Abstract
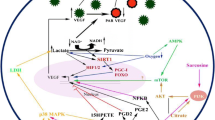
The primary transcript of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can be alternatively spliced and translated to pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic VEGF variants. We investigated the effect of sodium butyrate (NaB) on pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic VEGF variants production in immortalized human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMEC). These cells were cultured in the absence or in the presence of NaB, followed by total RNA and protein isolation. The transcript and protein levels of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic VEGF variants were evaluated by reverse transcription, real-time quantitative PCR and western blot analysis. We found that NaB significantly increased the anti-angiogenic transcript and protein levels of the VEGF 121b, VEGF165b and VEGF189b variants in HLMEC cells. We did not find the pro-angiogenic VEGF189a transcript variant either in control or NaB treated cells. By contrast, the pro-angiogenic VEGF121a and VEGF165a transcript variants were present in HLMEC cells, but their levels were slightly modulated in the cells treated with NaB compared to controls. Since anti-angiogenic VEGF variants inhibit angiogenesis and tumour progression, and NaB is considered an anticancer drug, our findings may have clinical significance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osinsky S, Zavelevich M, Vaupel P (2009) Tumor hypoxia and malignant progression. Exp Oncol 31:80–86
Folkman J (2003) Angiogenesis and apoptosis. Semin Cancer Biol 13:159–167
Miller-Kasprzak E, Jagodziński PP (2007) Endothelial progenitor cells as a new agent contributing to vascular repair. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 55:247–259
Rumpold H, Wolf D, Koeck R et al (2004) Endothelial progenitor cells: a source for therapeutic vasculogenesis? J Cell Mol Med 8:509–518
Zhang C, Zhang X, Liu C et al (2009) Expression of endostatin mediated by a novel non-viral delivery system inhibits human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Mol Biol Rep doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9600-9
Chung N, Jee BK, Chae SW et al (2009) HOX gene analysis of endothelial cell differentiation in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Biol Rep 36:227–235
Tang J, Wang J, Song H et al (2009) Adenovirus-mediated stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha gene transfer improves cardiac structure and function after experimental myocardial infarction through angiogenic and antifibrotic actions. Mol Biol Rep. doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9642-z
Bai X, Liang Z, Zhao S et al (2009) The porcine ANG, RNASE1 and RNASE6 genes: molecular cloning, polymorphism detection and the association with haematological parameters. Mol Biol Rep 36:2405–2411
Byrne AM, Bouchier-Hayes DJ, Harmey JH (2005) Angiogenic and cell survival functions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). J Cell Mol Med 9:777–794
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM (2005) Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 23:1011–1027
Onen IH, Konac E, Eroglu M et al (2008) No association between polymorphism in the vascular endothelial growth factor gene at position-460 and sporadic prostate cancer in the Turkish population. Mol Biol Rep 35:17–22
Wang T, Hu K, Ren J et al (2010) Polymorphism of VEGF-2578C/A associated with the risk and aggressiveness of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a Chinese population. Mol Biol Rep 37:59–65
Bates DO, Cui TG, Doughty JM et al (2002) VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 62:4123–4131
Woolard J, Wang WY, Bevan HS et al (2004) VEGF165b, an inhibitory vascular endothelial growth factor splice variant: mechanism of action, in vivo effect on angiogenesis and endogenous protein expression. Cancer Res 64:7822–7835
Miller-Kasprzak E, Jagodziński PP (2008) 5-Aza-2′-deoxycytidine increases the expression of anti-angiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor 189b variant in human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother 62:158–163
Rennel ES, Varey AH, Churchill AJ et al (2009) VEGF(121)b, a new member of the VEGF(xxx)b family of VEGF-A splice isoforms, inhibits neovascularisation and tumour growth in vivo. Br J Cancer 101:1183–1193
Qiu Y, Hoareau-Aveilla C, Oltean S et al (2009) The anti-angiogenic isoforms of VEGF in health and disease. Biochem Soc Trans 37:1207–1213
Thiagalingam S, Cheng KH, Lee HJ et al (2003) Histone deacetylases: unique players in shaping the epigenetic histone code. Ann N Y Acad Sci 983:84–100
Luczak MW, Jagodzinski PP et al (2006) The role of DNA methylation in cancer development. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 44:143–154
Pajak B, Orzechowski A, Gajkowska B (2007) Molecular basis of sodium butyrate-dependent proapoptotic activity in cancer cells. Adv Med Sci 52:83–88
Chang JG, Hsieh-Li HM, Jong YJ et al (2001) Treatment of spinal muscular atrophy by sodium butyrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9808–9813
Brichta L, Hofmann Y, Hahnen E et al (2003) Valproic acid increases the SMN2 protein level: a well-known drug as a potential therapy for spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet 12:2481–2489
Nissim-Rafinia M, Aviram M, Randell SH et al (2004) Restoration of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function by splicing modulation. EMBO Rep 5:1071–1077
Piotrowska H, Jagodzinski PP (2007) Trichostatin A, sodium butyrate, and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine alter the expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha and beta isoforms in Hut-78 T- and Raji B-lymphoma cell lines. Biomed Pharmacother 61:451–454
