Abstract
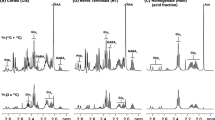
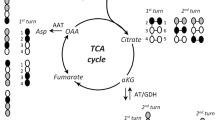
Mouse cerebral cortical mini-slices were used in a superfusion system to monitor depolarization-induced (55 mM K+) release of preloaded [2,3-3H]GABA and to investigate the biosynthesis of glutamate, GABA and aspartate during physiological and depolarizing (55 mM K+) conditions from either [1,6-13C]glucose or [U-13C]glutamine. Depolarization-induced GABA release could be reduced (50%) by the GABA transport inhibitor tiagabine (25 μM) or by replacing Ca2+ with Co2+. In the presence of both tiagabine and Co2+ (1 mM), release was abolished completely. The release observed in the presence of 25 μM tiagabine thus represents vesicular release. Superfusion in the presence of [1,6-13C]glucose led to considerable labeling in the three amino acids, the labeling in glutamate and aspartate being increased after depolarization. This condition had no effect on GABA labeling. For all three amino acids, the distribution of label in the different carbon atoms revealed on increased tricarboxylic acid (TCA) activity during depolarization. When [U-13C]glutamine was used as substrate, labeling in glutamate was higher than that in GABA and aspartate and the fraction of glutamate and aspartate being synthesized by participation of the TCA cycle was increased by depolarization, an effect not seen for GABA. However, GABA synthesis reflected TCA cycle involvement to a much higher extent than for glutamate and aspartate. The results show that this preparation of brain tissue with intact cellular networks is well suited to study metabolism and release of neurotransmitter amino acids under conditions mimicking neural activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- KR:
-
Krebs–Ringer
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid
References
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (1999) Synthesis of vesicular GABA from glutamine involves TCA cycle metabolism in neocortical neurons. J Neurosci Res 57:342–349
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Gegelashvili G, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (2001) Metabolic distinction between vesicular and cytosolic GABA in cultured GABAergic neurons using 13C MRS. J Neurosci Res 63:347–355
Machiyama Y, Balazs R, Richter D (1967) Effect of K+-stimulation on GABA metabolism in brain slices in vitro. J Neurochem 14:591–594
López-Colomé AM, Tapia R, Salceda R, Pasantes-Morales H (1978) K+-Stimulated release of labeled γ-aminobutyrate, glycine and taurine in slices of several regions of rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 3:1069–1074
Drejer J, Honoré T, Schousboe A (1987) Excitatory amino acid induced release of 3H-GABA from cultured mouse cerebral cortex interneurons. J Neurosci 7:2910–2916
Saransaari P, Oja SS (1992) Release of GABA and taurine from brain-slices. Prog Neurobiol 38:455–482
Saransaari P, Oja SS (1993) Characteristics of GABA release modified by glutamate receptors in mouse hippocampal slices. Neurochem Int 43:453–459
Belhage B, Hansen GH, Schousboe A (1993) Depolarization by K+ and glutamate activates different neurotransmitter release mechanisms in GABAergic neurons: vesicular versus non-vesicular release of GABA. Neuroscience 54:1019–1034
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (2000) Compartmentation of TCA cycle metabolism in cultured neocortical neurons revealed by 13C MR spectroscopy. Neurochem Int 36:349–358
Palaiologos G, Hertz L, Schousboe A (1988) Evidence that aspartate amino transferase activity and ketodicarboxylate carrier function are essential for biosynthesis of transmitter glutamate. J Neurochem 51:317–320
Timmermann DB, Lund TM, Belhage B, Schousboe A (2001) Localization and function of voltage dependent calcium channels in cultured neocortical neurons. Int J Dev Neurosci 19:1–10
Geddes JW, Wood JD (1984) Changes in the amino acid content of nerve endings (synaptosomes) induced by drugs that alter the metabolism of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid. J Neurochem 42:16–24
Bak LK, Schousboe A, Sonnewald U, Waagepetersen HS (2006) Glucose is necessary to maintain neurotransmitter homeostasis during synaptic activity in cultured glutamatergic neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1285–1297
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Waagepetersen HS, Bakken IJ, Larsson OM, Sonnewald U, Schousboe A (1998) Comparison of lactate and glucose metabolism in cultured neocortical neurons and astrocytes using 13C NMR spectroscopy. Dev Neurosci 20:310–320
