Abstract
Purpose
The optimal interfraction intervals for fractionated radiosurgery has yet to be established. We investigated the outcome of fractionated gamma knife radiosurgery (FGKRS) for large brain metastases (BMs) according to different interfraction intervals.
Methods
Between September 2016 and May 2018, a total of 45 patients who underwent FGKRS for BMs were enrolled in this study. They were divided into two groups (standard fractionation over 3 consecutive days with a 24-h interfraction interval versus prolonged fractionation over 4 or 5 days with an interfraction interval of at least 48-h). BMs with ≥ 2 cm in maximum diameter or ≥ 5 cm3 in volume were included in analysis.
Results
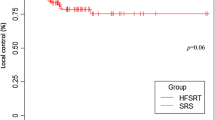
Among 52 BMs treated with 3-fraction GKRS, 25 (48.1%) were treated with standard fractionation scheme, and 27 (51.9%) with prolonged fractionation scheme. The median follow-up period was 10.5 months (range 5–25). Local tumor control rates of the standard group were 88.9% at 6 months and 77.8% at 12 months, whereas those of the prolonged group were 100% at 6 and 12 months (p = 0.023, log-rank test). In multivariate analysis, fractionation scheme (hazard ratio [HR] 0.294, 95% CI 0.099–0.873; p = 0.027) and tumor volume (HR 0.200, 95% CI 0.051–0.781; p = 0.021) were revealed as the only significant factors affecting the local tumor control after 3-fraction GKRS.
Conclusions
Our preliminary tumor control results suggest a promising role of 3-fraction GKRS with an interfraction interval of at least 48-h. This fractionation regimen could be an effective and safe treatment option in the management of large BMs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin X, DeAngelis LM (2015) Treatment of brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 33:3475–3484. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2015.60.9503
Hasegawa T, Kato T, Yamamoto T, Iizuka H, Nishikawa T, Ito H, Kato N (2017) Multisession gamma knife surgery for large brain metastases. J Neurooncol 131:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-016-2317-4
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV, Farace E, Cerhan JH, Anderson SK, Carrero XW, Barker FG 2nd, Deming R, Burri SH, Menard C, Chung C, Stieber VW, Pollock BE, Galanis E, Buckner JC, Asher AL (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 316:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.9839
Higuchi Y, Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Aiyama H, Sato Y, Barfod BE (2018) Modern management for brain metastasis patients using stereotactic radiosurgery: literature review and the authors' gamma knife treatment experiences. Cancer Manag Res 10:1889–1899. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S116718
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Yamamoto M, Matsunaga S, Nagano O, Sato Y, Aoyagi K, Yomo S, Koiso T, Hasegawa T, Nakazaki K, Moriki A, Kondoh T, Nagatomo Y, Okamoto H, Kohda Y, Kawai H, Shidoh S, Shibazaki T, Onoue S, Kenai H, Inoue A, Mori H (2018) Comparison of treatment results between 3- and 2-stage gamma knife radiosurgery for large brain metastases: a retrospective multi-institutional study. J Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.4.JNS172596
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Sato Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, Shuto T, Akabane A, Jokura H, Yomo S, Nagano O, Aoyama H (2017) A multi-institutional prospective observational study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901 study update): irradiation-related complications and long-term maintenance of mini-mental state examination scores. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.04.037
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Onimaru R, Kagei K, Ikeda J, Ishii N, Sawamura Y, Miyasaka K (2003) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone without whole-brain irradiation for patients with solitary and oligo brain metastasis using noninvasive fixation of the skull. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:793–800
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Nagano O, Sato Y, Yamamoto M, Ono J, Saeki N, Miyakawa A, Hirai T (2012) Analysis of 2000 cases treated with gamma knife surgery: validating eligibility criteria for a prospective multi-institutional study of stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of patients with 1–10 brain metastases (JLGK0901) in Japan. J Radiosurg SBRT 2:19–27
McTyre E, Helis CA, Farris M, Wilkins L, Sloan D, Hinson WH, Bourland JD, Dezarn WA, Munley MT, Watabe K, Xing F, Laxton AW, Tatter SB, Chan MD (2017) Emerging indications for fractionated gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 80:210–216. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001227
