Abstract
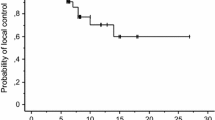
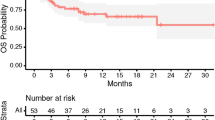
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) delivered in 2–5 fractions (multi-fraction SRS) has been employed in patients with brain metastases as an alternative to single-fraction SRS with the aim to reduce late radiation-induced toxicity while maintaining high local control rate. In the present study we have evaluated the efficacy and toxicity of multi-fraction SRS in patients with 1–3 brain metastases. Between March 2006 and October 2012, 135 patients (63 men and 72 women) with 171 brain metastases have been treated with multi-fraction SRS (3 × 9 Gy or 3 × 12 Gy). At a median follow-up of 11.4 months, 16 lesions recurred locally. The 1- and 2-year local control rates were 88 and 72 %, respectively. The 1- and 2-year survival rates were 57 and 25 %, and respective distant failure rates were 52 and 73 %. Seventy-eight percent of patients succumbed to their extracranial disease and 22 % died of progressive intracranial disease. Multivariate analysis showed that melanoma histology was predictive of local failure (p = 0.02; HR 6.1, 95 % CI 1.5–24). Specifically, the 1-year local control rates were 68 % for melanoma, 92 % for breast carcinoma, and 88 % for NSCLC, respectively. Stable extracranial disease (p = 0.004) and Karnofsky performance status (p = 0.01) were predictive of longer survival. Radiologic changes suggestive of radionecrosis occurred in 12 (7 %) out of 171 lesions, with an actuarial risk of 9 % at 1 year and 17 % at 2 years, respectively. In conclusion, multi-fraction SRS appears to be an effective and safe treatment modality for brain metastases. It may represent an alternative to single-dose SRS for patients with large lesions or lesions located near critical structures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patchell RA (2003) The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat Rev 29:533–540
Scoccianti S, Ricardi U (2012) Treatment of brain metastases: review of phase III randomized controlled trials. Radiother Oncol 102:168–179
Sneed PK, Suh JH, Goetsch SJ, Sanghavi SN, Chappell R, Buatti JM, Regine WF, Weltman E, King VJ, Breneman JC, Sperduto PW, Mehta MP (2002) A multi-institutional review of radiosurgery alone vs. radiosurgery with whole brain radiotherapy as the initial management of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:519–526
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, Kunieda E, Inomata T, Hayakawa K, Katoh N, Kobashi G (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villà S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Hassel MB, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, Farnan N (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Blonigen BJ, Steinmetz RD, Levin L, Lamba MA, Warnick RE, Breneman JC (2010) Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:996–1001
Minniti G, Clarke E, Lanzetta G, Osti MF, Trasimeni G, Bozzao A, Romano A, Enrici RM (2011) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat Oncol 6:48
Vogelbaum MA, Angelov L, Lee SY, Li L, Barnett GH, Suh JH (2006) Local control of brain metastases by stereotactic radiosurgery in relation to dose to the tumor margin. J Neurosurg 104:907–912
Yang HC, Kano H, Lunsford LD, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D (2011) What factors predict the response of larger brain metastases to radiosurgery? Neurosurgery 68:682–690
Han JH, Kim DG, Chung HT, Chung HT, Jung HW (2012) Radiosurgery for large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83:113–120
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Onimaru R, Kagei K, Ikeda J, Ishii N, Sawamura Y, Miyasaka K (2003) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone without whole brain irradiation for patients with solitary and oligo brain metastasis using noninvasive fixation of the skull. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:793–800
Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Sauer R, Grabenbauer G (2006) Phase II trial of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: results and toxicity. Radiother Oncol 8:18–24
Fahrig A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Grabenbauer G, Kleinert G, Sauer R, Hamm K (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases—results from three different dose concepts. Strahlenther Onkol 183:625–630
Narayana A, Chang J, Yenice K, Chan K, Lymberis S, Brennan C, Gutin PH (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using intensity-modulated radiotherapy in patients with one or two brain metastases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 85:82–87