Bræstrup C, Nielsen EB, Sonnewald U, Knutsen LJS, Andersen KE, Jansen JA, Frederiksen K, Andersen PH, Mortensen A, Suzdak PD (1990) (R)-N-[4,4-Bis(3-methyl-2-thienyl) but-3-en-1-yl]nipecotic acid binds with high affinity to the brain γ-aminobutyric acid uptake carrier. J Neurochem 54:639–647
Bernath S, Zigmond MJ (1988) Characterization of [3H]GABA release from striatal slices: evidence for a calcium-independent process via the GABA uptake system. Neuroscience 27:563–570
Bernath S (1992) Calcium-independent release of amino acid neurotransmitters: fact or artifact? Prog Neurobiol 38:57–91
Schousboe A (1981) Transport and metabolism of glutamate and GABA in neurons and glial cells. Int Rev Neurobiol 22:1–45
Larsson OM, Drejer J, Kvamme E, Svenneby G, Hertz L, Schousboe A (1985) Ontogenetic development of glutamate and GABA metabolizing enzymes in cultured cerebral cortex interneurons and in cerebral cortex in vivo. Int J Dev Neurosci 3:177–185
Mason GF, Gruetter R, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Shulman RG, Novotny EJ (1995) Simultaneous determination of the rates of the TCA cycle, glucose utilization, alpha-ketoglutarate/glutamate exchange, and glutamine synthesis in human brain by NMR. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:12–25
Balazs R, Machiyama Y, Hammond BJ, Julian T, Richter D (1970) The operation of the gamma-aminobutyrate bypath of the tricarboxylic acid cycle in brain tissue in vitro. Biochem J 116:445–461
Machiyama Y, Balazs R, Hammond BJ, Julian T, Richter D (1970) Metabolism of gamma-aminobutyrate and glucose in potassium ion-stimulated brain tissue in-vitro. Biochem J 116:469–481
Sonnewald U, Westergaard N, Krane J, Unsgård G, Petersen SB, Schousboe A (1991) First direct demonstration of preferential release of citrate from astrocytes using [13C]NMR spectroscopy of cultured neurons and astrocytes. Neurosci Lett 128:235–239
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (2000) A possible role of alanine for ammonia transfer between astrocytes and glutamatergic neurons. J Neurochem 75:471–479
Bouzier-Sore AK, Voisin P, Canioni P, Magistretti PJ, Pellerin L (2003) Lactate is a preferential oxidative energy substrate over glucose for neurons in culture. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:1298–1306
Peng L, Zhang X, Hertz L (1994) High extracellular potassium concentrations stimulate oxidative metabolism in a glutamatergic neuronal culture and glycolysis in cultured astrocytes but have no stimulatory effect in a GABAergic neuronal culture. Brain Res 663:168–172
Berl S, Clarke DD (1983) The metabolic compartmentation concept. In: Hertz L, Kvamme E, McGeer EG, Schousboe A (eds) Glutamine glutamate and GABA in the central nervous system. Alan R Liss Inc., New York, pp 205–217
Sonnewald U, Westergaard N, Schousboe A, Svendsen JS, Unsgaard G, Petersen SB (1993) Direct demonstration by [13C]NMR spectroscopy that glutamine from astrocytes is a precursor for GABA synthesis in neurons. Neurochem Int 22:19–29
Sonnewald U, Westergaard N, Hassel B, Müller TB, Unsgård G, Fonnum F, Hertz L, Schousboe A, Petersen SB (1993) NMR Spectroscopic studies of 13C acetate and 13C glucose metabolism in neocortical astrocytes: evidence for mitochondrial heterogeneity. Dev Neurosci 15:351–358
McKenna MC, Tildon JT, Stevenson JH, Hopkins IB (1994) Energy-metabolism in cortical synaptic terminals from weanling and mature rat-brain—evidence for multiple compartments of tricarboxylic-acid cycle activity. Dev Neurosci 16:291–300
Westergaard N, Sonnewald U, Petersen SB, Schousboe A (1995) Glutamate and glutamine metabolism in cultured GABAergic neurons studied by 13C NMR spectroscopy: evidence for compartmentation and mitochondrial heterogeneity. Neurosci Lett 185:24–28
Waagepetersen HS, Qu H, Sonnewald U, Shimamoto K, Schousboe A (2005) Role of glutamine and neuronal glutamate uptake in glutamate homeostasis and synthesis during vesicular release in cultured glutamatergic neurons. Neurochem Int 47:92–102
Acknowledgements
The expert secretarial assistance of Ms Hanne Danø and the skilful technical assistance of Ms Ann Lene Vigh are highly appreciated. The experimental work has been supported by grants from the Danish Medical Research Council (22-04-0314) and the Lundbeck, Hørslev and Novo Nordisk Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue article in honor of Dr. Ricardo Tapia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waagepetersen, H.S., Døring, S. & Schousboe, A. Metabolism of [1,6-13C]Glucose and [U-13C]Glutamine and Depolarization Induced GABA Release in Superfused Mouse Cerebral Cortical Mini-slices. Neurochem Res 33, 1610–1617 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9695-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9695-8