Abstract
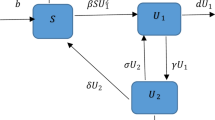
In this paper, the dynamical properties of a heroin model with nonlinear contact rate are discussed. We analyze the types of the equilibria and show that the model exhibits numerous kinds of bifurcation, such as the saddle-node bifurcation, the Hopf bifurcation, Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation of codimension 2 and so on as the parameters values vary. These results have certain effect to control the heroin prevalence.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime: World Drug Report 2012. United Nations, New York (2012)
Meiman, J., Tomasallo, C., Paulozzi, L.: Trends and characteristics of heroin overdoses in Wisconsin, 2003–2012. Drug Alcohol Depend. 152, 177–184 (2015)
Hedegaard, H., Chen, L., Warner, M.: Drug-poisoning deaths involving heroin: United States, 2000–2013. NCHS Data Brief. vol. 190 (2015)
Bowong, S., Kurths, J.: Modeling and analysis of the transmission dynamics of tuberculosis without and with seasonality. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(3), 2027–2051 (2012)
Hu, Z., Bi, P., Ma, W., Ruan, S.: Bifurcations of an SIRS epidemic model with nonlinear rate. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B. 15(1), 93–112 (2001)
Li, J., Zhao, Y., Li, S.: Fast and slow dynamics of Malaria model with relapse. Math. Biosci. 246(1), 94–104 (2013)
Li, J., Zhao, Y., Zhu, H.: Bifurcation of an SIS model with nonlinear contact rate. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 432(2), 1119–1138 (2015)
Liu, W., Levin, Simon A., Iwasa, Y.: Influence of nonlinear incidence rates upon the behavior of SIRS epidemiological models. J. Math. Biol. 23(2), 187–204 (1986)
Lizana, M., Rivero, J.: Multiparametric bifurcations for a model in epidemiology. J. Math. Biol. 35(1), 21–36 (1996)
Moghadas, S., Alexander, M.: Bifurcations of an epidemic model with nin-linear incidence and infection-dependent removal rate. Math. Med. Biol. 23(3), 231–254 (2006)
Tang, Y., Huang, D., Ruan, S., Zhang, W.: Coexistence of limit cycles and homoclinic loops in an SIRS model with a nonlinear incidence rate. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 69(2), 621–639 (2008)
Zhao, Z., Pang, L., Chen, Y.: Nonsynchronous bifurcation of SIRS epidemic model with birth pulse and pulse vaccination. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(4), 2371–2383 (2015)
Biswas, S., Saifuddin, M.D., Sasmal, K., et al.: A delayed prey–predator system with prey subject to the strong Allee effect and disease. Nonlinear Dyn. 84(3), 1569–1594 (2016)
Huang, J., Ruan, S., Song, J.: Bifurcations in a predator–prey system of Leslie type with generalized Holling type III functional response. J. Differ. Equ. 257(6), 1721–1752 (2014)
Jana, S., Guria, S., Das, U., et al.: Effect of harvesting and infection on predator in a prey–predator system. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(1), 917–930 (2015)
Li, Y., Xiao, D.: Bifurcations of a predator–prey system of Holling and Leslie types. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34(2), 606–620 (2007)
Tang, Y., Zhang, W.: Heteroclinic bifurcations in a ratio-dependent predator–prey system. J. Math. Biol. 50(6), 699–712 (2005)
Xiao, D., Ruan, S.: Bogdanov–Takens bifurcations in predator-prey systems with constant rate harvesting. Fields Inst. Commun. 21, 493–506 (1999)
White, E., Comiskey, C.: Heroin epidemics, treatment and ODE modelling. Math. Biosci. 208(1), 312–324 (2007)
Mulone, G., Straughan, B.: A note on heroin epidemics. Math. Biosci. 218(2), 138–141 (2009)
Fang, B., Li, X., Martcheva, M., Cai, L.: Global stability for a heroin model with two distributed delays. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B. 19(3), 715–733 (2014)
Huang, G., Liu, A.: A note on global stability for a heroin epidemic model with distributed delay. Appl. Math. Lett. 26(7), 687–691 (2013)
Liu, J., Zhang, T.: Global behaviour of a heroin epidemic model with distributed delays. Appl. Math. Lett. 24(10), 1685–1692 (2011)
Muroya, Y., Li, H., Kuniya, T.: Complete global analysis of an SIRS epidemic model with graded cure and incomplete recovery rates. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 410(2), 719–732 (2014)
Samanta, G.P.: Dynamic behaviour for a nonautonomous heroin epidemic model with time delay. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 35(1–2), 161–178 (2011)
Wang, X., Yang, J., Li, X.: Dynamics of a heroin epidemic model with very population. Appl. Math. 2(6), 732–738 (2011)
Zhang, Z., Ding, T., Huang, W., Dong, Z.: Qualitative Theory of Differential Equations. AMS, Providence (1992)
Perko, L.: Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems. Springer, New York (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research Supported by the NSF of China (No. 61373174).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, M., Liu, S. & Li, J. Bifurcation of a heroin model with nonlinear incidence rate. Nonlinear Dyn 88, 555–565 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3260-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3260-9