Abstract
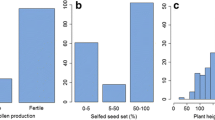
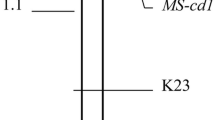
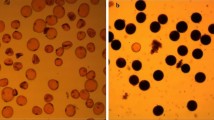
A causal gene for MALE STERILITY 4 (MS4), the CjTKPR1 gene, was recently identified in Cryptomeria japonica. To apply marker-assisted selection (MAS) to breeding of male-sterile C. japonica with MS4, we developed a Kompetitive Allele-Specific polymerase chain reaction (KASP) marker, as a highly cost-effective and accurate genotyping method based on the CjTKPR1 sequence. The accuracy of genotyping using the KASP marker was verified with a backcross family for MS4, and MS4 genotypes were accurately identified. Next, we attempted to select individuals carrying ms4 from 1,500 breeding materials collected throughout Japan. No new individuals with ms4 were detected beyond those already identified. Individuals with ms4 were estimated to be geographically restricted and distributed at extremely low frequency (0.13%). We also attempted to produce new breeding materials with double heterozygotes for MS1 and MS4 (Ms1/ms1, MS4/ms4). Artificial crossings were performed between ‘Shindai 11’ (ms1/ms1, Ms4/Ms4) or ‘Shindai 12’ (ms1/ms1, Ms4/Ms4) and ‘S8-94_sb1’ (Ms1/Ms1, Ms4/ms4). Of the 56 and 35 progenies produced from each family, 31 and 13 double-heterozygous individuals with MS1 and MS4 (Ms1/ms1, Ms4/ms4) were selected, respectively. The segregation ratio of genotypes for MS4 did not deviate from the expected 1:1 ratio in either family. The KASP marker developed in this study facilitates accurate genotyping that is less labor-intensive and less costly than conventional methods. This method is anticipated to contribute to greater efficiency in the breeding and seed production of male-sterile C. japonica with MS4.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author up-on reasonable request.
References
Ayalew H, Tsang PW, Chu C, Wang J, Liu S, Chen C et al (2019) Comparison of TaqMan, KASP and rhAmp SNP genotyping platforms in hexaploid wheat. PLoS ONE 14:e0217222. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217222
Das G, Patra JK, Baek KH (2017) Insight into MAS: a molecular tool for development of stress resistant and quality of rice through gene stacking. Front Plant Sci 9:985. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00985
Forest Tree Gene Symbol Notation Committee (2016) Revised standardization of genetic symbols for forest trees (in Japanese). Genet Tree Breed 5:134–137. https://doi.org/10.32135/fgtb.5.3_134
Forestry Agency (2021) Forest maintenance and conservation. In: Forestry Agency, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (ed) Statistical handbook of forest and forestry. National Forestry Extension Association in Japan, Tokyo, pp 65–116. https://www.rinya.maff.go.jp/j/kikaku/hakusyo/R2hakusyo/index.html (In Japanese with English summary)
Forestry Agency (2022) Forest maintenance and conservation. In: Forestry Agency, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (ed) Statistical handbook of forest and forestry. National Forestry Extension Association in Japan, Tokyo, pp 53–90. https://www.rinya.maff.go.jp/j/kikaku/hakusyo/r3hakusyo/index.html (In Japanese with English summary)
Hasegawa Y, Ueno S, Matsumoto A, Ujino-Ihara T, Uchiyama K, Totsuka S et al (2018) Fine mapping of the male-sterile genes (MS1, MS2, MS3, and MS4) and development of SNP markers for marker-assisted selection in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). PLoS ONE 13:e0206695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206695
Hasegawa Y, Ueno S, Wei FJ, Matsumoto A, Ujino-Ihara T, Uchiyama K, Moriguchi Y, Kasahara M, Fujino T, Shigenobu S, Yamaguchi K, Bino T, Hakamata T (2020) Development of diagnostic PCR and LAMP markers for MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. BMC Res Notes 13:457. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-020-05296-8
Hasegawa Y, Ueno S, Wei FJ, Matsumoto A, Uchiyama K, Ujino-Ihara T, Hakamata T, Fujino T, Kasahara M, Bino T, Yamaguchi K, Shigenobu S, Tsumura Y, Moriguchi Y (2021) Identification and genetic diversity analysis of a male-sterile gene (MS1) in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). Sci Rep 11:1496. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80688-1
Hirayama S, Iwai J, Higuchi Y, Kaneko T, Moriguchi Y (2021) Selection of trees with male sterile genes except for MALE STERILITY 1 in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. J Jpn Soc 103:161–167. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.103.161 (In Japanese with English summary)
Kakui H, Ujino-Ihara T, Hasegawa Y, Tsurisaki E, Futamura N, Iwai J et al (2023) A single-nucleotide substitution of CjTKPR1 determines pollen production in the gymnosperm plant Cryptomeria japonica. PNAS Nexus 2:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad236
Konieczny A, Ausubel FM (1993) A procedure for mapping Arabidopsis mutations using co-dominant ecotype-specific PCR-based markers. Plant J 4:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1993.04020403.x
