Abstract
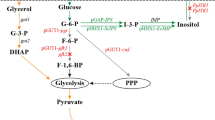
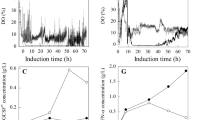
In the present study, the effects of individual as well as multiple genes of pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) on human interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) production were analyzed. With overexpression of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (GND2), 1.9-fold increase in hIFN-γ was achieved, while synergetic effect of 6-phosphogluconolactonase (SOL3) and d-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase (RPE1) resulted in 2.56-fold increase in hIFN-γ as compared to control. Fed batch fermentation using mixed feeding of gluconate and methanol (carbon source) was carried out, resulting in 80 and 123 mg L−1 of hIFN-γ enhancement in recombinant Pichia GS115 strain encoding codon optimized hIFN-γ (GS115/hIFN-γ) and Pichia GS115 strain encoding codon optimized hIFN-γ with co-expressed 6-phosphogluconolactonase(SOL3) and d-ribulose-5-phosphate 3-epimerase (RPE1) (GS115/hIFN-γ/SR) respectively. To get more insight of the flux distribution towards hIFN-γ, studies were carried out by applying flux balance analysis during methanol fed batch phase for both strains. In both strains (GS115/hIFN-γ and GS115/hIFN-γ/SR) more than 95% of formaldehyde flux is directed towards assimilatory pathway. The analysis revealed that with the overexpression of SOL3 and RPE1 the flux towards PPP triggering the alleviation in hIFN-γ production.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Vogl T, Hartner FS, Glieder A (2013) New opportunities by synthetic biology for biopharmaceutical production in Pichia pastoris. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24(6):1094–1101
Meehl MA, Stadheim TA (2014) Biopharmaceutical discovery and production in yeast. Curr Opin Biotechnol 30:120–127
Potvin G, Ahmad A, Zhang Z (2012) Bioprocess engineering aspects of heterologous protein production in Pichia pastoris: a review. Biochem Eng J 64:91–105
Ahmad M, Hirz M, Pichler H, Schwab H (2014) Protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(12):5301–5317
Looser V et al (2015) Cultivation strategies to enhance productivity of Pichia pastoris: a review. Biotechnol Adv 33(6):1177–1193
Macauley-Patrick S, Fazenda ML, McNeil B, Harvey LM (2005) Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast Chichester Engl 22(4):249–270
Cereghino JL, Cregg JM (2000) Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24(1):45–66
Prabhu AA, Bharali B, Singh AK, Allaka M, Sukumar P, Veeranki VD (2018) Engineering folding mechanism through Hsp70 and Hsp40 chaperones for enhancing the production of recombinant human interferon gamma (rhIFN-γ) in Pichia pastoris cell factory. Chem Eng Sci 181:58–67
Wu G, Yan Q, Jones JA, Tang YJ, Fong SS, Koffas MAG (2016) Metabolic burden: cornerstones in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering applications. Trends Biotechnol 34(8):652–664
Prabhu AA, Boro B, Bharali B, Chakraborty S, Dasu VV (2018) Gene and process level modulation to overcome the bottlenecks of recombinant proteins expression in Pichia pastoris. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 18(15):1200–1223
Glick BR (1995) Metabolic load and heterologous gene expression. Biotechnol Adv 13(2):247–261
Bentley WE, Mirjalili N, Andersen DC, Davis RH, Kompala DS (1990) Plasmid-encoded protein: the principal factor in the ‘metabolic burden’ associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 35(7):668–681
Heyland J, Fu J, Blank LM, Schmid A (2010) Quantitative physiology of Pichia pastoris during glucose-limited high-cell density fed-batch cultivation for recombinant protein production. Biotechnol Bioeng 107(2):357–368
Dragosits M et al (2009) The effect of temperature on the proteome of recombinant Pichia pastoris. J Proteome Res 8(3):1380–1392
Kim HU, Kim TY, Lee SY (2008) Metabolic flux analysis and metabolic engineering of microorganisms. Mol Biosyst 4(2):113–120
Varma A, Palsson BO (1994) Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110. Appl Environ Microbiol 60(10):3724–3731
Raman K, Chandra N (2009) Flux balance analysis of biological systems: applications and challenges. Brief Bioinform 10(4):435–449
Toya Y, Kono N, Arakawa K, Tomita M (2011) Metabolic flux analysis and visualization. J Proteome Res 10(8):3313–3323
Antoniewicz MR (2015) Methods and advances in metabolic flux analysis: a mini-review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42(3):317–325
Nocon J et al (2014) Model based engineering of Pichia pastoris central metabolism enhances recombinant protein production. Metab Eng 24:129–138
Nocon J et al (2016) Increasing pentose phosphate pathway flux enhances recombinant protein production in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:5955–5963
Prielhofer R et al (2015) Pichia pastoris regulates its gene-specific response to different carbon sources at the transcriptional, rather than the translational, level. BMC Genom 16:167
Prabhu AA, Veeranki VD, Dsilva SJ (2016) Improving the production of human interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) in Pichia pastoris cell factory: an approach of cell level. Process Biochem 51(6):709–718
Prabhu AA, Mandal B, Dasu VV (2017) Medium optimization for high yield production of extracellular human interferon-γ from Pichia pastoris: a statistical optimization and neural network-based approach. Korean J Chem Eng 34(4):1109–1121
Wang P et al (2017) Accurate analysis of fusion expression of Pichia pastoris glycosylphosphatidylinositol-modified cell wall proteins. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 44(9):1355–1365.
