Abstract
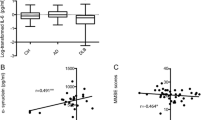
Amyloid β42 (Aβ42) and proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) have been suggested to contribute to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and vascular dementia (VaD). Our aim was to examine whether the changes in these parameters would be able to discriminate the patients with AD from those with VaD and from healthy individuals. We have analyzed the levels of Aβ42, IL-6 and TNF-α in the serum of newly diagnosed 28 AD patients, 16 VaD patients and 26 healthy non-demented controls. We also investigated whether there is an association between Aβ42, IL-6 and TNF-α levels and mini-mental state examination (MMSE) scores and body mass indexes (BMI) of patients. Our data showed a significant decrease in serum Aβ-42 levels in AD patients compared to VaD patients and controls. Levels of IL-6 and TNF-α were not different between AD patients, VaD patients and controls. We observed a correlation between Aβ-42 levels and MMSE scores and BMI levels in both AD and VaD patients. However, Aβ-42 levels were not correlated with IL-6 and TNF-α levels. Significantly lower levels of Aβ42 found in the serum of AD patients than that of VaD patients and controls suggests that it can be a specific biochemical marker for AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee YJ, Han SB, Nam SY et al (2010) Inflammation and alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 33:1539–1556
Moretti A, Gorini A, Villa RF (2011) Pharmacotherapy and prevention of vascular dementia. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10:370–390
Arslantaş D, Ozbabalik D, Metintaş S et al (2009) Prevalence of dementia and associated risk factors in Middle Anatolia, Turkey. J Clin Neurosci 16:1455–1459
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M et al (1984) Clinical diagnosis of alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of department of health and human services task force on alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Roman GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T et al (1993) Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies: report of the NINDS-AIREN international workshop. Neurology 43:250–260
Kawarabayashi T, Shoji M (2008) Plasma biomarkers of alzheimer’s disease. Curr Opin Psychiatry 21:260–267
Tuppo EE, Arias HR (2005) The role of inflammation in alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:289–305
Heneka MT, O’Banion MK, Terwel D et al (2010) Neuroinflammatory processes in alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 117:919–947
Teunissen CE, de Vente J, Steinbusch HW et al (2002) Biochemical markers related to alzheimer’s dementia in serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Neurobiol Aging 23(4):485–508
Solfrizzi V, D’Introno A, Colacicco AM, Capurso C, Todarello O, Pellicani V, Capurso SA, Pietrarossa G, Santamato V, Capurso A, Panza F (2006) Circulating biomarkers of cognitive decline and dementia. Clin Chim Acta 364:91–112
Qiu WQ, Sun X, Selkoe DJ et al (2007) Depression is associated with low plasma Abeta42 independently of cardiovascular disease in the homebound elderly. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 22:536–542
Cosentino SA, Stern Y, Sokolov E et al (2010) Plasma ß-amyloid and cognitive decline. Arch Neurol 67:1485–1490
Sun X, Bhadelia R, Liebson E et al (2011) The relationship between plasma amyloid-β peptides and the medial temporal lobe in the homebound elderly. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 26:593–601
Sundelöf J, Giedraitis V, Irizarry MC et al (2008) Plasma beta amyloid and the risk of alzheimer disease and dementia in elderly men: a prospective, population-based cohort study. Arch Neurol 65:256–263
Graff-Radford NR, Crook JE, Lucas J et al (2007) Association of low plasma Abeta42/Abeta40 ratios with increased imminent risk for mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 64:54–362
van Dijk EJ, Prins ND, Vermeer SE et al (2004) Plasma amyloid beta, apolipoprotein E, lacunar infarcts, and white matter lesions. Ann Neurol 55:570–575
Schupf N, Tang MX, Fukuyama H et al (2008) Peripheral Abeta subspecies as risk biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:14052–14057