Kumpatla SP, Buyyarapu R, Abdurakhmonov IY, Mammadov JA (2012) Genomics-assisted plant breeding in the 21st century: technological advances and progress. In: Abdurakhmonov IY (ed) Plant breeding. InTech, Rijeka, Croatia, pp 131–184. http://www.intechopen.com/books/plant-breeding
Liu JJ, Williams H, Zamany A, Li XR, Gellner S, Sniezko RA (2020) Development and application of marker-assisted selection (MAS) tools for breeding of western white pine (Pinus monticola Douglas ex D. Don) resistance to blister rust (Cronartium ribicola JC Fisch.) In British Columbia. Can J Plant Path 42:250–259. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060661.2019.1638454
Magar MM, Rani CVD, Anuradha G (2014) Marker assisted selection for bacterial leaf blight resistance in segregating populations of Cottondora Sannalu. Int J Appl Sci Biotechnol 2:229–237. https://doi.org/10.3126/ijasbt.v2i3.10570
Matsubara A, Sakashita M, Goto M, Kawashima K, Matsuoka T, Kondo S, Yamada T, Takeno S, Takeuchi K, Urashima M, Fujieda S, Okubo K (2020) Epidemiological survey of allergic rhinitis in Japan 2019. Nippon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho 123:485–490. https://doi.org/10.3950/jibiinkoka.123.485(In Japanese with English summary)
Michaels SD, Amasino RM (1998) A robust method for detecting single-nucleotide changes as polymorphic markers by PCR. Plant J 14:381–385. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00123.x
Miyajima D, Yoshii E, Hosoo Y, Taira H (2010) Cytological and genetic studies on male sterility in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don (Shindai 8). J Jpn Soc 92:106–109. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.92.106(In Japanese with English summary)
Moriguchi Y, Ujino-Ihara T, Uchiyama K, Futamura N, Saito M, Ueno S, Matsumoto A, Tani N, Taira H, Shinohara K, Tsumura Y (2012) The construction of a high-density linkage map for identifying SNP markers that are tightly linked to a nuclear-recessive major gene for male sterility in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. BMC Genom 13:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-95
Moriguchi Y, Ueno S, Higuchi Y, Miyajima D, Itoo S, Futamura N, Shinohara K, Tsumura Y (2014) Establishment of a microsatellite panel covering the sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) genome, and its application for localization of a male sterile gene (ms-2). Mol Breed 33:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9951-8
Moriguchi Y, Uchiyama K, Ueno S, Ujino-Ihara T, Matsumoto A, Iwai J, Miyajima D, Saito M, Sato M, Tsumura Y (2016) A high-density linkage map with 2,560 markers and its application for the localization of the male-sterile genes ms3 and ms4 in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Tree Genet Genomes 12:57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1011-1
Moriguchi Y, Totsuka S, Iwai J, Matsumoto A, Ueno S, Tsumura Y (2017) Pyramiding of male-sterile gene in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don with the aid of closely linked markers. Tree Genet Genomics 13:61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1149-5
Moriguchi Y, Ueno S, Hasegawa Y, Tadama T, Watanabe M, Saito R, Hirayama S, Iwai J, Konno Y (2020) Marker-assisted selection of trees with MALE STERILITY 1 in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don. Forests 11:734. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11070734
Muranty H, Jorge V, Bastien C, Lepoittevin C, Bouffier L, Sanchez L (2014) Potential for marker-assisted selection for forest tree breeding:lessons from 20 years of MAS in crops. Tree Genet Genomes 10:1491–1510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-014-0790-5
Nanasato Y, Mikami M, Futamura N, Endo M, Nishiguchi M, Ohmiya Y, Konagaya KI, Taniguchi T (2021) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). Sci Rep 11:16186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95547-w
Neale DB, Savolainen O (2004) Association genetics of complex traits in conifers. Trends Plant Sci 9:325–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.05.006
Neelam K, Brown-Guedira G, Huang L (2013) Development and validation of a breeder-friendly KASPar marker for wheat leaf rust resistance locus Lr21. Mol Breed 31:233–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9773-0
Nishihara Y (2021) Selection of male sterile tree in the control-pollinated progeny of Sosyun (Japanese cedar, Cryptomeria japonica D. Don) by SNP genotyping method using TaqMan probe. For Genet Tree Breed 10:26–135. https://doi.org/10.32135/fgtb.10.3_126(in Japanese with English summary)
Rasheed A, Hao Y, Xia X, Khan A, Xu Y, Varshney RK, He Z (2017) Crop breeding chips and genotyping platforms: progress, challenges, and perspectives. Mol Plant 10:1047–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.06.008
