Abstract
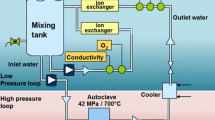
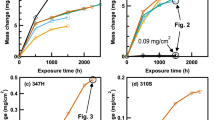
High temperature alloys are being investigated for use in cathode air pre-heater for solid oxide fuel cell systems because of their high thermal conductivity, formability, manufacturability, and superior mechanical properties. However, it is well-known that high temperature alloys often contain a high concentration of Cr which presents a risk of evaporation and contaminating the cathode of the solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC). The oxidation and Cr2O3 evaporation mechanisms of the alloys including alloy 625, SS309, and alloy 318 have been investigated by varying temperatures and water content of the exposure atmosphere. For the influence of water content, the alloys were isothermally exposed at 850 °C in dry air and air containing 1%, 3% and 9% of H2O at a high flow rate for 168 h. For the influence of temperature, the alloys were isothermally exposed at 650 °C, 750 °C and 850 °C in a 6.0 L/min air stream containing 3% H2O for 168 h. The results of this study show that Cr2O3 evaporation and oxidation rates were dramatically reduced with decreasing temperatures for alloy 625 and SS309. Alloy 318 exhibited a decreased oxidation rate with decreasing temperature, but it demonstrated a reverse trend to the temperature-dependent Cr2O3 evaporation compared to alloy 625 and SS309. The major effect of water vapour on the three tested materials appeared to be the further enhancement of Cr2O3 evaporation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. J. Naimaster and A. K. Sleiti, Energy Build. 61, 2013 (153–160).
M. Gandiglio, A. Lanzini, M. Santarelli, and P. Leone, Energy Build. 69, 2014 (381–393).
Lee H, Bush J, Hwang Y, Radermacher R. Modeling of micro-CHP (combined heat and power) unit and evaluation of system performance in building application in United States. 2013; doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.05.015.
A. Hawkes, I. Staffell, D. Brett, and N. Brandon, Energy and Environmental Science. 2, 2009 (729–744).
L. Barelli, G. Bidini, F. Gallorini, and A. Ottaviano, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 36, 2011 (3206–3214).
T. Elmer, M. Worall, S. Wu, and S. B. Riffat, Applied Thermal Engineering 90, 2015 (1082–1089).
HEATSTACK. Available at: http://www.heatstack.eu/. Accessed May 24, 2019.
H. C. Graham and H. H. Davis, Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 54, 1971 (89–93).
B. B. Ebbinghaus, Combustion and Flame 93, 1993 (119–137).
K. Hilpert, D. Das, M. Miller, D. H. Peck, and R. Weiss, Journal of Electrochemical Society 143, 1996 (3642–3647).
E. J. Opila, D. L. Myers, N. S. Jacobson, et al., Journal of Physical Chemistry A. 111, 2007 (1971–1980).
W. J. Quadakkers, J. Piron-Abellan, V. Shemet, and L. Singheiser, Materials at High Temperatures. 20, 2003 (115–127).
Asteman H, Svensson J-E, Norell M, Johansson L-G. Oxidation of Metals. 2000 54.
S. P. Jiang and X. Chen, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 39, 2014 (505–531).
R. Sachitanand, M. Sattari, J.-E.E. Svensson, and J. Froitzheim, International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 38, 2013 (15328–15334).
S. Geng, J. Zhu, M. P. Brady, H. U. Anderson, X.-D. Zhou, and Z. Yang, Journal of Power Sources. 172, 2007 (775–781).
B. A. Pint, Oxidation of Metals. 95, 2021 (335–357).
M. Stanislowski, J. Froitzheim, L. Niewolak, et al., Journal of Power Sources. 164, 2007 (578–589).
H. Falk-Windisch, J. E. Svensson, and J. Froitzheim, Journal of Power Sources. 287, 2015 (25–35).
Y. J. Park, G. Min, and J. Hong, Energy Conversion Management 182, 2019 (351–368).
C. Gindorf, L. Singheiser, and K. Hilpert, Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids. 66, 2005 (384–387).
E. J. Opila, N. S. Jacobson, D. L. Myers, and E. H. Copland, The Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materials Society. 58, 2006 (22–28).
X. Chen, Y. Zhen, J. Li, and S. P. Jiang, International Journal Hydrogen Energy 35, 2010 (2477–2485).
J. Froitzheim, H. Ravash, E. Larsson, L. G. Johansson, and J. E. Svensson, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 157, 2010 (B1295–B1300).
