Abstract
Background
Rice (Oryza sativa L.) is one of the staple foods worldwide. To feed the growing population, the improvement of rice cultivars is important. To make the improvement in the rice breeding program, it is imperative to understand the similarities and differences of the existing rice accessions to find out the genetic diversity. Previous studies demonstrated the existence of abundant elite genes in rice landraces. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) was performed for yield and yield related traits to find the genetic diversity.
Design
Experimental study.
Methods and results
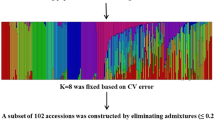
A total of 204 SSRs markers were used among 17 SSRs found to be located on each chromosome in the rice genome. The diversity was analyzed using different genetic characters i.e., the total number of alleles (TNA), polymorphic information content (PIC), and gene diversity by Power markers, and the values for each genetic character per marker ranged from 2 to 9, 0.332 to 0.887 and 0.423 to 0.900 respectively across the whole genome. The results of population structure identified four main groups. MTA identified several markers associated with many agronomically important traits. These results will be very useful for the selection of potential parents, recombinants, and MTAs that govern the improvements and developments of new high yielding rice varieties.
Conclusions
Analysis of diversity in germplasm is important for the improvement of cultivars in the breeding program. In the present study, the diversity was analyzed with different methods and found that enormous diversity was present in the studied rice germplasm. The structure analysis found the presence of 4 genetic groups in the existing germplasm. A total of 129 marker-trait associations (MTAs) have been found in this study.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All necessary data is provided in supplimentary file.
References
Zhang P, Zhong K, Zhong Z, Tong H (2019) Genome-wide association study of important agronomic traits within a core collection of rice (Oryza sativa L.) BMC plant bio. 19:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1842-7
Shah SM, Naveed SA, Arif M (2013) Genetic diversity in basmati and non-basmati rice varieties based on microsatellite markers. Pak J Bot 45:423–431. http://www.pakbs.org/…/56.pdf
Bhandari H, Bhanu A, Srivastava K, Singh M, Shreya HA (2017) Assessment of genetic diversity in crop plants-an overview. Adv plants agric Res 7:00255. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15406/apar.2017.07.00255
Chakravarthi BK, Naravaneni R (2006) SSR marker based DNA fingerprinting and diversity study in rice (Oryza sativa. L).Afr J Biotec5. https://www.ajol.info/index.php/ajb/article/view/42772
Bevan MW, Uauy C (2013) Genomics reveals new landscapes for crop improvement. Geno bio 14:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-6-206
Vaughan DA, Lu BR, Tomooka N (2008) The evolving story of rice evolution. Plant sci 174:394–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.01.016
Roy S, Marndi B, Mawkhlieng B, Banerjee A, Yadav R, Misra A, Bansal K (2016) Genetic diversity and structure in hill rice (Oryza sativa L.) landraces from the North-Eastern Himalayas of India. BMC genet 17:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0414-1
Emanuelli F, Lorenzi S, Grzeskowiak L, Catalano V, Stefanini M, Troggio M, Myles S, Martinez-Zapater JM, Zyprian E, Moreira FM (2013) Genetic diversity and population structure assessed by SSR and SNP markers in a large germplasm collection of grape. BMC plant bio 13:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-13-39
Ren X, Jiang H, Yan Z, Chen Y, Zhou X, Huang L, Lei Y, Huang J, Yan L, Qi Y (2014) Genetic diversity and population structure of the major peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars grown in China by SSR markers. PLoS ONE 9:e88091. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088091
Shirasawa K, Ishii K, Kim C, Ban T, Suzuki M, Ito T, Muranaka T, Kobayashi M, Nagata N, Isobe S (2013) Development of Capsicum EST–SSR markers for species identification and in silico mapping onto the tomato genome sequence. Mol Bree 31:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-012-9774-z
Lu J, Wang S, Zhao H, Liu J, Wang H (2012) Genetic linkage map of EST-SSR and SRAP markers in the endangered Chinese endemic herb Dendrobium (Orchidaceae). Genet Mol Res 11:4654–4667. https://doi.org/10.4238/2012.December.21.1
Adriani DE, Lafarge T, Dardou A, Fabro A, Clément-Vidal A, Yahya S, Dingkuhn M, Luquet D (2016) The qTSN positive effect on panicle and flag leaf size of rice is associated with an early down-regulation of tillering. FPLS 6:1197. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.01197
Xu J, Henry A, Sreenivasulu N (2020) Rice yield formation under high day and night temperatures—A prerequisite to ensure future food security. Plant, cell env 43: 1595–1608. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13748
Chen L, Wang Q, Tang M, Zhang X, Pan Y, Yang X, Gao G, Lv R, Tao W, Jiang L (2021) QTL mapping and identification of candidate genes for heat tolerance at the flowering stage in rice. Front Genet 1840. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.621871
Huang X, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Li C, Zhu C, Lu T, Zhang Z, Li M (2010) Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat genet 42:961–967. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.695
Kadam NN, Tamilselvan A, Lawas LM, Quinones C, Bahuguna RN, Thomson MJ, Dingkuhn M, Muthurajan R, Struik PC, Yin X (2017) Genetic control of plasticity in root morphology and anatomy of rice in response to water deficit. Plant phys 174:2302–2315. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00500
