Abstract
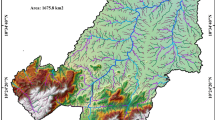
The agricultural land of the whole world is deteriorating due to the loss of top fertile soil reducing agricultural productivity and groundwater availability. Mainly, natural conditions and human manipulations have made soils extremely prone to soil erosion. Therefore, information on soil erosion status is of paramount importance to the policymakers for land conservation planning in a limited time. Spatial information systems like GIS and RS are known for their efficiencies. With that prospect, the GIS-based RUSLE model is used in this study to assess the soil erosion losses from Bhandara regions of Maharashtra, India. The study area comes under Wainganga sub-river basin, a portion of the Godavari River basin. We have prepared the required five potential parameters (R*K*LS*C*P) of RUSLE model on pixel-to-pixel basis. We have prepared the R factor map from monthly rainfall data of Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) and K factor map by digital the soil series map of NBSS & LUP, Govt. of India. We have used the digital elevation model data (DEM) of Cartosat-1 for LS-factor map, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2A satellite dataset to generate LULC and NDVI map to obtain C and P factors. The results and satellite data were validated using Google Earth Pro and field observations. The results showed significant soil erosion from the river banks and wastelands near water bodies, with the soil loss values ranging between 20 and 40 t ha−1 yr−1. The land under reserved forest was very slight erosion-prone soil with soil loss of < 5 t ha−1 yr−1, but few water bodies in forest land have resulted in more than 40 t ha−1 yr−1. Some steep sloppy land near the riverbank showed soil erosion loss ranging from 44.37 to 241.03 t ha−1 yr−1 due to higher water forces, most minor vegetation, high steep slopes, and sandy loam soils. The spatial techniques used for assessing soil erosion in the study area will be helpful for decision-makers and planners to take appropriate land management measures to counter the soil loss and protect the natural environment. Thus, the GIS-based RUSLE model is a convenient, time-efficient, and cost-effective tool to evaluate and map soil erosion on a pixel-to-pixel basis.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold CL, Gibbons CJ (1996) Impervious surface coverage: the emergence of a key environmental indicator. J Am Plann Assoc 62:243–258. https://doi.org/10.1080/01944369608975688
Babu R, Dhyani BL, Kumar N (2004) Assessment of erodibility status and refined iso-erodent map of India. Indian J Soil Conserv 32(3):171–177
Bai LZKZ, Wang MJ, Karthikeyan R (2019) Basin-scale spatial soil erosion variability: pingshuo opencast mine site in Shanxi Province, Loess Plateau of China. Nat Hazards 80:1213–1230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-2019-9
Bamutaze Y, Mukwaya P, Oyama S, Nadhomi D, Nsemire P (2021) Intersecting RUSLE modelled and farmers perceived soil erosion risk in the conservation domain on mountain Elgon in Uganda. Appl Geogr 126:102366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102366
Baskan O, Cebel H, Akgul S, Erpul G (2010) Conditional simulation of USLE/RUSLE soil erodibility factor by geostatistics in a Mediterranean catchment, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 60:1179–1187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0259-2
Benkobi L, Trlica MJ, Smith JL (1994) Evaluation of a refined surface cover subfactor for use in RUSLE. J Range Manag 47:74–78. https://doi.org/10.2307/4002845
Bhandari KP, Aryal J, Darnsawasdi R (2015) A geospatial approach to assessing soil erosion in a watershed by integrating socio-economic determinants and the RUSLE model. Nat Hazards 75:321–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1321-2
Bhattarai R, Dutta D (2007) Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield using GIS at catchment scale. Water Res Manage 21(10):1635–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9118-z