Yamamoto M, Kawabe T, Sato Y, Higuchi Y, Nariai T, Barfod BE, Kasuya H, Urakawa Y (2013) A case-matched study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases: comparing treatment results for 1–4 vs %3e/= 5 tumors: clinical article. J Neurosurg 118:1258–1268. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.3.JNS121900
Yamamoto M, Kawabe T, Sato Y, Higuchi Y, Nariai T, Watanabe S, Kasuya H (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases: a case-matched study comparing treatment results for patients with 2–9 versus 10 or more tumors. J Neurosurg 121(Suppl):16–25. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.8.GKS141421
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Paolini S, Lanzetta G, Romano A, Cicone F, Osti M, Enrici RM, Esposito V (2016) Single-Fraction Versus Multifraction (3 x 9 Gy) Stereotactic radiosurgery for large (%3e2 cm) brain metastases: a comparative analysis of local control and risk of radiation-induced brain necrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 95:1142–1148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.03.013
Minniti G, Esposito V, Clarke E, Scaringi C, Lanzetta G, Salvati M, Raco A, Bozzao A, Maurizi Enrici R (2013) Multidose stereotactic radiosurgery (9 Gy x 3) of the postoperative resection cavity for treatment of large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86:623–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.03.037
Harrison G, Kano H, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D (2016) Quantitative tumor volumetric responses after Gamma Knife radiosurgery for meningiomas. J Neurosurg 124:146–154. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.JNS141341
Da Silva AN, Nagayama K, Schlesinger D, Sheehan JP (2009) Early brain tumor metastasis reduction following gamma knife surgery. J Neurosurg 110:547–552. https://doi.org/10.3171/2008.4.17537
Huang CW, Tu HT, Chuang CY, Chang CS, Chou HH, Lee MT, Huang CF (2018) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for large vestibular schwannomas greater than 3 cm in diameter. J Neurosurg 128:1380–1387. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.12.JNS161530
Snell JW, Sheehan J, Stroila M, Steiner L (2006) Assessment of imaging studies used with radiosurgery: a volumetric algorithm and an estimation of its error. Tech Note J Neurosurg 104:157–162. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.104.1.157
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, Farnan N (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Kim JW, Park HR, Lee JM, Kim JW, Chung HT, Kim DG, Jung HW, Paek SH (2016) Fractionated stereotactic gamma knife radiosurgery for large brain metastases: a retrospective, single center study. PLoS ONE 11:e0163304. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163304
Jeong WJ, Park JH, Lee EJ, Kim JH, Kim CJ, Cho YH (2015) Efficacy and safety of fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58:217–224. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.217
Minniti G, D'Angelillo RM, Scaringi C, Trodella LE, Clarke E, Matteucci P, Osti MF, Ramella S, Enrici RM, Trodella L (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 117:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1388-3
Minniti G, Clarke E, Lanzetta G, Osti MF, Trasimeni G, Bozzao A, Romano A, Enrici RM (2011) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat Oncol 6:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-6-48
Fahrig A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Grabenbauer G, Kleinert G, Sauer R, Hamm K (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: results from three different dose concepts. Strahlenther Onkol 183:625–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1714-1
Brown JM, Carlson DJ, Brenner DJ (2014) The tumor radiobiology of SRS and SBRT: are more than the 5 Rs involved? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 88:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.07.022
Yang Y, Xing L (2005) Optimization of radiotherapy dose-time fractionation with consideration of tumor specific biology. Med Phys 32:3666–3677. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2126167
Shibamoto Y, Miyakawa A, Otsuka S, Iwata H (2016) Radiobiology of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: what are the optimal fractionation schedules? J Radiat Res 57(Suppl 1):i76–i82. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrw015
Shibamoto Y, Otsuka S, Iwata H, Sugie C, Ogino H, Tomita N (2012) Radiobiological evaluation of the radiation dose as used in high-precision radiotherapy: effect of prolonged delivery time and applicability of the linear-quadratic model. J Radiat Res 53:1–9
