Abstract
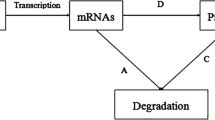
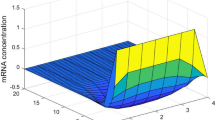
This paper presents an approach to identify the unknown parameters of genetic regulatory network (GRN) in finite-time. The adaptive synchronization-based method is used to solve this problem. Specifically, an auxiliary system with adaptive parameters is constructed, which is regarded as slave system of the GRN with unknown parameters. Then, effective update laws of adaptive parameters and variable structure controllers are designed. The criteria of synchronization and parameters identification in finite-time are derived by utilizing finite-time Lyapunov stability theorem. Finally, an illustrative example is given to show the effectiveness of the main results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guss KA, Nelson CE, Hudson A, Kraus ME, Carroll SB (2001) Control of a genetic regulatory network by a selector gene. Science 292(5519):1164–1167
De Jong H (2002) Modeling and simulation of genetic regulatory systems: a literature review. J Comput Biol 9(1):67–103
Hamey FK, Nestorowa S, Kinston SJ, Kent DG, Wilson NK, Gottgens B (2017) Reconstructing blood stem cell regulatory network models from single-cell molecular profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(23):5822–5829
Van de Sande B, Flerin C, Davie K, De Waegeneer M, Hulselmans G, Aibar S, Verbeiren T (2020) A scalable SCENIC workflow for single-cell gene regulatory network analysis. Nat Protoc 15(7):2247–2276
Tao B, Xiao M, Sun Q, Cao J (2018) Hopf bifurcation analysis of a delayed fractional-order genetic regulatory network model. Neurocomputing 275:677–686
Dong T, Zhang Q (2020) Stability and oscillation analysis of a gene regulatory network with multiple time delays and diffusion rate. IEEE Trans NanoBiosci 19(2):285–298
Guan ZH, Yue D, Hu B, Li T, Liu F (2017) Cluster synchronization of coupled genetic regulatory networks with delays via aperiodically adaptive intermittent control. IEEE Trans NanoBiosci 16(7):585–599
Wan X, Wang Z, Wu M, Liu X (2018) State estimation for discrete time-delayed genetic regulatory networks with stochastic noises under the round-robin protocols. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 17(2):145–154
Steggles LJ, Banks R, Wipat A (2006) Modelling and analysing genetic networks: from Boolean networks to Petri nets. International conference on computational methods in systems biology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg., pp 127–141
Li H, Yang X, Wang S (2020) Robustness for stability and stabilization of Boolean networks with stochastic function perturbations. IEEE Trans Autom Control 66(3):1231–1237
Sanchez- Castillo M, Blanco D, Tienda-Luna IM, Carrion MC, Huang Y (2018) A Bayesian framework for the inference of gene regulatory networks from time and pseudo-time series data. Bioinformatics 34(6):964–970
Zou C, Wang X (2020) Robust stability of delayed Markovian switching genetic regulatory networks with reaction Cdiffusion terms. Comput Math Appl 79(4):1150–1164
Manivannan R, Cao J, Chong KT (2020) Generalized dissipativity state estimation for genetic regulatory networks with interval time-delay signals and leakage delays. Commun Nonlinear Sci Simu 89:105326
Lu Q, Xiao M, Cheng Z, Song Y, Huang C, Cao J (2020) Stability and bifurcation analysis of a fractional-order single-gene regulatory model with delays under a novel PD control law. Int J Biomath 13(3):2050016
Chen L, Aihara K (2002) Stability of genetic regulatory networks with time delay. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I: Fundam Theor Appl 49(5):602–608
Sakthivel R, Sathishkumar M, Kaviarasan B, Anthoni SM (2016) Robust finite-time passivity for discrete-time genetic regulatory networks with Markovian jumping parameters. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung A 71(4):289–304
Anbuvithya R, Mathiyalagan K, Sakthivel R, Prakash P (2015) Sampled-data state estimation for genetic regulatory networks with time-varying delays. Neurocomputing 151:737–744
Xiao M, Zheng WX, Jiang G (2018) Bifurcation and oscillatory dynamics of delayed cyclic gene networks including small RNAs. IEEE Trans Cybern 49(3):883–896
Lai Q, Zhao XW, Huang JN, Pham VT, Rajagopal K (2018) Monostability, bistability, periodicity and chaos in gene regulatory network. Eur Phys J Spec Top 227(7–9):719–730