Biesemans J, Van Meirvenne M, Gabriels D (2000) Extending the RUSLE with the Monte Carlo error propagation technique to predict long-term average off-site sediment accumulation. J Soil Water Conserv 55:35
Biswas SS, Pani P (2015) Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS techniques: a case study of Barakar River basin, Jharkhand. India Model Earth Syst Environ 1(4):42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0040-3
Borrelli P, Robinson DA, Fleischer LR et al (2017) An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02142-7
Chakrabortty R, Chandra S, Mehebub P, Ayan S (2020) Soil erosion potential hotspot zone identification using machine learning and statistical approaches in eastern India. Springer, Berlin
Chatterjee S, Krishna AP, Sharma AP (2014) Geospatial assessment of soil erosion vulnerability at watershed level in some sections of the Upper Subarnarekha river basin, Jharkhand, India. Environ Earth Sci 71:357–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2439-3
Chaudhary BS, Kumar S (2018) Soil erosion estimation and prioritization of Koshalya-Jhajhara watershed in North India. Indian J Soil Conserv 46(3):305–311
Chen T, Niu RQ, Wang Y, Li PX, Zhang LP, Du B (2011) Assessment of spatial distribution of soil loss over the upper basin of Miyun reservoir in China based on RS and GIS techniques. Environ Monit Assess 179(1–4):605–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1766-z
Cohen MJ, Shepherd KD, Walsh MG (2005) Empirical reformulation of the universal soil loss equation for erosion risk assessment in a tropical watershed. Geoderma 124(3):235–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.05.003
da Cunha ER, Bacani VM, Panachuki E (2017) Modeling soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS in a watershed occupied by rural settlement in the Brazilian Cerrado. Nat Hazards 85(2):851–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2607-3
Demirci A, Karaburun A (2012) Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in a GIS framework: a case study in the Buyukcekmece Lake watershed, northwest Turkey. Environ Earth Sci. 66(3):903–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1300-9
Fernandez C, Wu JQ, McCool DK, Stöckle CO (2003) Estimating water erosion and sediment yield with GIS, RUSLE, and SEDD. J Soil Water Conserv. 58(3): 128–136. http://www.jswconline.org/content/58/3/128.abstract
Ferro V, Giordano G, Iovino M (1991) Isoerosivity and erosion risk map for Sicily. Hydrolog Sci J 36(6):549–564. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626669109492543
Fu BJ, Zhao WW, Chen LD, Zhang QJ, Lü YH, Gulinck H, Poesen J (2005) Assessment of soil erosion at large watershed scale using RUSLE and GIS: a case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad Dev 16(1):73–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.646
Fu S, Liu B, Liu H, Xu L (2011) The effect of slope on interrill erosion at short slopes. CATENA 84:29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2010.08.013
Ganasri BPP, Ramesh H (2016) Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS - a case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci Front 7(6):953–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2015.10.007
Gaubi I, Chaabani A, Ben Mammou A, Hamza MH (2017) A GIS-based soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) (Lebna watershed, Cap Bon, Tunisia). Nat Hazards 86:219–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2684-3
Gupta S, Kumar S (2017) Simulating climate change impact on soil erosion using RUSLE model − a case study in a watershed of mid-Himalayan landscape. J Earth Syst Sci 126(3):43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0823-1
Haan CT, Barfield BJ, Hayes JC (1994) Design hydrology and sedimentology for small catchments. Academic Press
Hu Y, Tian G, Mayer AL (2015) Risk assessment of soil erosion by application of remote sensing and GIS in Yanshan Reservoir catchment, China. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1841-4