Seppälä TT, Herukka SK, Hänninen T et al (2010) Plasma Abeta42 and Abeta40 as markers of cognitive change in follow-up: a prospective, longitudinal, population-based cohort study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:1123–1127
van Oijen M, Hofman A, Soares HD et al (2006) Plasma Abeta(1–40) and Abeta(1–42) and the risk of dementia: a prospective case-cohort study. Lancet Neurol 5:655–660
Bibl M, Esselmann H, Mollenhauer B et al (2007) Blood-based neurochemical diagnosis of vascular dementia: a pilot study. J Neurochem 103:467–474
Meyer JS, Xu G, Thornby J et al (2002) Is mild cognitive impairment prodromal for vascular dementia like alzheimer’s disease? Stroke 33:1981–1985
Zuliani G, Ranzini M, Guerra G et al (2007) Plasma cytokines profile in older subjects with late onset alzheimer’s disease or vascular dementia. J Psychiatr Res 41:686–693
Licastro F, Pedrini S, Caputo L et al (2000) Increased plasma levels of interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and alpha-1-antichymotrypsin in patients with alzheimer’s disease: peripheral inflammation or signals from the brain? J Neuroimmunol 103:97–102
Zuliani G, Guerra G, Ranzini M et al (2007) High interleukin-6 plasma levels are associated with functional impairment in older patients with vascular dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 22:305–311
Angelis P, Scharf S, Mander A et al (1998) Serum interleukin-6 and interleukin-6 soluble receptor in alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 244:106–108
Swardfager W, Lanctôt K, Rothenburg L et al (2010) A meta-analysis of cytokines in alzheimer’s disease. Biol Psychiatry 68:930–941
Spooren A, Kolmus K, Laureys G, Clinckers R, De Keyser J, Haegeman G, Gerlo S (2011) Interleukin-6, a mental cytokine. Brain Res Rev 67:157–183
Engelhart MJ, Geerlings MI, Meijer J et al (2004) Inflammatory proteins in plasma and the risk of dementia: the rotterdam study. Arch Neurol 61:668–672
Tarkowski E, Blennow K, Wallin A et al (1999) Intracerebral production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, a local neuroprotective agent, in alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. J Clin Immunol 19:223–230
Park KM, Bowers WJ (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated signaling in neuronal homeostasis and dysfunction. Cell Signal 22:977–983
Paganelli R, Di Iorio A, Patricelli L et al (2002) Proinflammatory cytokines in sera of elderly patients with dementia: levels in vascular injury are higher than those of mild-moderate alzheimer’s disease patients. Exp Gerontol 37:257–263
Alvarez A, Cacabelos R, Sanpedro C et al (2007) Serum TNF-alpha levels are increased and correlate negatively with free IGF-I in alzheimer disease. Neurobiol Aging 28:533–536
van Exel E, Eikelenboom P, Comijs H et al (2009) Vascular factors and markers of inflammation in offspring with a parental history of late-onset alzheimer disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:1263–1270
Magaki S, Mueller C, Dickson C et al (2007) Increased production of inflammatory cytokines in mild cognitive impairment. Exp Gerontol 42:233–240
Yasutake C, Kuroda K, Yanagawa T et al (2006) Serum BDNF, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels in dementia patients: comparison between Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:402–406
Whitmer RA, Gunderson EP Jr, Quesenberry CP et al (2007) Body mass index in midlife and risk of alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Curr Alzheimer Res 4:103–109
Chen YC, Chen TF, Yip PK et al (2010) Body mass index (BMI) at an early age and the risk of dementia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 50(Suppl 1):S48–S52
Anstey KJ, Cherbuin N, Budge M et al (2011) Body mass index in midlife and late-life as a risk factor for dementia: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Obes Rev 12:426–437
Beydoun MA, Beydoun HA, Wang Y (2008) Obesity and central obesity as risk factors for incident dementia and its subtypes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 9:204–218
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uslu, S., Akarkarasu, Z.E., Ozbabalik, D. et al. Levels of Amyloid Beta-42, Interleukin-6 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia. Neurochem Res 37, 1554–1559 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0750-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-012-0750-0



