Abstract
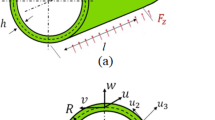
Solitary waves in hyperelastic structures propagate stably in absence of external forces. However, as the external forces increase, the stability of solitary waves may lose and then chaotic behaviors may appear. In this paper, solitary waves and chaotic motions of an infinitely long cylinder with an internal heat source are investigated. Moreover, the cylinder is composed of nearly compressible thermo-hyperelastic neo-Hookean materials. Based on the variational principle, in a non-uniform steady-state temperature field and under a uniformly distributed radial periodic load, a mathematical model describing motions of the infinite cylinder is established. The governing equations are analyzed by qualitative and bifurcation theorems. The effects of structure boundary temperature on the qualitative properties of traveling waves are examined, and the types of traveling waves are identified. By using Melnikov functions, the sufficient conditions for chaos are derived. Numerical simulations of Lyapunov exponents, bifurcation diagrams, trajectories, and time travel curves are presented to illustrate the process of the associated dynamical system from order to chaotic motions in some bifurcation sets. The numerical results are consistent with those of the theoretical analysis. The thresholds of physical parameters and sufficient conditions for chaos may provide critical information for nondestructive testing of structures.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leng, D.X., Xu, K., Qin, L.P., Ma, Y., Liu, G.J.: A hyper-elastic creep approach and characterization analysis for rubber vibration systems. Polymers 11(6), 988 (2019)
Khalajmasoumi, M., Koloor, S.S.R., Arefnia, A., Ibrahim, I.S., Mohd Yatim, J.: Hyperelastic analysis of high density polyethylene under monotonic compressive load. Appl. Mech. Mater. 229, 309–313 (2012)
Michopoulos, A., Kyriakis, N.: A new energy analysis tool for ground source heat pump systems. Energy Build. 41(9), 937–941 (2009)
Ingersoll, L.R.: Theory of the ground pipe heat source for the heat pump. Heat. Pip. Air Cond. 20, 119–122 (1948)
Kavanaugh, S. P.: Simulation and experimental verification of vertical ground-coupled heat pump systems, Ph. D. dissertation, Oklahoma State University, Stillwater (1985)
Yi, M., Yang, H., Diao, N., Liu, J., Fang, Z.: A new model and analytical solutions for borehole and pile ground heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 53(13–14), 2593–2601 (2010)
Broda, D., Staszewski, W.J., Martowicz, A., Uhl, T., Silberschmidt, V.V.: Modelling of nonlinear crack–wave interactions for damage detection based on ultrasound-a review. J. Sound Vib. 333(4), 1097–1118 (2014)
Ding, X.M., Luan, L.B., Zheng, C.J., Mei, G.X., Zhou, H.: An analytical solution for wave propagation in a pipe pile with multiple defects. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 33(2), 251–267 (2020)
Yu, Z.X., Xu, C., Du, F., Cao, S.C., Gu, L.X.: Time-domain spectral finite element method for wave propagation analysis in structures with breathing cracks. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 33, 812–822 (2020)
Korteweg, D.J., de Vries, G.: On the change of form of long waves advancing in a rectangular canal, and on a new type of long stationary waves. Philos. Mag. 39(5), 422–443 (1895)
Liu, Z.G., Zhang, J.L., Wang, Y.S., Huang, G.L.: Analytical solutions of solitary waves and their collision stability in a pre-compressed one-dimensional granular crystal. Nonlinear Dyn. 104, 4293–4309 (2021)
Zhang, N.M., Yang, G.T.: Solitary waves and chaos in nonlinear visco-elastic rod. Eur. J. Mech. 22(6), 917–923 (2003)
Zhao, G.H., Zhang, N.M., Yang, G.T.: Nonlinear complex dynamic phenomena of the perturbed metallic bar considering dissipating effect. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. 26(2), 142–149 (2005)
Wright, T.W.: Nonlinear waves in a rod: results for incompressible elastic materials. Stud. Appl. Math. 72(2), 149–160 (1985)
Cohen, H., Dai, H.H.: Nonlinear axisymmetric waves in compressible hyperelastic rods: long finite amplitude waves. Acta Mech. 100(3), 223–239 (1993)
Dai, H.H., Fan, X.: Asmptoticaliy approximate model equations for weakly nonlinear long waves in compressible elastic rods and their comparisons with other simplified model equations. Math. Mech. Solids. 9(1), 61–79 (2004)
Liu, Z., Long, Y.: Generalized kink waves in a general compressible hyperelastic rod. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 15(8), 2671–2679 (2005)
Rushchitsky, J.J.: Quadratically nonlinear cylindrical hyperelastic waves: primary analysis of evolution. Int. Appl. Mech. 41(7), 770–777 (2005)
Motaghian, S., Rahimian, M.: Nonlinear traveling wave propagation in a neo-Hookean cylindrical rod with torsional eigenstrain. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 120, 103411 (2020)
Motaghian, S., Rahimian, M.: The effects of axisymmetric radial, circumferential and longitudinal eigenstrains on the traveling wave solution in a neo-Hookean cylindrical rod. Int. J. Solids Struct. 219, 81–91 (2021)
Chen, R.M.: Some nonlinear dispersive waves arising in compressible hyperelastic plates. Int. J. Eng. Sci 44(18–19), 1188–1204 (2006)
Shearer, T., Abrahams, I.D., Parnell, J.W., Daros, H.C.: Torsional wave propagation in a pre-stressed hyperelastic annular circular cylinder. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 66(4), 465–487 (2013)