Jain MK, Das D (2010) Estimation of sediment yield and areas of soil erosion and deposition for watershed prioritization using GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour Manag 24(10):2091–2112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9540-0
Jain SK, Kumar S, Varghese J (2001) Estimation of soil erosion for a himalayan watershed using GIS technique. Water Resour Manag 15(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012246029263
Jat MK, Khare D, Garg PK, Shankar V (2009) Remote sensing and GIS-based assessment of urbanisation and degradation of watershed health. Urban Water J 6(3):251–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/15730620801971920
Jena RK, Padua S, Ray P, Ramachandran S, Bandyopadhyay S, Roy PD, Obi Reddy GP, Singh SK, Ray SK (2018) Assessment of soil erosion in sub tropical ecosystem of Meghalaya, India using remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE. Indian J Soil Conserv 46(3):273–282
Jiang L, Yao Z, Liu Z, Wu S, Wang R, Wang L (2015) Estimation of soil erosion in some sections of Lower Jinsha River based on RUSLE. Nat Hazards 76(3):1831–1847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1569-6
Joshi VU (2018) Soil loss estimation based on RUSLE along the Central Hunter Valley Region, NSW, Australia. J Geol Soc India 91:554–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0904-z
Kano T, Yoshida M, Wada H, Satish-Kumar M, Roy A, Bandhopadyay BK, Khan AS, Pal T, Huin AK, Bhowmik SK, Chattopadhyay A (2001) Field studies in the sakoli and sausar belts of the central indian tectonic zode, 1999–2000. J Geosci Osaka City Univ 44:17–39
Karamage F, Zhang C, Liu T, Maganda A, Isabwe A (2017) Soil erosion risk assessment in Uganda. Forests 8(2):1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8020052
Karan SK, Ghosh S, Samadder SR (2019) Identification of spatially distributed hotspots for soil loss and erosion potential in mining areas of Upper Damodar Basin – India. CATENA 182:104144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104144
Kashiwar SR, Dongarwar UR, Kundu MC, Kumar D, Dongarwar L, Verma H, Awatade S (2018) Evaluation of long term rainfall variability of Bhandara (Maharashtra), India using GIS. Int J Curr Microbiol Applied Sci 7(7):3846–3854. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.707.447
Kayet N, Pathak K, Chakrabarty A, Sahoo S (2018) Evaluation of soil loss estimation using the RUSLE model and SCS-CN method in hillslope mining areas. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 6:31–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2017.11.002
Khare D, Mondal A, Kundu S, Mishra PK (2017) Climate change impact on soil erosion in the Mandakini River Basin. North India Applied Water Sci 7(5):2373–2383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0419-y
Kouli M, Soupios P, Vallianatos F (2009) Soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete. Greece Environ Geol 57(3):483–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1318-9
Kourgialas NN, Koubouris GC (2016) Assessing water erosion in Mediterranean tree crops using GIS techniques and field measurements : the effect of climate change. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2354-5
Kumar A, Devi M, Deshmukh B (2014) Integrated remote sensing and geographic information system based RUSLE modelling for estimation of soil loss in Western Himalaya. India Water Resour Manag 28(10):3307–3317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0680-5
Kumar S, Kumar A, Saha SK, Kumar A (2008) Stereo Cartosat-1 satellite remote sensing data in assessing topographic potential of soil erosion. J Indian Soc Remote Sensing 36(2):159–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-008-0016-0
Lakew M, Sewnet D, Mohammedyasin MS et al (2018) Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE, GIS and remote sensing in NW Ethiopia. Geoderma Reg 12:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2018.01.002
Lal R, Stewart BA (1990) Soil degradation. Springer
Lal R (1990) Soil erosion in the tropics: principles and management. New York, NY 10020: McGraw-Hill Inc.