Piotrowska H, Jagodzinski PP (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor alpha and beta variant expression is associated with ASF/SF2 splicing factor upregulation in HT-29 colon cancer and MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Arch Med Res 40:156–162
Perrin RM, Konopatskaya O, Qiu Y et al (2005) Diabetic retinopathy is associated with a switch in splicing from anti- to pro-angiogenic isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor. Diabetologia 48:2422–2447
Kieda C, Paprocka M, Krawczenko A et al (2002) New human microvascular endothelial cell lines with specific adhesion molecules phenotypes. Endothelium 9:247–261
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Szabo A, Perou CM, Karaca M (2004) Statistical modeling for selecting housekeeper genes. Genome Biol 5:R59
Debicki S, Jagodzinski PP (2009) Apicidin decreases phospholipase C gamma-1 transcript and protein in Hut-78 T lymphoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother 63:543–547
Díaz R, Peña C, Silva J et al (2008) p73 Isoforms affect VEGF, VEGF165b and PEDF expression in human colorectal tumors: VEGF165b downregulation as a marker of poor prognosis. Int J Cancer 123:1060–1067
Pritchard-Jones RO, Dunn DB, Qiu Y et al (2007) Expression of VEGF(xxx)b, the inhibitory isoforms of VEGF, in malignant melanoma. Br J Cancer 97:223–230
Rennel ES, Hamdollah-Zadeh MA, Wheatley ER et al (2008) Recombinant human VEGF165b protein is an effective anti-cancer agent in mice. Eur J Cancer 44:1883–1894
Rennel E, Waine E, Guan H et al (2008) The endogenous anti-angiogenic VEGF isoform, VEGF165b inhibits human tumour growth in mice. Br J Cancer 98:1250–1257
Nishi M, Abe Y, Tomii Y et al (2005) Cell binding isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF189) contribute to blood flow-distant metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol 26:1517–1524
Scharlau D, Borowicki A, Habermann N et al (2009) Mechanisms of primary cancer prevention by butyrate and other products formed during gut flora-mediated fermentation of dietary fibre. Mutat Res 682:39–53
Lu Q, Yang YT, Chen CS et al (2004) Zn2+-chelating motif-tethered short-chain fatty acids as a novel class of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem 47:467–474
Gozzini A, Rovida E, Dello Sbarba P et al (2003) Butyrates, as a single drug, induce histone acetylation and granulocytic maturation: possible selectivity on core binding factor-acute myeloid leukemia blasts. Cancer Res 63:8955–8961
Blank-Porat D, Gruss-Fischer T, Tarasenko N et al (2007) The anticancer prodrugs of butyric acid AN-7 and AN-9, possess antiangiogenic properties. Cancer Lett 256:39–48
Louis M, Rosato RR, Brault L et al (2004) The histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate induces breast cancer cell apoptosis through diverse cytotoxic actions including glutathione depletion and oxidative stress. Int J Oncol 25:1701–1711
Terao Y, Nishida J, Horiuchi S et al (2001) Sodium butyrate induces growth arrest and senescence-like phenotypes in gynecologic cancer cells. Int J Cancer 94:257–267
Roy MJ, Dionne S, Marx G et al (2009) In vitro studies on the inhibition of colon cancer by butyrate and carnitine. Nutrition 25:1193–1201
Park JK, Cho CH, Ramachandran S et al (2006) Augmentation of sodium butyrate-induced apoptosis by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition in the human cervical cancer cell-line. Cancer Res Treat 38:112–117
Sonnemann J, Hartwig M, Plath A et al (2006) Histone deacetylase inhibitors require caspase activity to induce apoptosis in lung and prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 232:148–160
Choi YH (2006) Apoptosis of U937 human leukemic cells by sodium butyrate is associated with inhibition of telomerase activity. Int J Oncol 29:1207–1312
Xi L, Chen G, Zhou J et al (2006) Inhibition of telomerase enhances apoptosis induced by sodium butyrate via mitochondrial pathway. Apoptosis 11:789–798
Zgouras D, Wächtershäuser A, Frings D et al (2003) Butyrate impairs intestinal tumor cell-induced angiogenesis by inhibiting HIF-1alpha nuclear translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300:832–838
Kim SH, Kim KW, Jeong JW (2007) Inhibition of hypoxia-induced angiogenesis by sodium butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, through hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha suppression. Oncol Rep 17:793–797
Ogawa H, Rafiee P, Fisher PJ et al (2003) Sodium butyrate inhibits angiogenesis of human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells through COX-2 inhibition. FEBS Lett 554:88–94
Tarasenko N, Nudelman A, Tarasenko I et al (2008) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: the anticancer, antimetastatic and antiangiogenic activities of AN-7 are superior to those of the clinically tested AN-9 (Pivanex). Clin Exp Metastasis 25:703–716
Pellizzaro C, Coradini D, Daidone MG (2002) Modulation of angiogenesis-related proteins synthesis by sodium butyrate in colon cancer cell line HT29. Carcinogenesis 23:735–740
Black DL (2003) Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem 72:291–336
Acknowledgements
Supported by a grant No 502-01-01124182-07474, Poznań University of Medical Sciences. We would like to acknowledge Dr. Margarita Lianeri for her assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciura, J., Jagodziński, P.P. Butyrate increases the formation of anti-angiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor variants in human lung microvascular endothelial cells . Mol Biol Rep 37, 3729–3734 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0026-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0026-1