Abstract
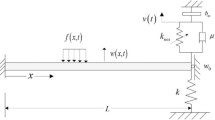
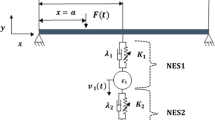
As a simplified model of structures of many kinds, the Euler Bernoulli beam has proved useful for studying vibration suppression. In order to meet engineering design requirements, inertial nonlinear energy sinks (I-NESs) can be installed on the boundaries of an elastic beam to suppress its vibration. The geometric nonlinearity of the elastic beam is here considered. Based on Hamilton's principle, the dynamic governing equations of an elastic beam are established. The steady-state response of nonlinear vibration is obtained by the harmonic balance method and verified by numerical calculation. It is found that the geometric nonlinearity of the beam principally affects the first-order main resonance and reduces the response amplitude. An uncoupled system and the coupled I-NES system both show strong nonlinear hardening characteristics. I-NES achieves good vibration suppression. Finally, the optimal range of parameters for different damping is discussed. The results show that the vibration reduction effect of an optimized inertial nonlinear energy sink can reach 90%.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerschen, G., Lee, Y.S., Vakakis, A.F., Mcfarland, D.M., Bergman, L.A.: Irreversible passive energy transfer in coupled oscillators with essential nonlinearity. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 66, 648–679 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1137/040613706
Gendelman, O., Manevitch, L.I., Vakakis, A.F., M’Closkey, R.: Energy pumping in nonlinear mechanical oscillators: part I—dynamics of the underlying hamiltonian systems. J. Appl. Mech. 68, 34–41 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1345524
Blanchard, A., Bergman, L.A., Vakakis, A.F.: Vortex-induced vibration of a linearly sprung cylinder with an internal rotational nonlinear energy sink in turbulent flow. Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 593–609 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-04775-3
Viguié, R., Peeters, M., Kerschen, G., Golinval, J.C.: Energy transfer and dissipation in a duffing oscillator coupled to a nonlinear attachment. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 4, 1–13 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3192130
Viguié, R., Kerschen, G.: Nonlinear vibration absorber coupled to a nonlinear primary system: a tuning methodology. J. Sound Vib. 326, 780–793 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2009.05.023
Gourc, E., Michon, G., Seguy, S., Berlioz, A.: Experimental investigation and design optimization of targeted energy transfer under periodic forcing. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME. 136, 1–8 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4026432
Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Designs, analysis, and applications of nonlinear energy sinks, (2020)
Bergeot, B., Bellizzi, S., Cochelin, B.: Passive suppression of helicopter ground resonance instability by means of a strongly nonlinear absorber. Adv. Aircr. Spacecr. Sci. 3, 271–298 (2016). https://doi.org/10.12989/aas.2016.3.3.271
Yang, K., Zhang, Y.W., Ding, H., Yang, T.Z., Li, Y., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear energy sink for whole-spacecraft vibration reduction. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4035377
Wang, J., Li, H., Wang, B., Liu, Z., Zhang, C.: Development of a two-phased nonlinear mass damper for displacement mitigation in base-isolated structures. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 123, 435–448 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2019.05.007
Lu, X., Liu, Z., Lu, Z.: Optimization design and experimental verification of track nonlinear energy sink for vibration control under seismic excitation. Struct. Control Heal. Monit. 24, e2033 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2033
Chen, L.Q., Li, X., Lu, Z.Q., Zhang, Y.W., Ding, H.: Dynamic effects of weights on vibration reduction by a nonlinear energy sink moving vertically. J. Sound Vib. 451, 99–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2019.03.005
Xue, J.-R., Zhang, Y.-W., Ding, H., Chen, L.-Q.: Vibration reduction evaluation of a linear system with a nonlinear energy sink under a harmonic and random excitation. Appl. Math. Mech. 41, 1–14 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2560-6
Zhang, Y., Xu, K., Zang, J., Ni, Z., Zhu, Y., Chen, L.: Dynamic design of a nonlinear energy sink with NiTiNOL-steel wire ropes based on nonlinear output frequency response functions. Appl. Math. Mech. 40, 1791–1804 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2548-9
Lu, Z., Wang, Z., Zhou, Y., Lu, X.: Nonlinear dissipative devices in structural vibration control: a review. J. Sound Vib. 423, 18–49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.02.052
Bitar, D., Ture Savadkoohi, A., Lamarque, C.H., Gourdon, E., Collet, M.: Extended complexification method to study nonlinear passive control. Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 1433–1450 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05365-z
AL-Shudeifat, M.A.: Nonlinear energy sinks with nontraditional kinds of nonlinear restoring forces. J. Vib. Acoust. 139, 1–5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4035479
AL-Shudeifat, M.A., Wierschem, N.E., Bergman, L.A., Vakakis, A.F.: Numerical and experimental investigations of a rotating nonlinear energy sink. Meccanica 52, 763–779 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-016-0422-2
Farid, M., Gendelman, O.V.: Tuned pendulum as nonlinear energy sink for broad energy range. J. Vib. Control. 23, 373–388 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546315578561
Tsiatas, G.C., Charalampakis, A.E.: A new hysteretic nonlinear energy sink (HNES). Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 60, 1–11 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2017.12.014
Habib, G., Romeo, F.: The tuned bistable nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 179–196 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3444-y
Farid, M., Gendelman, O.V., Babitsky, V.I.: Dynamics of a hybrid vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech./Zeitschrift für Angew. Math. Und. Mech. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/zamm.201800341
Zang, J., Cao, R.-Q., Zhang, Y.-W., Fang, B., Chen, L.-Q.: A lever-enhanced nonlinear energy sink absorber harvesting vibratory energy via giant magnetostrictive-piezoelectricity. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 95, 105620 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CNSNS.2020.105620
Smith, M.C.: Synthesis of mechanical networks: the inerter’. (2002)
Papageorgiou, C., Houghton, N.E., Smith, M.C.: Experimental testing and analysis of inerter devices. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 131, 1–11 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3023120