Kauffman KJ, Prakash P, Edwards JS (2003) Advances in flux balance analysis. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14(5):491–496
Çelik E, Çalık P, Oliver SG (2010) Metabolic flux analysis for recombinant protein production by Pichia pastoris using dual carbon sources: effects of methanol feeding rate. Biotechnol Bioeng 105(2):317–329
Förster J, Famili I, Fu P, Palsson B, Nielsen J (2003) Genome-scale reconstruction of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic network. Genome Res 13(2):244–253
De Schutter K et al (2009) Genome sequence of the recombinant protein production host Pichia pastoris. Nat Biotechnol 27(6):561–566
Fiaux J, Çakar ZP, Sonderegger M, Wüthrich K, Szyperski T, Sauer U (2003) Metabolic-flux profiling of the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis. Eukaryot Cell 2(1):170–180
Solà A, Maaheimo H, Ylönen K, Ferrer P, Szyperski T (2004) Amino acid biosynthesis and metabolic flux profiling of Pichia pastoris. Eur J Biochem 271(12):2462–2470
Prabhu AA, Purkayastha A, Mandal B, Kumar JP, Mandal BB, Dasu VV (2017) A novel reverse micellar purification strategy for histidine tagged human interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) protein from Pichia pastoris. Int J Biol Macromol 107:2512–2524
Prabhu AA, Dasu VV (2017) Dual-substrate inhibition kinetic studies for recombinant human interferon gamma producing Pichia pastoris. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47(10):953–962
A AP, Chityala S, Garg Y, Dasu VV (2017) Reverse micellar extraction of papain with cationic detergent based system: an optimization approach. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47(3):236–244
Wells E, Robinson AS (2017) Cellular engineering for therapeutic protein production: product quality, host modification, and process improvement. Biotechnol J 12(1):1600105
Zubay GL, Atkinson DE (1988) Biochemistry. Macmillan, Collier Macmillan, New York
Zampar GG et al (2013) Temporal system-level organization of the switch from glycolytic to gluconeogenic operation in yeast. Mol Syst Biol 9:651
Castelli LM et al (2011) Glucose depletion inhibits translation initiation via eIF4A loss and subsequent 48S preinitiation complex accumulation, while the pentose phosphate pathway is coordinately up-regulated. Mol Biol Cell 22(18):3379–3393
Rebnegger A et al (2014) In Pichia pastoris, growth rate regulates protein synthesis and secretion, mating and stress response. Biotechnol J 9(4):511–525
Stratton J, Chiruvolu V, Meagher M (1998) High cell-density fermentation. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 103:107–120
Zhang W, Inan M, Meagher MM (2000) Fermentation strategies for recombinant protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 5(4):275–287
Celik E, Calik P, Oliver SG (2009) Fed-batch methanol feeding strategy for recombinant protein production by Pichia pastoris in the presence of co-substrate sorbitol. Yeast Chichester Engl 26(9):473–484
Çalık P et al (2010) Fermentation and oxygen transfer characteristics in recombinant human growth hormone production by Pichia pastoris in sorbitol batch and methanol fed-batch operation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85(2):226–233
Soyaslan E, Çalık P (2011) Enhanced recombinant human erythropoietin production by Pichia pastoris in methanol fed-batch/sorbitol batch fermentation through pH optimization. Biochem Eng J 55(1):59–65
Çalık P et al (2013) Effect of co-substrate sorbitol different feeding strategies on human growth hormone production by recombinant Pichia pastoris. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 88(9):1631–1640
Inan M, Meagher MM (2001) The effect of ethanol and acetate on protein expression in Pichia pastoris. J Biosci Bioeng 92(4):337–341
Solà A, Jouhten P, Maaheimo H, Sánchez-Ferrando F, Szyperski T, Ferrer P (2007) Metabolic flux profiling of Pichia pastoris grown on glycerol/methanol mixtures in chemostat cultures at low and high dilution rates. Microbiology 153:281–90
Çelik Eda, Çalık Pınar, Oliver Stephen G (2010) Metabolic flux analysis for recombinant protein production by Pichia pastoris using dual carbon sources: effects of methanol feeding rate. Biotechnol Bioeng 105:317–329
Werten MW, van den Bosch TJ, Wind RD, Mooibroek H, de Wolf FA (1999) High-yield secretion of recombinant gelatins by Pichia pastoris. Yeast Chichester Engl 15(11):1087–1096
Kang HA et al (2000) Proteolytic stability of recombinant human serum albumin secreted in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53(5):575–582
Muthuraj M, Palabhanvi B, Misra S, Kumar V, Sivalingavasu K, Das D (2013) Flux balance analysis of Chlorella sp. FC2 IITG under photoautotrophic and heterotrophic growth conditions. Photosynth Res 118(1–2):167–179
Hirasawa T, Shimizu H (2016) Recent advances in amino acid production by microbial cells. Curr Opin Biotechnol 42:133–146
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, Guwahati, Assam, India for financially supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhu, A.A., Veeranki, V.D. Metabolic engineering of Pichia pastoris GS115 for enhanced pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) flux toward recombinant human interferon gamma (hIFN-γ) production. Mol Biol Rep 45, 961–972 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4244-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4244-2