Abstract
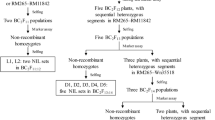
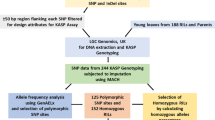
Grain size is one of the key traits that determines the quality of Basmati rice from the consumers’ as well as the traders’ point of view. Though many genes governing grain size have been identified in indica and japonica, little work has been done in Basmati rice. The present study aims at dissection of a QTL region governing grain size traits in Basmati employing association and linkage mapping approaches. Association mapping revealed that three markers, i.e., RM 6024 (grain breadth), RM1237 and RM18582 (grain length-breadth ratio), which cover 889 kb in the targeted QTL region have been significantly associated with grain size traits. Using linkage mapping, the targeted QTL region has been further delimited to a physical distance of 268 kb that comprises 24 annotated genes. The gene expression analysis of parents, revealed 19 genes differentially expressing within the QTL. Of them, 15 genes showed high expression in Basmati370, while four were expressed in Jaya, and whereas five genes did not show any differential expression between parents. Among differentially expressed genes, a highly expressed gene in Basmati370, Os05g0374200 (Cytokinin dehydrogenase 1 precursor) seems to be involved in accumulation of cytokinins, thus affecting the grain size. Therefore, our findings demonstrated that by complimenting association and linkage mapping, it is likely to dissect a QTL governing grain size traits in Basmati rice and also the QTL could be a potential target for marker-assisted breeding and map-based cloning studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrama HA, Eizenga GC, Yan W (2007) Association mapping of yield and its components in rice cultivars. Mol Breed 19:341–356
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnik M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, McCouch SR (1997) Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Theor Appl Genet 95:553. doi:10.1007/s001220050596
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Fan C, Xing YZ, Mao HL, Lu TT, Han B, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang Q (2006) GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor Appl Genet 112:1164–1171
Hu G, Zhang D, Pan H, Li B, Wu J, Zhou X, Zhang Q, Zhou L, Yao G, Li J, Li J, Zhang H, Li Z (2011) Fine mapping of the awn gene on chromosome 4 in rice by association and linkage analyses. Chin Sci Bull 56(9):835–839
Ishimaru K, Hirotsu N, Madoka Y, Murakami N, Hara N, Onodera H, Kashiwagi T, Ujiie K, Shimizu B, Onishi A, Miyagawa H, Katoh E (2013) Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield. Nat Genet 45:707–711
Kitagawa K, Kurinami S, Oki K, Abe Y, Ando T, Kono I, Yano M, Kitano H, Iwasaki Y (2010) A novel kinesin 13 protein regulating rice seed length. Plant Cell Physiol 51(8):1315–1329
Li Y, Fan C, Xing Y, Jiang Y, Luo L, Sun L, Shao D, Xu C, Li X, Xiao J, He Y, Zhang Q (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43:1266–1269
Li N, Li Y (2014) Ubiquitin-mediated control of seed size in plants. Front Plant Sci 5:332
Li X, Zhou Z, Ding J, Wu Y, Zhou B, Wang R, Ma J, Wang S, Zhang X, Xia Z, Chen J, Wu J (2016) Combined linkage and association mapping reveals QTL and candidate genes for plant and ear height in maize. Front Plant Sci 7:833
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander E (1993) Constructing genetic linkage maps with MAPMAKER/EXP version 3.0: a tutorial and reference manual. 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute for Biometrical Research Cambridge, mass.
