Abstract
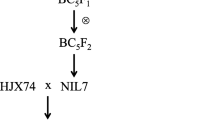
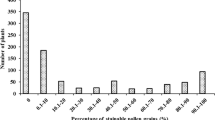
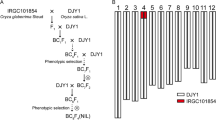
Thermo-sensitive genic male sterility (TGMS) is an important genetic means of two-line hybrid rice breeding. Pollen fertility in TGMS lines is regulated by a single point mutation in TGMS genes. Based on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertion-deletion mutations, Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR (KASP) markers were developed and utilized in rice molecular breeding via high-throughput detection, which saves time and money. In this study, we converted the SNPs on TGMS genes (including p/tms12-1and tms9-1) to functional co-dominant KASP markers and bred the resultant two-line hybrid rice. We differentiated the TGMS lines carrying p/tms12-1 or tms9-1 from other TGMS lines using the KASP assay. Pei’ai64S and Hua201S (containing p/tms12-1) had a homozygous GG genotype generating a blue signal. HengnongS-1 (containing tms9-1) had a homozygous CC genotype generating a red signal. The KASP assay for tms9-1 was identified as a recessive Mendelian trait. Seed purity was tested using the KASP marker for the two-line hybrid varieties of Liangyoupeijiu and Hualiangyou1206, which was consistent with findings by the dCAPS marker. Moreover, new TGMS lines were generated by pyramiding tms12-1 and tms9-1 gene under the same genetic background. Therefore, the KASP marker to detect the TGMS genes developed in this study can be widely used in two-line hybrid rice breeding. It provides a visually convenient toolkit for breeders to select individual target plants using high-throughput screening in two-line rice breeding.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison CK, Angira B, Kongchum M, Harrell DL, Baisakh N, Linscombe SD, Famoso AN (2020) Characterization of haplotype diversity in the BADH2 aroma gene and development of a KASP SNP assay for predicting aroma in US rice. Rice 13(1):47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-020-00410-7
Cabral AL, Jordan MC, McCartney CA, You FM, Humphreys DG, MacLachlan R, Pozniak CJ (2014) Identification of candidate genes, regions and markers for pre-harvest sprouting resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 14(1):340. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0340-1
Chen T, Zhang Y, Zhao L, Zhu Z, Lin J, Zhang S, Wang C (2009) A cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence marker to detect variation in Wx locus conditioning translucent endosperm in Rice. Rice Sci 16(2):106–110
Cheng SH, Zhuang JY, Fan YY, Du JH, Cao LY (2007) Progress in research and development on hybrid rice: a super-domesticate in China. Ann Bot 100(5):959–966
Ding JH, Lu Q, Ouyang YD, Mao HL, Zhang PB, Yao JL, Xu CG, Li XH, Xiao JH, Zhang QF (2012) A long noncoding RNA regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility, an essential component of hybrid rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(7):2654–2659. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1121374109
Fan Y, Zhang Q (2018) Genetic and molecular characterization of photoperiod and thermo-sensitive male sterility in rice. Plant Reprod 31(1):3–14
Fang T, Lei L, Li G, Powers C, Hunger RM, Carver BF, Yan L (2020) Development and deployment of KASP markers for multiple alleles of Lr34 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 133(7):2183–2195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03589-x
Gaudet M, Fara A-G, Beritognolo I, Sabatti M (2009) Allele-specific PCR in SNP genotyping. Method Mol Biol 578:415–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-411-1_26
Khush GS (2001) Green revolution: the way forward. Nat Rev Genet 2(10):815–822. https://doi.org/10.1038/35093585
Kim MS, Yang JY, Yu JK, Lee Y, Park YJ, Kang KK, Cho YG (2021) Breeding of high cooking and eating quality in rice by marker-assisted backcrossing (MABc) using KASP markers. Plants (basel) 10(4):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040804
Kumar S, Banks TW, Cloutier S (2012) SNP discovery through Next-Generation sequencing and its applications. Int J Plant Genomics 2012:831460. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/831460
le Thanh P, Khoo K (2014) Temperature switch PCR (TSP): a gel-based molecular marker technique for investigating single nucleotide polymorphisms. Methods MolBiol 1145:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0446-4_3
Leal-Bertioli SCM, Cavalcante U, Gouvea EG, Ballén-Taborda C, Shirasawa K, Guimarães PM, Jackson SA, Moretzsohn MC (2015) Identification of QTLs for rust resistance in the peanut wild species Arachis magna and the development of KASP markers for marker-assisted selection. G3 Genes Genomes Genetics 5(7):1403–1413
Li Z, Yu H, Li X, Zhang B, Ren W, Liu X, Fang Z, Yang L, Zhuang M, Lv H, Zhang Y (2020) Kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) genotyping and heterotic group classification of 244 inbred lines in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Euphytica 216(4):1086–1099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-020-02640-8
Mackay IJ, Bansept-Basler P, Barber T, Bentley AR, Cockram J, Gosman N, Greenland AJ, Horsnell R, Howells R, O’Sullivan DM, Rose GA (2014) An eight-parent multiparent advanced generation inter-cross population for winter-sown wheat: creation, properties, and validation. G3 Genes Genomes Genetics 4(9):1603–1610
Makhoul M, Rambla C, Voss-Fels KP, Hickey LT, Snowdon RJ, Obermeier C (2020) Overcoming polyploidy pitfalls: a user guide for effective SNP conversion into KASP markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 133(8):2413–2430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03608-x
Mou T (2016) The research progress and prospects of two-line hybrid rice in China. Chinese Sci Bull 61:3761–3769