Yue D, Guan ZH, Li J, Liu F, Xiao JW, Ling G (2019) Stability and bifurcation of delay-coupled genetic regulatory networks with hub structure. J Franklin Inst 356(5):2847–2869
Mercatelli D, Scalambra L, Triboli L, Ray F, Giorgi F. M (2020) Gene regulatory network inference resources: a practical overview. Biochim et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 1863(6):194430
Sanguinetti G (2019) Gene regulatory network inference: an introductory survey. Gene Regulatory Networks. Humana Press, New York, NY., pp 1–23
Chen S, Lv J (2002) Parameters identification and synchronization of chaotic systems based upon adaptive control. Phys Lett A 299(4):353–358
Hu M, Xu Z, Zhang R, Hu A (2007) Parameters identification and adaptive full state hybrid projective synchronization of chaotic (hyper-chaotic) systems. Phys. Lett. A 361(3):231–237
Lu J, Cao J (2007) Synchronization-based approach for parameters identification in delayed chaotic neural networks. Phys A: Stat Mech Appl 382(2):672–682
Malisoff M (2020) Tracking and parameter identification for model reference adaptive control. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 30(4):1582–1606
Zhang J, Xia P (2017) An improved PSO algorithm for parameter identification of nonlinear dynamic hysteretic models. J Sound Vib 389:153–167
Xiong G, Zhang J, Shi D, Yuan X (2020) A simplified competitive swarm optimizer for parameter identification of solid oxide fuel cells. Energy Convers Manage 203
Yu J, Yang X, Gao F, Tao D (2016) Deep multimodal distance metric learning using click constraints for image ranking. IEEE Trans Cybern 47(12):4014–4024
Yu J, Tan M, Zhang H, Tao D, Rui Y (2019) Hierarchical deep click feature prediction for fine-grained image recognition. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2932058
Tang Y, Wang Z, Fang JA (2011) Parameters identification of unknown delayed genetic regulatory networks by a switching particle swarm optimization algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 38(3):2523–2535
Liu C (2020) Wang F (2020) Parameter identification of genetic regulatory network with time-varying delays via adaptive synchronization method. Adv Differ Equ 1:1–15
Bhat SP, Bernstein DS (2000) Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM J Control Opt 38(3):751–766
Li X, Ho DW, Cao J (2019) Finite-time stability and settling-time estimation of nonlinear impulsive systems. Automatica 99:361–368
Li X, Yang X, Song S (2019) Lyapunov conditions for finite-time stability of time-varying time-delay systems. Automatica 103:135–140
Mei J, Jiang M, Xu W, Wang B (2013) Finite-time synchronization control of complex dynamical networks with time delay. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(9):2462–2478
Zhang Z, Chen M, Li A (2020) Further study on finite-time synchronization for delayed inertial neural networks via inequality skills. Neurocomputing 373:15–23
Li HL, Cao J, Jiang H, Alsaedi A (2019) Finite-time synchronization and parameter identification of uncertain fractional-order complex networks. Phys A: Stat Mech Appl 533
Mei J, Jiang M, Wang B, Long B (2013) Finite-time parameter identification and adaptive synchronization between two chaotic neural networks. J Frankl Inst 350(6):1617–1633
Sun Y, Wu X, Bai L, Wei Z, Sun G (2016) Finite-time synchronization control and parameter identification of uncertain permanent magnet synchronous motor. Neurocomputing 207:511–518
Zhao H, Zheng M, Li S, Wang W (2018) New results on finite-time parameter identification and synchronization of uncertain complex dynamical networks with perturbation. Mod Phys Lett B 32(09):1850112
Tang Y (1998) Terminal sliding mode control for rigid robots. Automatica 34(1):51–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was jointly supported by the Project funded by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation No. 2020M672027, the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China under Grant No. ZR2019MA034, the Youth Creative Team Sci-Tech Program of Shandong Universities (Grant no. 2019KJI007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61973183.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Wang, F. & Zheng, Z. Adaptive Synchronization-Based Approach for Finite-Time Parameters Identification of Genetic Regulatory Networks. Neural Process Lett 54, 3141–3156 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10754-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10754-4