Abstract
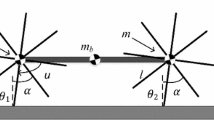
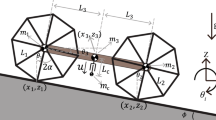
We propose the feed-forward and feedback (FaF) control systems for generating the limit cycle walking at a target walking speed by the combined rimless wheel (CRW) model. The proposed FaF control systems can calculate a control input constantly based on the mathematical analysis of the current and target walking states. As a result, first, the limit cycle walking at the target walking speed is generated by numerical simulations when the walker is driven by the constant FaF control system. Second, for controlling the convergence speed, we extend the FaF control to the two-period stepwise control systems. The limit cycle walking at the target walking speed is still generated, and the convergence speed is controlled by the settling time parameter. Finally, the real-time walking state updating is considered in the FaF control systems to handle the disturbances. In this case, we find that for generating a target walking speed, a precise mathematical model is not necessary for generating the target state, but can make the control input stable and efficient.

























Similar content being viewed by others
References
McGeer, T.: Passive dynamic walking. Int. J. Robot. Res. 9(2), 62–82 (1990)
Coleman, M.J., Chatterjee, A., Ruina, A.: Motions of a rimless spoked wheel: a simple three-dimensional system with impacts. Dyn. Stab. Syst. 12(3), 139–159 (1997)
Coleman, M.J.: Dynamics and stability of a rimless spoked wheel: a simple 2D system with impacts. Dyn. Syst. 25(2), 215–238 (2010)
Asano, F.: Stability analysis of underactuated compass gait based on linearization of motion. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 33(1), 93–111 (2015)
Asano, F.: Fully analytical solution to discrete behavior of hybrid zero dynamics in limit cycle walking with constraint on impact posture. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 35(2), 191–213 (2015)
Hobbelen, D.G.E., Wisse, M.: A disturbance rejection measure for limit cycle walkers: the gait sensitivity norm. IEEE Trans. Robot. 23(6), 1213–1224 (2007)
Hobbelen, D.G.E., Wisse, M.: Controlling the walking speed in limit cycle walking. Int. J. Robot. Res. 27(9), 989–1005 (2008)
Xiao, X., Asano, F.: Analytical solution of steady step period in 1-DOF limit cycle walking driven by stepwise control inputs. In: Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), pp. 245–250 (2014)
Kajita, S., Kanehiro, F., Kaneko, K., et al.: The 3D linear inverted pendulum mode: a simple modeling for a biped walking pattern generation. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2001, pp. 239–246. IEEE Press, New York (2001)
Juang, J.G.: Fuzzy neural network approaches for robotic gait synthesis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B, Cybern. 30(4), 594–601 (2000)
Asano, F.: Stability analysis of passive compass gait using linearized model. In: Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 557–562 (2011)
Asano, F., Xiao, X.: Role of deceleration effect in efficient and fast convergent gait generation. In: Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 5649–5654 (2013)
Xiao, X., Asano, F.: Analytical solution of target steady walking speed in 1-DOF limit cycle walking. In: Proc. of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4525–4531 (2015)
Xiao, X., Asano, F.: Generating 1-DOF limit cycle walking at target walking speed by feedforward limit cycle control. In: IEEE 54th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), pp. 1316–1321. IEEE Press, New York (2015)
Jain, A., Kuo, C., Sinkarenko, I.: Feedforward dynamics for the control of articulated multi-limb robots. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 37(1), 49–68 (2016)
Kelly, M., Ruina, A.: Non-linear robust control for inverted-pendulum 2D walking. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 4353–4358. IEEE Press, New York (2015)
Yi, S.J., Zhang, B.T., Hong, D., et al.: Practical bipedal walking control on uneven terrain using surface learning and push recovery. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 3963–3968. IEEE Press, New York (2011)
Hill, J., Fahimi, F.: Active disturbance rejection for walking bipedal robots using the acceleration of the upper limbs. Robotica 33(2), 264–281 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, X., Asano, F. Generating 1-DOF limit cycle walking at target walking speed by feed-forward and feedback limit cycle control. Multibody Syst Dyn 40, 155–175 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-017-9568-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11044-017-9568-5