Lal R (2001) Soil degradation by erosion. Land Degrad Dev 12:519–539. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.472
Mahala A (2018) Soil erosion estimation using RUSLE and GIS techniques-a study of a plateau fringe region of tropical environment. Arabian J Geosci 11(13):335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3703-3
Markose VJ, Jayappa KS (2016) Soil loss estimation and prioritization of sub-watersheds of Kali River basin, Karnataka, India, using RUSLE and GIS. Environ Monit Assess. 188(4). doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5218-2
Mitasova H, Hofierka J, Zlocha M, Iverson LR, Iversont LR (1996) Modelling topographic potential for erosion and deposition using GIS. Int J Geogra Inform Sys 10(5):629–641. https://doi.org/10.1080/02693799608902101
Moges DM, Bhat HG (2017) Integration of geospatial technologies with RUSLE for analysis of land use/cover change impact on soil erosion: case study in Rib watershed, north-western highland Ethiopia. Environ Earth Sci 76(22):765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7109-4
Mohammed S, Alsafadi K, Talukdar S et al (2020) Remote sensing applications : society and environment estimation of soil erosion risk in southern part of Syria by using RUSLE integrating geo informatics approach. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 20:100375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2020.100375
Moore ID, Wilson JP (1992) Length-slope factors for the revised universal soil loss equation: simplified method of estimation. J Soil Water Conserv 47(5):423–428
Narayana DV, Babu R (1983) Estimation of soil erosion in India. J Irrig Drain Eng 109(4):419–434. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9437(1983)109:4(419)
Nasir N, Selvakumar R (2018) Influence of land use changes on spatial erosion pattern, a time series analysis using RUSLE and GIS: the cases of Ambuliyar sub-basin, India. Acta Geophys 66:1121–1130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-018-0186-2
Obi Reddy GP, Singh SK (2018) Geospatial technologies in land resources mapping, monitoring and management. Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-78711-4
Pal S, Debanshi S (2018) Influences of soil erosion susceptibility toward overloading vulnerability of the gully head bundhs in Mayurakshi River basin of eastern Chottanagpur Plateau. Environ Dev Sustain 20:1739–1775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-9963-3
Pan J, Wen Y (2014) Estimation of soil erosion using RUSLE in Caijiamiao watershed, China. Nat Hazards 71:2187–2205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-1006-2
Pandey A, Chowdary VM, Mal BC (2007) Identification of critical erosion prone areas in the small agricultural watershed using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour Manag 21(4):729–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9061-z
Patil RJ, Sharma SK, Tignath S, Sharma APM (2017) Use of remote sensing, GIS and C++ for soil erosion assessment in the Shakkar River basin. India Hydrol Sci J 62(2):217–231. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2016.1217413
Patil RJ, Sharma SK, Tignath S (2015) Remote Sensing and GIS based soil erosion assessment from an agricultural watershed. Arab J Geosci 8(9):6967–6984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1718-y
Pimentel D, Kounang N (1998) Ecology of soil erosion in ecosystems. Ecosystems 1(5):416–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100219900035
Pimentel D, Harvey C, Resosudarmo P, Sinclair K, Kurz D, McNair M, Crist S, Shpritz L, Fitton L, Saffouri R, Blair R (1995) Environmental and economic costs of soil erosion and conservation benefits. Science. 267(5201): 1117 LP – 1123. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.267.5201.1117
Pradhan B, Chaudhari A, Adinarayana J, Buchroithner MF (2012) Soil erosion assessment and its correlation with landslide events using remote sensing data and GIS: A case study at Penang Island. Malaysia Environ Monit Assess 184(2):715–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-1996-8
Prasannakumar V, Shiny R, Geetha N, Vijith H (2011) Spatial prediction of soil erosion risk by remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE approach: a case study of Siruvani river watershed in Attapady valley, Kerala. India Environ Earth Sci 64(4):965–972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0913-3
Prasannakumar V, Vijith H, Abinod S, Geetha N (2012) Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous sub-watershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci Front 3(2):209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.11.003
Ramakrishnan M, Vaidyanadhan R (2010) Geology of India (Vol. 1 & 2). GSI Publications, 2(1).
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, McCool DK, Yoder DC (1997) Predicting soil erosion by water: a guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). Agriculture Handbook, Washington. Washington: US Government Printing Office.