K. Zhang, A. El-Kharouf, J. E. Hong, and R. Steinberger-Wilckens, Corrosion Science 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108612.
C. Key, J. Eziashi, J. Froitzheim, R. Amendola, R. Smith, and P. Gannon, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 161, 2014 (C373–C381).
I. G. Wright and R. B. Dooley, International Materials Reviews. 55, 2010 (129–167).
E. A. Lass, M. R. Stoudt, M. E. Williams, et al., Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A. 48A, 2017 (5549).
D. M. Gorman, R. L. Higginson, H. Du, G. McColvin, A. T. Fry, and R. C. Thomson, Oxidation of Metals. 79, 2013 (553–566).
N. K. Othman, N. Othman, J. Zhang, and D. J. Young, Corrosion Science 51, 2009 (3039–3049).
D. J. Young, Materials Science Forum. 595–598, 2008 (1189–1197).
J. Zurek, D. J. Young, E. Essuman, et al., Materials Science and Engineering A. 477, 2008 (259–270).
P. Alnegren, M. Sattari, J. E. Svensson, and J. Froitzheim, Journal of Power Sources. 392, 2018 (129–138).
L. Jian, P. Jian, X. Jianzhong, and Q. Xiaoliang, Journal of Power Sources. 139, 2005 (182–187).
M. G. C. Cox, B. McEnaney, and V. D. Scott, Philosophical Magazine. 26, 1972 (839–851).
B. Hua, Y. Kong, W. Zhang, J. Pu, B. Chi, and L. Jian, Journal of Power Sources. 196, 2011 (7627–7638).
T. Liu, L. Wang, C. Wang, and H. Shen, Corrosion Science 104, 2016 (17–25).
P. Y. Hou and J. Stringer, Materials Science and Engineering: A. 202, 1995 (1–10).
Birks N, Meier GH, Pettit FS. Mechanisms of oxidation. In: Introduction to the High-Temperature Oxidation of Metals. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2006:39–74. doi:https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139163903.005.
Young DJ. 2016 The Nature of High Temperature Oxidation. In: High Temperature Oxidation and Corrosion of Metals, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-100101-1.00001-7.
D. Zou, Y. Zhou, X. Zhang, W. Zhang, and Y. Han, Materials Characterization 136, 2018 (435–443).
Y. Behnamian, A. Mostafaei, A. Kohandehghan, et al., Corrosion Science 106, 2016 (188–207).
K. A. Unocic and B. A. Pint, Surface Coatings Technology 237, 2013 (8–15).
F. Liu, H. Götlind, J.-E.E. Svensson, L.-G.G. Johansson, and M. Halvarsson, Corrosion Science 50, 2008 (2272–2281).
H. Buscail, S. Heinze, Ph. Dufour, and J. P. Larpin, Oxidation of Metals 47, 1997 (445–464).
H. Götlind, A. F. Liu, J.-E. Svensson, et al., Oxidation of Metals 67, 2007 (251–266).
J. Engkvist, S. Canovic, K. Hellström, et al., Oxidation of Metals 73, 2010 (233–253).
S. R. J. Saunders, M. Monteiro, and F. Rizzo, Progress in Materials Science 53, 2008 (775–837).
H. El Kadiri, R. Molins, Y. Bienvenu, and M. F. Horstemeyer, Oxidation of Metals. 64, 2005 (63–97).
I. Kvernes, M. Oliveira, and P. Kofstad, Corrosion Science 17, 1977 (237–252).
H. Al-Badairy, D. Naumenko, J. Le Coze, G. J. Tatlock, and W. J. Quadakkers, Materials at High Temperatures. 20, 2014 (405–412).
K. Onal, M. C. Maris-Sida, G. H. Meier, and F. S. Pettit, Materials at High Temperatures. 20, 2003 (327–337).
Acknowledgements
This work was part of the HEATSTACK project which was funded by the European Union’s H2020 Programme through the Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Joint Technology (FCH-JU) under grant agreement No. 700564.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KZ, AEK contributed to conception and design of study. KZ, TC contributed to acquisition of data. KZ, AEK contributed to analysis and/or interpretation of data. KZ contributed to drafting the manuscript. AEK, RSW contributed to revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. RSW contributed to approval of the version of the manuscript to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., El-Kharouf, A., Caykara, T. et al. Effect of Temperature and Water Content on the Oxidation Behaviour and Cr Evaporation of High-Cr Alloys for SOFC Cathode Air Preheaters. High Temperature Corrosion of mater. 100, 21–45 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-023-10167-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-023-10167-1