yao F, Wang X, Wanga D, Li X, Zeng G (2017) Photocatalytic degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate in water: a critical review. Chem Eng J 328:927–942
Jiang B, Zheng J, Qiu S, Wu M, Zhang Q, Yan Z, Xue Q (2014) Review on electrical discharge plasma technology for wastewater remediation. Chem Eng J 236:348–368
Magureanu M, Bradu C, Parvulescu VI (2018) Plasma processes for the treatment of water contaminated with harmful organic compounds. J Phys D Appl Phys 51:313002
Obo H, Takeuchi N, Yasuoka K (2015) Decomposition of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) by multiple alternating argon plasmas in bubbles with gas circulation. Int J Plasma Environ Sci Technol 9:62–68
Stratton GR, Dai F, Bellona CL, Holsen TM, Dickenson ERV, Mededovic-Thagard S (2017) Plasma-based water treatment: efficient transformation of perfluoroalkyl substances in prepared solutions and contaminated groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 51:1643–1648
Mededovic-Thagard S, Stratton GR, Dai F, Bellona CL, Holsen TM, Bohl DG, Eunsu P, Dickenson ERV (2017) Plasma-based water treatment: development of a general mechanistic model to estimate the treatability of different types of contaminants. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:1–13
Hama Aziz KH, Miessner H, Mueller S, Kalass D, Moeller D, Khorshid I, Rashid MAM (2017) Degradation of pharmaceutical diclofenac and ibuprofen in aqueous solution, a direct comparison of ozonation, photocatalysis, and non-thermal plasma. Chem Eng J 313:1033–1041
Hama Aziz KH, Miessner H, Mueller S, Mahyar A, Kalass D, Moeller D, Khorshid I, Rashid MAM (2018) Comparative study on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,4-dichlorophenol removal from aqueous solutions via ozonation, photocatalysis and non-thermal plasma using a planar falling film reactor. J Hazard Mater 343C:107–115
Hama Aziz KH, Mahyar A, Miessner H, Mueller S, Kalass D, Moeller D, Khorshid I, Rashid MAM (2018) Application of a planar falling film reactor for decomposition and mineralization of methylene blue in the aqueous media via ozonation, Fenton, photocatalysis and non-thermal plasma: a comparative study. Process Saf Environ 113:319–329
Malik MA (2010) Water purification by plasmas: which reactors are most energy efficient? Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30:21–31
Simister EA, Lee EM, Lu JR, Thomas RK, Ottewill RH, Rennie AR, Penfold J (1992) Adsorption of ammonium perfluorooctanoate and ammonium decanoate at the air/solution interface. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 88:3033–3041
Zhang L, Wu P, Wei Q, Shen JW, Liu Z, Ren T, Zhang W, Wang X (2016) The effect of spacer on the structure of surfactant at liquid/air interface: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J Mol Liq 222:988–994
Lin AYC, Panchangam SC, Chang CY, Hong PKA, Hsueh HF (2012) Removal of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate via ozonation under alkaline condition. J Hazard Mater 243:272–277
Hayashi R, Obo H, Takeuchi N, Yasuoka K (2015) Decomposition of perfluorinated compounds in water by DC plasma within oxygen bubbles. Electr Eng Jpn 190(3):9–16
Huang J, Wang X, Pan Z, Li X, Ling Y, Li L (2016) Efficient degradation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by photocatalytic ozonation. Chem Eng J 296:329–334
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi, Grant Number ZF4296101CR6). Our special thanks go to Vladimir Efanov and FID GmbH for providing the nano-pulse generator.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahyar, A., Miessner, H., Mueller, S. et al. Development and Application of Different Non-thermal Plasma Reactors for the Removal of Perfluorosurfactants in Water: A Comparative Study. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 39, 531–544 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-019-09977-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-019-09977-6