Iwata H, Matsufuji N, Toshito T, Akagi T, Otsuka S, Shibamoto Y (2013) Compatibility of the repairable-conditionally repairable, multi-target and linear-quadratic models in converting hypofractionated radiation doses to single doses. J Radiat Res 54:367–373. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrs089
Song CW, Glatstein E, Marks LB, Emami B, Grimm J, Sperduto PW, Kim MS, Hui S, Dusenbery KE, Cho LC (2019) Biological principles of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and stereotactic radiation surgery (SRS): indirect cell death. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.02.047
Coffey RJ (1993) Boost Gamma Knife radiosurgery in the treatment of primary glial tumors. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 61(Suppl 1):59–64. https://doi.org/10.1159/000100661
Giubilei C, Ingrosso G, D'Andrea M, Benassi M, Santoni R (2009) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in combination with whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. J Neurooncol 91:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-008-9700-8
Shibamoto Y, Hashizume C, Baba F, Ayakawa S, Manabe Y, Nagai A, Miyakawa A, Murai T, Iwata H, Mori Y, Mimura M, Ishikura S (2012) Stereotactic body radiotherapy using a radiobiology-based regimen for stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer: a multicenter study. Cancer 118:2078–2084. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26470
Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Nagano O, Matsuda S, Ono J, Sato M, Iwadate Y, Saeki N (2009) Three-staged stereotactic radiotherapy without whole brain irradiation for large metastatic brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:1543–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.10.035
Yomo S, Hayashi M, Nicholson C (2012) A prospective pilot study of two-session gamma knife surgery for large metastatic brain tumors. J Neurooncol 109:159–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0882-8
Yomo S, Hayashi M (2014) A minimally invasive treatment option for large metastatic brain tumors: long-term results of two-session Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery. Radiat Oncol 9:132. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-9-132
Brenner DJ, Martel MK, Hall EJ (1991) Fractionated regimens for stereotactic radiotherapy of recurrent tumors in the brain. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21:819–824
Park HR, Park KW, Lee JM, Kim JH, Jeong SS, Kim JW, Chung HT, Kim DG, Paek SH (2019) Frameless fractionated Gamma Knife radiosurgery with ICON for large metastatic brain tumors. J Korean Med Sci 34:e57. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e57
Kim YJ, Cho KH, Kim JY, Lim YK, Min HS, Lee SH, Kim HJ, Gwak HS, Yoo H, Lee SH (2011) Single-dose versus fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.05.033
Cha J, Kim ST, Kim HJ, Kim BJ, Kim YK, Lee JY, Jeon P, Kim KH, Kong DS, Nam DH (2014) Differentiation of tumor progression from pseudoprogression in patients with posttreatment glioblastoma using multiparametric histogram analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:1309–1317. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3876
Dohm A, McTyre ER, Okoukoni C, Henson A, Cramer CK, LeCompte MC, Ruiz J, Munley MT, Qasem S, Lo H-W, Xing F, Watabe K, Laxton AW, Tatter SB, Chan MD (2018) Staged stereotactic radiosurgery for large brain metastases: local control and clinical outcomes of a one-two punch technique. Neurosurgery 83(1):114–121
Angelov L, Mohammadi AM, Bennett EE, Abbassy M, Elson P, Chao ST, Montgomery JS, Habboub G, Vogelbaum MA, Suh JH, Murphy ES, Ahluwalia MS, Nagel SJ, Barnett GH (2018) Impact of 2-staged stereotactic radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases >/= 2 cm. J Neurosurg 129:366–382. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.3.JNS162532
Yamamoto M, Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Kawabe T, Nagano O, Sato Y, Koiso T, Watanabe S, Aiyama H, Kasuya H (2018) Three-stage Gamma Knife treatment for metastatic brain tumors larger than 10 cm3: a 2-institute study including re-analyses of earlier results using competing risk analysis. J Neurosurg 129:77–85. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.7.GKS181392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This study was approved by our institutional review board as minimal risk, thus negating need for written consent from each patient.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeon, C., Cho, K.R., Choi, J.W. et al. Outcome of three-fraction gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases according to fractionation scheme: preliminary results. J Neurooncol 145, 65–74 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03267-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03267-z