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acid Res 8(19):4321–4325. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Pariasca-Tanaka J, Lorieux M, He C, McCouch S, Thomson MJ, Wissuwa M (2015) Development of a SNP genotyping panel for detecting polymorphisms in Oryza glaberrima/O. sativa interspecific crosses. Euphytica 201(1):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1183-4
Patil G, Chaudhary J, Vuong TD, Jenkins B, Qiu D, Kadam S, Shannon GJ, Nguyen HT (2017) Development of SNP genotyping assays for seed composition traits in soybean. Int J Plant Genomics 2017:6572969. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6572969
Qi Y, Liu Q, Zhang L, Mao B, Yan D, Jin Q, He Z (2014) Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of the novel thermo-sensitive genic male sterility tms9-1 gene in rice. Theor Appl Genet 127:1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2289-8
Qi Y, Wang L, Gui J, Zhang L, Liu Q, Wang J (2017) Development and validation of a functional co-dominant SNP marker for the photoperiod thermo-sensitive genic male sterility pms3 (p/tms12-1) gene in rice. Breed Sci 67(5):535–539. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.16138
Semagn K, Babu R, Hearne S, Olsen M (2014) Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using kompetitive allele specific PCR (KASP): overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol Breeding 33:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9917-x
Si HM, Liu WZ, Fu YP, Sun ZX, Hu GC (2011) Current situation and suggestions for development of two-line hybrid rice in China. Chin J Rice Sci 25(5):544–552
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG (2012) Primer3-new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 40(15):115. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks596
Virmani S, Sun Z, Mou T, Jauhar AA, Mao C (2003) Two-line hybrid rice breeding manual. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños
Wu JH, Wang QL, Kang ZS, Liu SJ, Li HY, Mu JM, Dai MF, Han DJ, Zeng QD, Chen XM (2017) Development and validation of KASP-SNP markers for QTL underlying resistance to stripe rust in common wheat cultivar P10057. Plant Dis 101:2079–2087. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-04-17-0468-RE
Yang G, Chen S, Chen L, Sun K, Huang C, Zhou D, Huang Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wang H, Chen Z, Guo T (2019a) Development of a core SNP arrays based on the KASP method for molecular breeding of rice. Rice 12(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-019-0272-3
Yang G, Chen S, Chen L, Gao W, Huang Y, Huang C, Zhou D, Wang J, Liu Y, Huang M, Xiao W, Wang H, Guo T, Chen Z (2019b) Development and utilization of functional KASP markers to improve rice eating and cooking quality through MAS breeding. Euphytica 215(4):66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2392-7
Yuan LP (1990) Progress of two-line system hybrid rice breeding. Sci Agric Sin 23(3):1–6
Yuan LP (2004) Hybrid rice technology for food security in the world. Crop Res 18:185–186
Zhang H, Huang J, Liu Q, Nawaz LuH, Gong J, Zhu Y, Yan W, Shu Q (2014) Characterization of an RNase Z nonsense mutation identified exclusively in environment-conditioned genic male sterile rice. Mol Breeding 34(2):481–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0051-1
Zhang HL, Chen X, Huang J, Zhi-Guo E, Gong J, Shu Q (2015) Identification and transition analysis of photo- /thermo-sensitive genic male sterile genes in two-line hybrid rice in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 48(1):1–9
Zhang J, Yang J, Zhang L, Luo J, Zhao H, Zhang J, Wen C (2020) A new SNP genotyping technology Target SNP-seq and its application in genetic analysis of cucumber varieties. Sci Rep 11(1):8010. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86981-x
Zhou H, Liu QJ, Li J, Jiang DG, Zhou LY, Wu P, Lu S, Li F, Zhu LY, Liu ZL, Chen LT, Liu YG, Zhuang CX (2012) Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA. Cell Res 22(4):649–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.28
Zhou H, Zhou H, Zhou M, Yang Y, Li J, Zhu L, Jiang D, Dong J, Liu Q, Gu L, Zhou L, Feng M, Qin P, Hu X, Song C, Shi J, Song X, Ni E, Wu X, Deng Q, Liu Z, Chen M, Liu YG, Cao X, Zhuang C (2014) RNase ZS1 processes UbL40 mRNAs and controls thermosensitive genic male sterility in rice. Nat Commun 5:4884–4892. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5884
Zhu D, Deng XW (2012) A non-coding RNA locus mediates environment-conditioned male sterility in rice. Cell Res 22:791–792. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.43
Acknowledgements
Financial support was provided for this research partly by the Project of the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province, China (Grant Number LGN21C130005, 2016C02050), the Project of the Molecular Designed Japonica Breeding with High Quality and Yield in the Middle-Low Reaches of Yangzi River (Grant Number 2017YFD0100302), and the Talent Training Project of Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Grant Number 2018R16R08E01).We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YQ and JW conceived and designed the study. YQ, LW, JS, and GM performed the study test. YQ, LW, and JS contributed to the KASP assay. YQ and GM prepared the materials and populations. YQ and JW wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This study complied with the ethical standards of China, where this research was carried out.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Y., Wang, L., Song, J. et al. Development and utilization of the functional co-dominant KASP marker for thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice Oryza sativa L.. Genet Resour Crop Evol 69, 635–643 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-021-01249-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-021-01249-7