Abstract
Background
Long non-coding RNAs are broadly dysregulated in disease conditions, especially cancer, and are associated with tumor initiation, invasion, and overall survival. This study aimed to elucidate the expression level of Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 4 (SNHG4) lncRNA in colorectal cancer (CRC) and its effect on cell cycle progression, invasion, and death.
Methods and results
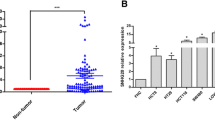
We evaluated the expression level of SNHG4 in clinical samples, including CRC tissues, adenomatous colorectal polyps (ACP), and their marginals. SNHG4-silenced SW1116 cells were used to evaluate the cell viability, cycle arrest, invasion, and apoptosis using MTT assay, scratching, flow cytometry, and immunoblotting. We also predicted molecular networks related to the SNHG4 involvement in CRC development. Results showed that SNHG4 expresses in cancerous tissues significantly higher than in polyps and marginals. This overexpression discriminated CRC from marginals and ACP with a suitable prognostic potential. Silencing of SNHG4 arrested the cell cycle at S and G2 phases and promoted early apoptosis in SW1116. It affected the active form of MMP2 and prevented cell invasion. Sponging of miRNAs which promotes the choline metabolism is the probable mechanism of SNHG4 involvement in CRC.
Conclusions
In conclusion, SNHG4 promotes CRC by dysregulating apoptosis and cell migration, and shows significant prognostic potential for CRC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Khan S, Masood M, Gaur H, Ahmad S, Syed MA (2021) Long non-coding RNA: an immune cells perspective. Life Sci 271:119152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119152
Khodayi-Shahrak M, Khalaj-Kondori M, Hosseinpour Feizi MA, Talebi M (2022) Insights into the mechanisms of non-coding RNAs’ implication in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. EXCLI J 21:921–940. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2022-5006
Khajehdehi M, Khalaj-Kondori M, Hosseinpour Feizi MA (2022) Expression profiling of cancer-related long non-coding RNAs revealed upregulation and biomarker potential of HAR1B and JPX in colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep 49(7):6075–6084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07396-z
Khajehdehi M, Khalaj-Kondori M, Ghasemi T, Jahanghiri B, Damaghi M (2021) Long noncoding RNAs in gastrointestinal Cancer: Tumor suppression Versus Tumor Promotion. Dig Dis Sci 66(2):381–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06200-x
Khodayi M, Khalaj-Kondori M, Hoseinpour Feizi MA, Jabarpour Bonyadi M, Talebi M (2022) Plasma lncRNA profiling identified BC200 and NEAT1 lncRNAs as potential blood-based biomarkers for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Excli j 21:772–785. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2022-4764
Ghasemi T, Khalaj-Kondori M, Hosseinpour Feizi MA, Asadi P (2020) lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA interaction network for colorectal cancer; an in silico analysis. Comput Biol Chem 89:107370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107370
Biagioni A, Tavakol S, Ahmadirad N, Zahmatkeshan M, Magnelli L, Mandegary A et al (2021) Small nucleolar RNA host genes promoting epithelial–mesenchymal transition lead cancer progression and metastasis. IUBMB Life 73(6):825–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2501
Chu Q, Gu X, Zheng Q, Guo Z, Shan D, Wang J et al (2021) Long noncoding RNA SNHG4: a novel target in human diseases. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):583. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02292-1
Jiao Y, Li Y, Jia B, Chen Q, Pan G, Hua F et al (2020) The prognostic value of lncRNA SNHG4 and its potential mechanism in liver cancer. Biosci Rep 40(1). https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20190729
Cao J, Xiao C, Fong CTH, Gong J, Li D, Li X et al (2022) Expression and Regulatory Network analysis of function of small nucleolar RNA host gene 4 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Clin Transl Hepatol 10(2):297–307. https://doi.org/10.14218/jcth.2020.00175
Cheng XB, Zhang T, Zhu HJ, Ma N, Sun XD, Wang SH et al (2021) Knockdown of lncRNA SNHG4 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting miR-204-5p. Neoplasma 68(3):546–556. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2021_200914N981
Wu J, Liu T, Sun L, Zhang S, Dong G (2020) Long noncoding RNA SNHG4 promotes renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis and invasion by acting as ceRNA to sponge mir-204-5p and upregulate RUNX2. Cancer Cell Int 20(1):514. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01606-z
Wang ZY, Duan Y, Wang P (2020) SP1-mediated upregulation of lncRNA SNHG4 functions as a ceRNA for miR-377 to facilitate prostate cancer progression through regulation of ZIC5. J Cell Physiol 235(4):3916–3927. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29285
Tang Y, Wu L, Zhao M, Zhao G, Mao S, Wang L et al (2019) LncRNA SNHG4 promotes the proliferation, migration, invasiveness, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells by regulating miR-98-5p. Biochem Cell Biol 97(6):767–776. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2019-0065