Zhang, L., Wang, J., Shchepakina, E., Sobolev, V.: New type of solitary wave solutions with coexisting crest and trough for a perturbed wave equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 106, 3479–3493 (2021)
Chen, L.L., Chang, Z., Qin, T.Y.: Elastic wave propagation in simple-sheared hyperelastic materials with different constitutive models. Int. J. Solids Struct. 126, 1–7 (2017)
Cheviakov, A.F., Ganghoffer, J.F., Jean, S.S.: Fully non-linear wave models in fiber-reinforced anisotropic incompressible hyperelastic solids. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 71, 8–21 (2015)
Galich, P.I., Slesarenko, V., Li, J., Rudykh, S.: Elastic instabilities and shear waves in hyperelastic composites with various periodic fiber arrangements. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 130, 51–61 (2018)
Il’ichev, A.T., Shargatov, V.A., Fu, Y.B.: Characterization and dynamical stability of fully nonlinear strain solitary waves in a fluid-filled hyperelastic membrane tube. Acta Mech. 231(10), 4095–4110 (2020)
Cheviakov, A., Lee, C., Naz, R.: Radial waves in fiber-reinforced axially symmetric hyperelastic media. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 95, 105649 (2021)
Xin, F.X., Lu, T.J.: Self-controlled wave propagation in hyperelastic media. Sci. Rep. 7, 7581 (2017)
Wang, R., Ding, H., Yuan, X.G., Lv, N., Chen, L.Q.: Different types of solitary waves in a thermo-hyperelastic neo-Hookean cylindrical shell. Compos. Struct. 243, 112178 (2020)
Wang, R., Ding, H., Yuan, X.G., Lv, N., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear singular traveling waves in a slightly compressible thermo-hyperelastic cylindrical shell. Nonlinear Dyn. 107, 1495–1509 (2022)
Li, J., Slesarenko, V., Rudykh, S.: Microscopic instabilities and elastic wave propagation in finitely deformed laminates with compressible hyperelastic phases. Eur. J. Mech. A-Solid. 73, 126–136 (2019)
Ramabathiran, A.A., Gopalakrishnan, S.: Time and frequency domain finite element models for axial wave analysis in hyperelastic rods. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struc. 19, 79–99 (2012)
Vallikivi, M., Salupere, A., Dai, H.H.: Numerical simulation of propagation of solitary deformation waves in a compressible hyperelastic rod. Math. Comput. Simulat. 82, 1348–1362 (2012)
Naranjo-Pérez, J., Riveiro, M., Callejas, A., Gus, G., Melchor, J.: Nonlinear torsional wave propagation in cylindrical coordinates to assess biomechanical parameters. J. Sound Vib. 445, 103–116 (2019)
Rauter, N., Lammering, R.: Investigation of the higher harmonic lamb wave generation in hyperelastic isotropic material. Phys. Procedia. 70, 309–313 (2015)
Li, G.Y., He, Q., Mangan, R., Xu, G.Q., Mo, C., Luo, J.W., Michel, D., Cao, Y.P.: Guided waves in pre-stressed hyperelastic plates and tubes: application to the ultrasound elastography of thin-walled soft materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 102, 67–79 (2017)
Mirparizi, M., Fotuhi, A.R.: Nonlinear coupled thermo-hyperelasticity analysis of thermal and mechanical wave propagation in a finite domain. Phys. A. 537, 122755 (2020)
Cheng, L.L.: Numerical modeling of flow and scour below a pipeline in currents: part I flow simulation. Coast. Eng. 52(1), 25–42 (2005)
Nicholson, D.W., Lin, B.: Theory of thermohyperelasticity for near-incompressible elastomers. Acta Mech. 116, 15–28 (1996)
Bechir, H., Benslimane, A.: On the propagation of weak shock waves in compressible thermohyperelastic solids. Acta Mech. 229(1), 87–97 (2018)
Yan, H., Tang, Y.: Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotube/natural rubber composite from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Theor. Comput. Chem. 12(3), 1350011 (2013)
Xu, F., Guo, G., Hu, K., Han, S.Y., Ma, X.N., Li, Z.S.: The research on heat transfer of combustible porous media with inner heat source. Pe. Ind. Appl. 31(2), 28–32 (2012)
Jin, H.: Design and construction of a large-diameter crude oil pipeline in Northeastern China: a special issue on permafrost pipeline. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 64(3), 209–212 (2010)
Pu, Q., Li, K., Gao, F.P.: Scour of the seabed under a pipeline in oscillating flow. China Ocean Eng. 15(1), 129–137 (2001)
Cao, H., Chi, X., Chen, G.: Suppressing or inducing chaos in a model of robot arms and mechanical manipulators. J. Sound Vib. 271(3–5), 705–724 (2004)
Amabili, M., Balasubramanian, P., Breslavsky, I.D., Ferrari, G., Garziera, R., Riabova, K.: Experimental and numerical study on vibrations and static deflection of a thin hyperelastic plate. J. Sound Vib. 385, 81–92 (2016)
Breslavsky, I.D., Amabili, M., Legrand, M.: Nonlinear vibrations of thin hyperelastic plates. J. Sound Vib. 333(19), 4668–4681 (2014)
Steinmann, P., Hossain, M., Possart, G.: Hyperelastic models for rubber-like materials: consistent tangent operators and suitability for Treloar’s data. Arch. Appl. Mech. 82(9), 1183–1217 (2012)
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 12102242, 12172199, 12172086) and the Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. 2019-01-07-00-09- E00018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, R., Ding, H., Zhang, L. et al. Solitary waves and chaos in nearly compressible thermo-hyperelastic cylinder. Nonlinear Dyn 111, 5615–5628 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-08099-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-08099-7