Kraakman AT, Niks RE, Van den Berg PM, Stam P, Van Eeuwijk FA (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics 168:435–446. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.026831
Nie X, Huang C, You C, Li W, Zhao W, Shen C, Zhang B, Wang H, Yan Z, Dai B (2016) Genome-wide SSR-based association mapping for fiber quality in nation-wide upland cotton inbreed cultivars in China. BMC Genomics 17:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-2662-x
Chao DY, Silva A, Baxter I, Huang YS, Nordborg M, Danku J, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Salt DE (2012) Genome-wide association studies identify heavy metal ATPase3 as the primary determinant of natural variation in leaf cadmium in Arabidopsis thaliana. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002923
Tian F, Bradbury PJ, Brown PJ, Hung H, Sun Q, Flint Garcia S, Rocheford TR, McMullen MD, Holland JB, Buckler (2011) ES, Genome-wide association study of leaf architecture in the maize nested association mapping population. Nat genet 43: 159–162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.746
Kraakman AT, Niks RE, Van den Berg PM, Stam P, Van Eeuwijk FA, (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics, 168: 435-446. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.104.026831
Zhao L, Lei J, Huang Y, Zhu S, Chen H, Huang R, Peng Z, Tu Q, Shen X, Yan S, (2016) Mapping quantitative trait loci for heat tolerance at anthesis in rice using chromosomal segment substitution lines. Bree sci 15084. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.15084
Yano K, Yamamoto E, Aya K, Takeuchi H, Lo PC, Hu L, Yamasaki M, Yoshida S, Kitano H, Hirano K (2016) Genome-wide association study using whole-genome sequencing rapidly identifies new genes influencing agronomic traits in rice. Nat genet 48:927–934. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3596
Huang X, Yang S, Gong J, Zhao Y, Feng Q, Gong H, Li W, Zhan Q, Cheng B, Xia J (2015) Genomic analysis of hybrid rice varieties reveals numerous superior alleles that contribute to heterosis. Nat com 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7258
Shi Y, Gao L, Wu Z, Zhang X, Wang M, Zhang C, Zhang F, Zhou Y, Li Z (2017) Genome-wide association study of salt tolerance at the seed germination stage in rice. BMC plant bio 17:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1044-0
Lekklar C, Pongpanich M, Suriya-Arunroj D, Chinpongpanich A, Tsai H, Comai L, Chadchawan S, Buaboocha T (2019) Genome-wide association study for salinity tolerance at the flowering stage in a panel of rice accessions from Thailand. BMC Genomics 20:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-018-5317-2
Patishtan J, Hartley TN, Fonseca de Carvalho R, Maathuis FJ, (2018) Genome?wide association studies to identify rice salt?tolerance markers. Plant, cell & environ 41: 970-982. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12975
Murray M, Thompson WF, Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA (1980) Nucl acids res 8: 4321-4326. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/8.19.4321
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Geno res 11:1441–1452. http://www.genome.org/cgi/doi/https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.184001
McCouch SR, Teytelman L, Xu Y, Lobos KB, Clare K, Walton M, Fu B, Maghirang R, Li Z, Xing Y (2002) Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice (Oryza sativa L. DNA res 9:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/9.6.199
Liu J, Muse S, PowerMarker (2017) V3. 0 Manual. PowerMarker V3. 0 Manual http://www.powermarker.net
Earl DA (2012) STRUCTURE HARVESTER: a website and program for visualizing STRUCTURE output and implementing the Evanno method. Cons genet reso 4:359–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-011-9548-7
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, De Bakker PI, Daly MJ, PLINK (2007) a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Ameri J hum genet 81:559–575. https://doi.org/10.1086/519795
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat genet 38:904–909. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1847
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh Bi I, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat genet 38:203–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1702
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinfo 23:2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genet 155:945–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/155.2.945
Roy PS, Rao GJN, Jena S, Samal R, Patnaik A, Patnaik SSC, Jambhulkar NN, Sharma S, Mohapatra T, (2016) Nuclear and chloroplast DNA variation provides insights into population structure and multiple origin of native aromatic rices of Odisha, India. PloS one 11: e0162268. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162268
Rana MM, Islam MA, Imran S, Rubani S, Hassan L, (2018) Genetic diversity analysis of NERICA lines and parents using SSR markers. Int J plant & soil sci 1–10. https://journalbank.org/index.php/IJPSS/article/view/607
Ahmed S, Anik TR, Islam A, Uddin I, Haque MS (2019) Screening of some rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for salinity tolerance using morphological and molecular markers. Biosci biotec res asia 16:377–390. https://doi.org/10.13005/bbra/2753
Verma H, Borah J, Sarma R (2019) Variability assessment for root and drought tolerance traits and genetic diversity analysis of rice germplasm using SSR markers. Sci Rep 9:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52884-1