Wang F, Quan Q (2021) The long non-coding RNA SNHG4/microRNA-let-7e/KDM3A/p21 pathway is involved in the development of non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics 20:634–645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2020.12.010
Li H, Hong J, Wijayakulathilaka W (2019) Long non-coding RNA SNHG4 promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating c-Met via targeting miR-148a-3p. Cell Cycle 18(23):3313–3324. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1674071
Huang YF, Lu L, Shen HL, Lu XX (2020) LncRNA SNHG4 promotes osteosarcoma proliferation and migration by sponging miR-377-3p. Mol Genet Genomic Med 8(8):e1349. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.1349
Yang H, Guo JF, Zhang ML, Li AM (2020) LncRNA SNHG4 promotes neuroblastoma proliferation, migration, and invasion by sponging miR-377-3p. Neoplasma 67(5):1054–1062. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2020_191023N1081
Yuan Z, Wang W (2020) LncRNA SNHG4 regulates miR-10a/PTEN to inhibit the proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Hematology 25(1):160–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/16078454.2020.1754636
Wang X, Tian W, Wu L, Wei Z, Li W, Xu Y et al (2020) LncRNA SNHG4 regulates miR-138/c-Met axis to promote the proliferation of glioblastoma cells. NeuroReport 31(9):657–662. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnr.0000000000001469
Li Z, Zhuo Y, Li J, Zhang M, Wang R, Lin L (2021) Long non-coding RNA SNHG4 is a potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Indicator in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann Clin Lab Sci 51(5):654–662
Khalaj-Kondori M, Hosseinnejad M, Hosseinzadeh A, Behroz Sharif S, Hashemzadeh S (2020) Aberrant hypermethylation of OGDHL gene promoter in sporadic colorectal cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 44(1):100471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2019.03.001
Ghasemi T, Khalaj-Kondori M, Hosseinpour Feizi MA, Asadi P (2021) Long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1 is up regulated in colorectal cancer. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 40(8):829–844. https://doi.org/10.1080/15257770.2021.1956530
Wang S, Zhu W, Qiu J, Chen F (2021) lncRNA SNHG4 promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process via sponging mir-204-5p in gastric cancer. Mol Med Rep 23(1). https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11724
Zhou N, Chen Y, Yang L, Xu T, Wang F, Chen L et al (2021) LncRNA SNHG4 promotes malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the miR-144-3p/MET axis. Am J Transl Res 13(10):11144–11161
Zhou Z, Tan F, Pei Q, Li C, Zhou Y, Li Y et al (2021) lncRNA SNHG4 modulates colorectal cancer cell cycle and cell proliferation through regulating miR-590-3p/CDK1 axis. Aging 13(7):9838–9858. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202737
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z, Quan C et al (2021) Correction to: MiR-139-5p inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR and NOTCH1. Protein Cell 12(8):668–670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-021-00826-x
Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Merhautova J, Machackova T, Gutierrez-Garcia I, Garcia-Solano J, Radova L et al (2017) MiR-215-5p is a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer targeting EGFR ligand epiregulin and its transcriptional inducer HOXB9. Oncogenesis 6(11):399. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-017-0006-6
Ren XL, He GY, Li XM, Men H, Yi LZ, Lu GF et al (2016) MicroRNA-206 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting FMNL2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142(3):581–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-015-2053-8
Hu F, Min J, Cao X, Liu L, Ge Z, Hu J et al (2016) MiR-363-3p inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and suppresses metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting Sox4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 474(1):35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.04.055
Eldaly MN, Metwally FM, Shousha WG, El-Saiid AS, Ramadan SS (2020) Clinical potentials of miR-576-3p, miR-613, NDRG2 and YKL40 in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 21(6):1689–1695. https://doi.org/10.31557/apjcp.2020.21.6.1689
Zhang JL, Zheng HF, Li K, Zhu YP (2022) Mir-495-3p depresses cell proliferation and migration by downregulating HMGB1 in colorectal cancer. World J Surg Oncol 20(1):101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-022-02500-w
Ding Q, Zhang W, Cheng C, Mo F, Chen L, Peng G et al (2020) Dioscin inhibits the growth of human osteosarcoma by inducing G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and GSDME-dependent cell death in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Physiol 235(3):2911–2924. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29197
