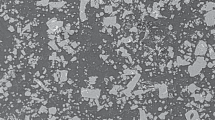
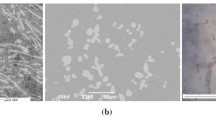
An Al – 5% Ti – 1% B master alloy with a lanthanum addition is prepared by improved technology employing halides. The effect of adding lanthanum to master alloy, introduced into melts of pure aluminum and of Al – 7% Si alloy, on the microstructure and degree of casting grain refinement is established. Asignificant modifying effect of adding lanthanum to Al – 5% Ti – 1% B master alloy during treatment of pure aluminum and its weak effect on modifying Al – 7% Si alloy are established.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Here and subsequently through the text elements are given in weight fraction expressed as a %.
References
T. Wang, H. Fu, Z. Chen, et al., “A novel fading-resistant Al – 3Ti – 3B grain refiner for Al – Si alloys,” J. Alloy Compd., 511, 45 – 49 (2012).
Z. Fan, Y.Wang, Y. Zhang, et al., “Grain refining mechanism in the Al/Al – Ti – B system,” Acta Mater., 84, 292 – 304 (2015).
T. E. Quested, “Understanding mechanisms of grain refinement of aluminium alloys by inoculation,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 20, 1357 – 1369 (2004).
Y. Birol, “A novel Al – Ti – B alloy for grain refining Al – Si foundry alloys,” J. Alloys Compd., 486, 219 – 222 (2009).
C. D. Mayes, M. D. McCartney, and G. J. Tatlock, “Influence of microstructure on grain refining performance of Al – Ti – B master alloys,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 9, 97 – 103 (1993).
G. P. Jones and J. Pearson, “Factors affecting the grain-refinement of aluminum using titanium and boron additives,” Metall. Trans. B, 7B, 223 – 234 (1976).
B. S. Terry and M. S. Lee, “Effects of processing parameters on aluminide morphology in aluminium grain refining master alloys,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 7, 608 – 612 (1991).
M. Easton and D. S. St John, “Grain refinement of aluminum alloys: Part I. The nucleant and solute paradigms a review of the literature,” Metall. Mater. Trans., 30A, 1613 – 1623 (1999).
P. Schumacher, A. L. Greer J. Worth, et al., “New studies of nucleation mechanisms in aluminium alloys: applications for grain refinement practice,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 14, 394 – 404 (1998).
P. Li, Y. Li, J. Nie, and X. Liu, “Influence of forming process on three-dimensional morphology of TiB2 particles in Al – Ti – B alloys,” J. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 22(3), 564 – 570 (2012).
F. Cao, J.Wen, H. Ding, et al., “Force analysis and experimental study of pure aluminum and Al – 5% Ti – 1% B alloy continuous expansion extrusion forming process,” Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 23(1), 201 – 207 (2013).
G. Han, X. Liu, and H. Ding, “Grain refinement of AZ31 magnesium alloy by new Al – Ti – C master alloys,” Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 19(5), 1057 – 1064 (2009).
J. A. Spittle and S. Sadli, “Effect of alloy variables on grain refinement of binary aluminium alloys with Al – Ti – B,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 11, 533 – 537 (1995).
T. Sritharan and H. Li, “Influence of titanium and boron on the ability to grain refine aluminum-silicon alloys,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 63, 585 – 589 (1997).
A. Arjuna Rao, B. S. Murty, and M. Chakraborty, “Response of an Al – Cr alloy towards grain refinement by Al – 5Ti – 1B master alloy,” Int. J. Cast Metals Res., 9, 125 – 132 (1996).
A. Arjuna Rao, B. S. Murty, and M. Chakraborty, “Role of zirconium and impurities in grain refinement of aluminium with Al – Ti – B,” Mater. Sci. Technol., 13, 769 – 777 (1997).
Y. P. Y. Chen, T. Lu, S. Tao, and J. Wu, “Effects of combinative addition of lanthanum and boron on grain refinement of Al – Si casting alloys,” Mater. Design, 64, 423 – 426 (2014).
X. L. Cui, Y. Wy, T. Gao, and X. F. Liu, “Preparation of a novel Al – 3B – 5Sr master alloy and its modification and refinement performance on A356 alloy,” J. Alloys Compd., 615, 906 – 911 (2014).
K. Wang, C. Cui, Q. Wang, et al. “The microstructure and formation mechanism of core — shell-like TiAl3/Ti2Al20Ce in melt-spun Al – Ti – B – Re grain refiner,” Mater. Lett., 85, 153 – 156 (2012).
X.-J.Wang, C. Xu, A. Muhammad, S. Hanada, et al., “Effects of Al – Ti – B – RE grain refiner on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al – 7.0 Si – 0.55 Mg alloy,” Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 24, 2244 – 2250 (2014).
Y. Birol, “An improved practice to manufacture Al – Ti – B master alloys by reacting halide salts with molten aluminium,” J. Alloy Compd. 420, 71 – 76 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 5, pp. 14 – 21, May, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yufei, Z., Bing, Z., Yanjun, Z. et al. Effect of Adding Lanthanum to Al – 5% Ti – 1% B Master Alloy on the Efficiency of Grain Refinement in Aluminum and Al – 7% Si Alloy. Met Sci Heat Treat 63, 243–250 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-021-00678-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-021-00678-6