Shi, X., Zhu, S.: Dynamic characteristics of stay cables with inerter dampers. J. Sound Vib. 423, 287–305 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.02.042
Zhang, Y.W., Lu, Y.N., Zhang, W., Teng, Y.Y., Yang, H.X., Yang, T.Z., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear energy sink with inerter. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 125, 52–64 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.08.026
Zhang, Z., Lu, Z.Q., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: An inertial nonlinear energy sink. J. Sound Vib. 450, 199–213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2019.03.014
Yang, T.Z., Yang, X.D., Li, Y., Fang, B.: Passive and adaptive vibration suppression of pipes conveying fluid with variable velocity. JVC/J. Vib. Control. 20, 1293–1300 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546313480547
Mamaghani, A.E., Khadem, S.E., Bab, S.: Vibration control of a pipe conveying fluid under external periodic excitation using a nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. 86, 1761–1795 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2992-x
Geng, X., Ding, H., Wei, K., Chen, L.: Suppression of multiple modal resonances of a cantilever beam by an impact damper. Appl. Math. Mech. 41, 383–400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-020-2588-9
Ding, H., Yang, Y., Chen, L.Q., Yang, S.P.: Vibration of vehicle-pavement coupled system based on a Timoshenko beam on a nonlinear foundation. J. Sound Vib. 333, 6623–6636 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2014.07.016
Ding, H., Huang, L., Mao, X., Chen, L.: Primary resonance of traveling viscoelastic beam under internal resonance. Appl. Math. Mech. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-016-2152-6
Ding, H., Lu, Z.Q., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear isolation of transverse vibration of pre-pressure beams. J. Sound Vib. 442, 738–751 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2018.11.028
Chouvion, B.: A wave approach to show the existence of detached resonant curves in the frequency response of a beam with an attached nonlinear energy sink. Mech. Res. Commun. 95, 16–22 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechrescom.2018.11.006
Zang, J., Zhang, Y.W., Ding, H., Yang, T.Z., Chen, L.Q.: The evaluation of a nonlinear energy sink absorber based on the transmissibility. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 125, 99–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.061
Lu, Z., Li, K., Ding, H., Chen, L.: Nonlinear energy harvesting based on a modified snap-through mechanism. Appl. Math. Mech. 40, 167–180 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2408-9
Vakakis, A.F.: Passive nonlinear targeted energy transfer. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2017.0132
Li, X., Zhang, Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.: Integration of a nonlinear energy sink and a piezoelectric energy harvester. Appl. Math. Mech. 38, 1019–1030 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-017-2220-6
Parseh, M., Dardel, M., Ghasemi, M.H.: Investigating the robustness of nonlinear energy sink in steady state dynamics of linear beams with different boundary conditions. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 29, 50–71 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2015.04.020
Yang, Y., Wang, X.: Investigation into the linear velocity response of cantilever beam embedded with impact damper. JVC/J. Vib. Control. 25, 1365–1378 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546318821711
Zhang, Y.W., Hou, S., Zhang, Z., Zang, J., Ni, Z.Y., Teng, Y.Y., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear vibration absorption of laminated composite beams in complex environment. Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 2605–2622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-019-05442-3
Zhang, T., Ouyang, H., Zhang, Y.O., Lv, B.L.: Nonlinear dynamics of straight fluid-conveying pipes with general boundary conditions and additional springs and masses. Appl. Math. Model. 40, 7880–7900 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2016.03.050
Li, Y.X., Sun, L.Z.: Transverse vibration of an undamped elastically connected double-beam system with arbitrary boundary conditions. J. Eng. Mech. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889
Ding, H., Zhu, M., Chen, L.: Dynamic stiffness method for free vibration of an axially moving beam with generalized boundary conditions. Appl. Math. Mech. 40, 911–924 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2493-8
Wang, Y.R., Fang, Z.W.: Vibrations in an elastic beam with nonlinear supports at both ends. J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 56, 337–346 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021894415020200
Zang, J., Cao, R.-Q., Zhang, Y.-W.: Steady-state response of a viscoelastic beam with asymmetric elastic supports coupled to a lever-type nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dyn. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06625-7
Zhang, Z., Ding, H., Zhang, Y.W., Chen, L.Q.: Vibration suppression of an elastic beam with boundary inerter-enhanced nonlinear energy sinks. Acta Mech. Sin. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-01062-6
Ding, H., Zhu, M.H., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear vibration isolation of a viscoelastic beam. Nonlinear Dyn. 92, 325–349 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4058-8
Ding, H., Li, Y., Chen, L.Q.: Nonlinear vibration of a beam with asymmetric elastic supports. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 2543–2554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4705-0
Ding, H., Dowell, E.H., Chen, L.Q.: Transmissibility of bending vibration of an elastic beam. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4038733
Mao, X.Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Vibration of flexible structures under nonlinear boundary conditions. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037883
Mao, X.Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Passive isolation by nonlinear boundaries for flexible structures. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4042932
Acknowledgements
The work presented in this paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (12002217, 11902203, 12022213) and Liaoning Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1807172).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Gao, ZT., Fang, B. et al. Vibration suppression of a geometrically nonlinear beam with boundary inertial nonlinear energy sinks. Nonlinear Dyn 109, 1259–1275 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07490-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-022-07490-8