Renard KG, Foster GR, Weesies GA, Porter JI (1991) RUSLE revised universal soil loss equation. J Soil Water Conserv 46(1):30–33
Sadeghi SH, Zabihi M, Vafakhah M, Hazbavi Z (2017) Spatiotemporal mapping of rainfall erosivity index for different return periods in Iran. Nat Hazards 87:35–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-2752-3
Shit PK, Nandi AS, Bhunia GS (2015) Soil erosion risk mapping using RUSLE model on jhargram sub-division at West Bengal in India. Model Earth Syst Environ 1(3):28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0032-3
Singh G, Babu R, Narain P, Bhushan LS, & Abrol IP (1992) Soil erosion rates in India. J Soil Water Conserv, 47(1)
Srinivas CV, Maji AK, Obi Reddy GP, Chary GR (2002) Assessment of soil erosion using remote sensing and GIS in Nagpur district, Maharashtra for prioritisation and delineation of conservation units. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 30(4):197–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03000363
Sujatha ER, Sridhar V (2019) Mapping of erosion susceptibility using a weighted linear combination model: A case study of a hill sub-watershed in Kodaikkanal, Western Ghats, South India. Remote Sens Appl Soc Environ 14:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2019.02.004
Terranova O, Antronico L, Coscarelli R, Iaquinta P (2009) Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: an application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 112(3–4):228–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.06.009
Thomas J, Joseph S, Thrivikramji KP (2018) Assessment of soil erosion in a tropical mountain river basin of the southern Western Ghats, India using RUSLE and GIS. Geosci Front 9:893–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2017.05.011
Toubal AK, Achite M, Ouillon S, Dehni A (2018) Soil erodibility mapping using the RUSLE model to prioritize erosion control in the Wadi Sahouat basin. North-West of Algeria Environ Monit Assess 190(4):210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6580-z
Van der Knijff JM, Jones RJA, Montanarella L (1999) Soil erosion risk assessment in Italy. Ispra: European Commission Directorate General JRC, Joint Research Centre Space Applications Institute European Soil Bureau. Publications Office of the European Union.
Van der Knijff JM, Jones RJA, Montanarella L (2000) Soil erosion risk assessment in Europe. Publications Office of the European Union
Wachal DJ, Banks KE, Hudak PF, Harmel RD (2009) Modeling erosion and sediment control practices with RUSLE 2.0: a management approach for natural gas well sites in Denton County, TX, USA. Environ Geol, 56(8): 1615–1627. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-008-1259-3
Wang G, Hapuarachchi P, Ishidaira H, Kiem AS, Takeuchi K (2009) Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield during individual rainstorms at catchment scale. Water Resour Manag 23(8):1447–1465. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-008-9335-8
Weil RC, BradyNC (2012) The nature and properties of soils. Pearson education, New Delhi.
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting rainfall erosion losses. A guide to conservation planning. Trans Am Geophys Union 39:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR039i002p00285
Xu Y, Tang H, Wang B, Chen J (2017) Effects of landscape patterns on soil erosion processes in a mountain–basin system in the North China. Nat Hazards 87:1567–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-2833-3
Xu YQ, Shao XM, Kong X, Bin Jian P, Cai YL (2008) Adapting the RUSLE and GIS to model soil erosion risk in a mountains karst watershed, Guizhou Province. China Environ Monit and Assess 141(1–3):275–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9894-9
Yang D, Kanae S, Oki T, Koike T, Musiake K (2003) Global potential soil erosion with reference to land use and climate changes. Hydrol Process 17(14):2913–2928. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1441
Yue-Qing X, Xiao-Mei S, Xiang-Bin K, Jian P, Yun-Long C (2008) Adapting the RUSLE and GIS to model soil erosion risk in a mountains karst watershed, Guizhou Province. China Environ Monit Assess 141(1):275–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9894-9
Zakerinejad R, Maerker M (2015) An integrated assessment of soil erosion dynamics with special emphasis on gully erosion in the Mazayjan. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1700-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kashiwar, S.R., Kundu, M.C. & Dongarwar, U.R. Soil erosion estimation of Bhandara region of Maharashtra, India, by integrated use of RUSLE, remote sensing, and GIS. Nat Hazards 110, 937–959 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04974-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04974-5