Saito M (2008) Development status and future prospect of male sterile Japanese cedar. Shinrin Kagaku 54:17–20. https://doi.org/10.11519/jjsk.54.0_17(In Japanese)
Saito M (2009) Effectiveness of an indoor miniature seed orchard arranged in lines for Cryptomeria japonica retaining male-sterile genes. J Jpn Soc 91:168–172. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.91.168(In Japanese with English summary)
Saito M (2010) Breeding strategy for the pollinosis preventive cultivars of Cryptomeria japonica D Don. J Jpn Soc 92:316–323. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.92.316(In Japanese with English summary)
Saito H (2020) Development and verification of precision of a simple screening method for male sterility in seedling production of Japanese Cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). J Jpn Soc 102:311–316. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.102.311 (In Japanese with English summary)
Saito M, Taira H (2005a) Plus tree of Cryptomeria japonica D. Don with a heterozygous male-sterility gene. J Res 10:391–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-005-0157-8
Saito M, Taira H (2005b) Establishment of a model miniature seed orchard of Cryptomeria japonica trees with a heterozygous male-sterility gene. J Jpn Soc 87:383–386. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.87.383 (in Japanese with English summary)
Semagn K, Babu R, Hearne S, Olsen M (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele specific PCR (KASP): overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol Breed 33:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9917-x
Strauss SH, Slavov GT, DiFazio SP (2022) Gene-editing for production traits in forest trees: challenges to integration and gene target identification. Forests 13:1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13111887
Tadama T, Totsuka S, Iwai J, Uchiyama K, Hasegawa Y, Moriguchi Y (2019) Genetic evaluation of Cryptomeria japonica breeding materials for male-sterile trees. Silvae Genet 68:67–72. https://doi.org/10.2478/sg-2019-0012
Taira H, Saito M, Furuta Y (1999) Inheritance of the trait of male sterility in Cryptomeria japonica. J Res 4:271–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02762782
Takahashi M, Miura M, Fukatsu E, Hiraoka Y, Kurita M (2023) Research and project activities for breeding of Cryptomeria japonica D. Don in Japan. J Res 28:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1080/13416979.2023.2172794
Tsumura Y (2023) Review: genetic structure and local adaptation in natural forests of Cryptomeria japonica. Ecol Res 38:64–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1703.12320
Watanabe M, Ueno S, Hasegawa Y, Moriguchi Y (2022) Efficient low-cost marker-assisted selection of trees with MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don) using bulk DNA samples. Tree Genet Genomes 18:29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-022-01561-y
Wei FJ, Ueno S, Ujino-Ihara T, Saito M, Tsumura Y, Higuchi Y, Hirayama S, Iwai J, Hakamata T, Moriguchi Y (2021) Construction of a reference transcriptome for the analysis of male sterility in sugi (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don) focusing on MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1). PLoS ONE 16:e0247180. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0247180
Woodward J (2014) Bi-allelic SNP genotyping using the TaqMan® assay. Methods Mol Biol 1145:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0446-4_6
Yoshii E, Taira H (2007) Cytological and genetical studies on male sterile sugi (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don), Shindai 1 and Shindai 5. J Jpn Soc 89:26–30. https://doi.org/10.4005/jjfs.89.26(in Japanese with English summary)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Y. Abe and M. Komada for their assistance with laboratory works. We also thank Y. Sato for assistance with artificial crossing, and T. Ihara for providing the Sanger sequencing data. We also thank the 20 Prefectural Forest Experiment Stations for providing breeding materials.
Funding
This research was supported by Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution (BRAIN) Grant (JPJ007097; Project ID 28013B) to YM, FFPRI Grant (#201421, #201906) to SU, and JSPS KAKENHI (21K05666) to YM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments, YM; performed the experiments and analyzed the data, MW; rearing and collection of families by artificial crossing, SH, JI; methodology, MW, SU, YH, HK, and YM; funding acquisition, SU and YM; writing—original draft, MW; writing—review and editing, YM, SU, YH, HK and JI. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, M., Ueno, S., Hasegawa, Y. et al. Development and application of a KASP marker for marker-assisted selection against the male-sterile gene MALE STERILITY 4 (MS4) in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). New Forests (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-024-10036-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-024-10036-y