Kwon AK, Dibiase SJ, Wang B, Hughes SL, Milcarek B, Zhu Y (2009) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of brain metastases. Cancer 115:890–898
Ogura K, Mizowaki T, Ogura M, Sakanaka K, Arakawa Y, Miyamoto S, Hiraoka M (2012) Outcomes of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for metastatic brain tumors with high risk factors. J Neurooncol 109:425–432
Jiang XS, Xiao JP, Zhang Y, Xu YJ, Li XP, Chen XJ, Huang XD, Yi JL, Gao L, Li YX (2012) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases larger than three centimeters. Radiat Oncol 7:36
Kim YJ, Cho KH, Kim JY, Lim YK, Min HS, Lee SH, Kim HJ, Gwak HS, Yoo H, Lee SH (2011) Single-dose versus fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:483–489
Fokas E, Henzel M, Surber G, Kleinert G, Hamm K, Engenhart-Cabillic R (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: comparison of efficacy and toxicity in 260 patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 109:91–98
Wiggenraad R, Verbeek-de Kanter A, Mast M, Molenaar R, Kal HB, Lycklama à Nijeholt G, Vecht C, Struikmans H (2012) Local progression and pseudo progression after single fraction or fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for large brain metastases. A single centre study. Strahlenther Onkol 188:696–701
Minniti G, Scaringi C, Clarke E, Valeriani M, Osti M, Enrici RM (2011) Frameless linac-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for brain metastases: analysis of patient repositioning using a mask fixation system and clinical outcomes. Radiat Oncol 6:158
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30:419–425
Wiggenraad R, Verbeek-de Kanter A, Kal HB, Taphoorn M, Vissers T, Struikmans H (2011) Dose-effect relation in stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases. A systematic review. Radiother Oncol 98:292–297
Joiner MC (2002) Models of radiation cell killing. In: Steel GG (ed) Basic clinical radiobiology, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press Inc., London, pp 64–70
Hasegawa T, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Germanwala A, Lunsford LD (2003) Brain metastases treated with radiosurgery alone: an alternative to whole brain radiotherapy? Neurosurgery 52:1318–1326
Molenaar R, Wiggenraad R, Verbeek-de Kanter A, Walchenbach R, Vecht C (2009) Relationship between volume, dose and local control in stereotactic radiosurgery of brain metastasis. Br J Neurosurg 23:170–178
Yang HC, Kano H, Lunsford LD, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D (2011) What factors predict the response of larger brain metastases to radiosurgery? Neurosurgery 68:682–690
Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ 3rd, Shiu AS, Lang FF, Allen PK, Sawaya R, Maor MH (2003) The role of tumor size in the radiosurgical management of patients with ambiguous brain metastases. Neurosurgery 53:272–280
Manon R, O’Neill A, Knisely J, Werner-Wasik M, Lazarus HM, Wagner H, Gilbert M, Mehta M, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (2005) Phase II trial of radiosurgery for one to three newly diagnosed brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and sarcoma: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study (E 6397). J Clin Oncol 23:8870–8876
Selek U, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ III, Shiu AS, Lang FF, Allen P, Weinberg J, Sawaya R, Maor MH (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment in 103 patients for 153 cerebral melanoma metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1097–1106
Minniti G, Esposito V, Clarke E, Scaringi C, Lanzetta G, Salvati M, Raco A, Bozzao A, Maurizi Enrici R (2013) Multidose stereotactic radiosurgery (9 Gy × 3) of the postoperative resection cavity for treatment of large brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86:623–629
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044
Korytko T, Radivoyevitch T, Colussi V, Wessels BW, Pillai K, Maciunas RJ, Einstein DB (2006) 12 Gy gamma knife radiosurgical volume is a predictor for radiation necrosis in non-AVM intracranial tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:419–424
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Alessandro Bozzao, dr Andrea Romano and dr Guido Trasimeni, neuroradiologists, at Sant’Andrea Hospital, Neuroradiology Unit, for reviewing all MRI scans.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minniti, G., D’Angelillo, R.M., Scaringi, C. et al. Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 117, 295–301 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1388-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1388-3