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Tavaud M, Aranzana M, Poizat C, Zanetto A, Arus P, Laigret F (2002) Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theo Appli Genet 105:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-0867-7
Hasnaoui N, Buonamici A, Sebastiani F, Mars M, Zhang D, Vendramin GG (2012) Molecular genetic diversity of Punica granatum L.(pomegranate) as revealed by microsatellite DNA markers (SSR). Gene 493:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2011.11.012
Shiferaw E, Pè M, Porceddu E, Ponnaiah M (2012) Exploring the genetic diversity of Ethiopian grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) using EST-SSR markers. Mol Bree 30:789–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9662-y
Nachimuthu VV, Muthurajan R, Duraialaguraja S, Sivakami R, Pandian BA, Ponniah G, Gunasekaran K, Swaminathan M, Sabariappan R (2015) Analysis of Population structure and genetic diversity in rice germplasm using SSR markers: An initiative towards association mapping of agronomic traits in Oryza sativa. Rice 8:30. doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-015-0062-5
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Amer J of hum genet 32:314. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1686077/
Babu BK, Meena V, Agarwal V, Agrawal P (2014) Population structure and genetic diversity analysis of Indian and exotic rice (Oryza sativa L.) accessions using SSR markers. Mol bio rep 41:4329–4339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3304-5
Shahriar M, Robin A, Begum S, Hoque A (2014) Diversity analysis of some selected rice genotypes through SSR-based molecular markers. J Bangla Agric uni 12:307–311. https://www.banglajol.info/index.php/JBAU/article/view/28689
Anandan A, Anumalla M, Pradhan SK, Ali J (2016) Population structure, diversity and trait association analysis in rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm for early seedling vigor (ESV) using trait linked SSR markers. PLoS ONE 11:e0152406. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0152406
Belamkar V, Selvaraj MG, Ayers JL, Payton PR, Puppala N, Burow MD (2011) A first insight into population structure and linkage disequilibrium in the US peanut minicore collection. Genet 139:411. DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-011-9556-2
Zhao WG, Chung JW, Kwon SW, Lee JH, Ma KH, Park YJ (2013) Association analysis of physicochemical traits on eating quality in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 191:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0820-z
Edzesi WM, Dang X, Liang L, Liu E, Zaid IU, Hong D (2016) Genetic diversity and elite allele mining for grain traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by association mapping. FPLS 7:787. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00787
Donde R, Kumar J, Gouda G, Gupta MK, Mukherjee M, Baksh SY, Mahadani P, Sahoo KK, Behera L, Dash SK (2019) Assessment of genetic diversity of drought tolerant and susceptible rice genotypes using microsatellite markers. Rice Sci 26:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2019.01.004
Zhang P, Zhong K, Shahid MQ, Tong H (2016) Association analysis in rice: from application to utilization. FPLS 7:1202. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01202
Pandit E, Tasleem S, Barik SR, Mohanty DP, Nayak DK, Mohanty SP, Das S, Pradhan SK (2017) Genome-wide association mapping reveals multiple QTLs governing tolerance response for seedling stage chilling stress in indica rice. FPLS 8:552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00552
Suji K, Biji K, Poornima R, Prince KSJ, Amudha K, Kavitha S, Mankar S, Babu RC (2012) Mapping QTLs for plant phenology and production traits using indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) lines adapted to rainfed environment. Mol biotec 52:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-011-9482-7
Horii H, Nemoto K, Miyamoto N, Harada J (2006) Quantitative trait loci for adventitious and lateral roots in rice. Plant Bree 125: 198–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2006.01124.x
Qu Y, Mu P, Zhang H, Chen CY, Gao Y, Tian Y, Wen F, Li Z (2008) Mapping QTLs of root morphological traits at different growth stages in rice. Genetica 133:187–200. DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-007-9199-5
Singh N, Choudhury DR, Tiwari G, Singh AK, Kumar S, Srinivasan K, Tyagi R, Sharma A, Singh N, Singh R (2016) Genetic diversity trend in Indian rice varieties: an analysis using SSR markers. BMC genet 17:1–13. DOI https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0437-7
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to very thankful to the College for Agriculture and Biotechnology, Zhejiang University China for supporting and helping to complete this research work timely. Many thanks and greetings to Higher Education Commission (HEC), the Government of Pakistan financially supported to complete the project in early dates.
Funding
The project was supported by University of the Punjab, Lahore Pakistan and Higher Education Commission, Government of Pakistan Islamabad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA, AR and MA design the experiment. MA, AR, MS, BR, AA and SS collect and analyze the data. AA and SS write the manuscripts and analyze the data. MSA, UM help in data analysis and scientific writing and MAJ revise the manuscripts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashfaq, M., Rasheed, A., Sajjad, M. et al. Genome wide association mapping of yield and various desirable agronomic traits in Rice. Mol Biol Rep 49, 11371–11383 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07687-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07687-5