Wang H, Zhang T, Sun W, Wang Z, Zuo D, Zhou Z et al (2016) Erianin induces G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via the ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Death Dis 7(6):e2247–e. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.138
Li J, Chen W, Zhang P, Li N (2006) Topoisomerase II trapping agent teniposide induces apoptosis and G2/M or S phase arrest of oral squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol 4:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7819-4-41
Carneiro BA, El-Deiry WS (2020) Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 17(7):395–417. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41571-020-0341-y
Bai HL, Kang CM, Sun ZQ, Li XH, Dai XY, Huang RY et al (2020) TTDA inhibited apoptosis by regulating the p53-Bax/Bcl2 axis in glioma. Exp Neurol 331:113380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113380
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J et al (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275(5303):1129–1132. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.275.5303.1129
Kharbanda S, Pandey P, Schofield L, Israels S, Roncinske R, Yoshida K et al (1997) Role for Bcl-xL as an inhibitor of cytosolic cytochrome C accumulation in DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(13):6939–6942. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.13.6939
Si L, Fu J, Liu W, Hayashi T, Nie Y, Mizuno K et al (2020) Silibinin inhibits migration and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells through induction of mitochondrial fusion. Mol Cell Biochem 463(1–2):189–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03640-6
Freitas JT, Jozic I, Bedogni B (2021) Wound Healing Assay for Melanoma Cell Migration. Methods Mol Biol 2265:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1205-7_4
Zeng F, Yu N, Han Y, Ainiwaer J (2020) The long non-coding RNA MIAT/miR-139-5p/MMP2 axis regulates cell migration and invasion in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Biosci 45
Wang X, Yang B, She Y, Ye Y (2018) The lncRNA TP73-AS1 promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via modulation of MMP2 and MMP9. J Cell Biochem 119(9):7790–7799. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27158
Zhu X, Luo C, Bu F, Lin K, Zhu Z (2020) Long non-coding RNA RP11-59H7.3 promotes cell proliferation and invasion metastasis in colorectal cancer by miR-139-5p/NOTCH1 axis. Aging 12(12):11653–11666. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103331
Zhang X, Shi H, Yao J, Li Y, Gao B, Zhang Y et al (2020) FAM225A facilitates colorectal cancer progression by sponging miR-613 to regulate NOTCH3. Cancer Med 9(12):4339–4349. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3053
Zhu X, Zhu J, Tan T, Bu F, Zhao J, Luo C et al (2021) RP11-51O6.1 sponges miR-206 to accelerate colorectal cancer carcinogenesis and metastasis through upregulating YAP1. Carcinogenesis 42(7):984–994. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgab044
Zhang L, Wu H, Zhang Y, Xiao X, Chu F, Zhang L (2022) Induction of lncRNA NORAD accounts for hypoxia-induced chemoresistance and vasculogenic mimicry in colorectal cancer by sponging the miR-495-3p/ hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α). Bioengineered 13(1):950–962. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.2015530
Zhang Y, Peng C, Li J, Zhang D, Zhang C, Jin K et al (2022) Long non-coding RNA CCDC144NL-AS1 promotes cell proliferation by regulating the miR-363-3p/GALNT7 axis in colorectal cancer. J Cancer 13(3):752–763. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.65885
Sonkar K, Ayyappan V, Tressler CM, Adelaja O, Cai R, Cheng M et al (2019) Focus on the glycerophosphocholine pathway in choline phospholipid metabolism of cancer. NMR Biomed 32(10):e4112–e. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.4112
Bae S, Ulrich CM, Neuhouser ML, Malysheva O, Bailey LB, Xiao L et al (2014) Plasma choline metabolites and colorectal cancer risk in the women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Cancer Res 74(24):7442–7452. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-1835
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the kind cooperation of Dr. Ghalamfarsa and his coworkers in Yasuj University of Medical Sciences, Yasuj-Iran, mainly Mis. Khosravani in preparation of SW1116 colorectal cell line.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mina Khajehdehi: Writing- Original draft preparation, Investigation, Software, Methodology. Mohammad Khalaj-Kondori: Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing- Reviewing and Editing. Behzad Baradaran: Conceptualization, Methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the University of Tabriz (IR.TABRIZU.REC.1398.027).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for the publication of clinicopathological characteristics in Table 1.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khajehdehi, M., Khalaj-Kondori, M. & Baradaran, B. The siRNA-mediated knockdown of SNHG4 efficiently induced pro-apoptotic signaling and suppressed metastasis in SW1116 colorectal cancer cell line. Mol Biol Rep 50, 8995–9006 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08742-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08742-5