Lu L, Shao D, Qiu X, Sun L, Yan W, Zhou X, Yang L, He Y, Yu S, Xing Y (2013) Natural variation and artificial selection in four genes determine grain shape in rice. New Phytol 200:1269–1280
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11–13 http://www.gramene.org/newsletters/rice_genetics/rgn14/v14p11.html
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Qi P, Lin YS, Song XJ, Shen JB, Huang W, Shan JX, Zhu MZ, Jiang L, Gao JP, Lin HX. (2012) The novel quantitative trait locus GL3.1 controls rice grain size and yield by regulating cyclin-T1. Cell Res 22(12):1666–1680
Qiu X, Gong R, Tan Y, Yu S (2012) Mapping and characterization of the major quantitative trait locus qSS7 associated with increased length and decreased width of rice seeds. Theor Appl Genet 125:1717
Ramkumar G, Sivaranjani AKP, Pandey MK, Sakthivel K, Shobha Rani N, Sudarshan I, Prasad GSV, Neeraja CN, Sundaram RM, Viraktamath B, Madhav MS (2010) Development of a PCR-based SNP marker system for effective selection of kernel length and kernel elongation in rice. Mol Breed 26(4):735–740
Segami S, Kono I, Ando T, Yano M, Kitano H, Miura K, Iwasaki Y (2012a) Small and round seed 5 gene encodes alpha tubulin regulating seed cell elongation in rice. Rice 5:4
Segami S, Kono I, Ando T, Yano M, Kitano H, Miura K, Iwasaki Y (2012b) Small and round seed 5 gene encodes alpha-tubulin regulating seed cell elongation in rice. Rice 5(4)
Shao GN, Tang SQ, Luo J, Jiao GA, Wei XJ, Tang A, Wu JL, Zhuang JY, Hu PS (2010) Mapping of qGL7–2, a grain length QTL on chromosome 7 of rice. J Genet and Genomics 37:523–531
She KC, Kusano H, Koizumi K, Yamakawa H, Hakata M, Imamura T, Fukuda M, Naito N, Tsurumaki Y, Yaeshima M, Tsuge T, Matsumoto K, Kudoh M, Itoh E, Kikuchi S, Kishimoto N, Yazaki J, Ando T, Yano M, Aoyama T, Sasaki T, Satoh H, Shimada H (2010) A novel factor FLOURY ENDOSPERM2 is involved in regulation of rice grain size and starch quality. Plant Cell 22(10):3280–3294. doi:10.1105/tpc.109.070821
Shomura A, Izawa T, Ebana K, Ebitani T, Kanegae H, Konishi S, Yano M (2008) Deletion in a gene associated with grain size increased yields during rice domestication. Nat Genet 40:1023–1028
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39:623–630
Sun P, Zhang W, Wang Y, He Q, Shu F, Liu H, Wang J, Wang J, Yuan L, Deng H (2016) OsGRF4 controls grain shape, panicle length and seed shattering in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 58:836–847
Vemireddy LR, Archak S, Nagaraju J (2007) Capillary electrophoresis is essential for microsatellite marker based detection and quantification of adulteration of Basmati rice (Oryza sativa). J Agric Food Chem 55:8112–8117
Vemireddy LR, Noor S, Satyavathi VV, Srividya A, Kaliappan A, Parimala SRN, Bharathi PM, Deborah DAK, Sudhakar Rao KV, Shobharani N, Siddiq EA, Nagaraju J (2015) Discovery and mapping of genomic regions governing economically important traits of Basmati rice. BMC Plant Biol 15:207
Wang JK, Wan XY, Crossa J, Crouch J, Weng JF, Zhai HQ, Wan JM (2006) QTL mapping of grain length in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using chromosome segment substitution lines. Genet Res 88:93–104
Wang ET, Wang JJ, Zhu XD, Hao W, Wang LY, Li Q, Zhang LX, He W, Lu BR, Lin HX, Ma H, Zhang GQ, He ZH (2008) Control of rice grain-filling and yield by a gene with a potential signature of domestication. Nat Genet 40:1370–1374
Wang SK, Wu K, Yuan QB, Liu XY, Liu ZB, Lin XY, Zeng RZ, Zhu HT, Dong GJ, Qian Q, Zhang GQ, Fu XD (2012) Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat Genet 44:950–954
Xie XB, Song MH, Jin FX, Ahn SN, Suh JP, Hwang HG, McCouch SR (2006) Fine mapping of a grain weight quantitative trait locus on rice chromosome 8 using near-isogenic lines derived from a cross between Oryza sativa and Oryza rufipogon. Theor Appl Genet 113:885–894
Yan WG, Li Y, Agrama HA, Luo D, Gao F (2009) Association mapping of stigma and spikelet characteristics in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Mol Breed 24:277–292
Zhang P, Liu X, Tong H, Lu Y, Li J (2014) Association mapping for important agronomic traits in core collection of rice (Oryza sativa L.) with SSR markers. PLoS One 9(10):e111508
Zheng J, Zhang Y, Wang C (2015) Molecular functions of genes related to grain shape in rice. Breed Sci 65:120–126
Zuo J, Li J (2014) Molecular genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci regulating rice grain size. Annu Rev Genet 48:99–118
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Acharya N G Ranga Agricultural University and CDFD for providing lab, field and financial support to carry out this work and also special thanks to the Department of Science and Technology for providing the INSPIRE fellowship to DAD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LRV designed the experiment. LRV and DAD collected the germplasm and developed the mapping population. DAD performed all the experiments. VR, SP, GPC, GMK and RKC performed part of phenotypic data collection. AK, SR, and SN performed part of SSR genotyping. DAD constructed the association map, genetic linkage map; performed QTL analysis and wrote the manuscript. LRV and AS performed part of the genotypic analysis. LRV supported the bioinformatics analysis. LRV, AS, VVS and EAS revised the manuscript. All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
Frequency distribution of grain size related traits in association mapping panel (A) and in F2 populations derived from the cross of Basmati370 and Jaya (B). (JPEG 418 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Genotypic variability of grain size in the representative association mapping panel of rice germplasm. The grain size of Pusa1121 is 8.2 mm. (JPEG 444 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Genetic relationship of 96 rice genotypes estimated using Unbiased Neighbor-Joining method of DARwin 5.0 software. Aromatic (1–27)- Red colored, Indica (28–72) - Green colored; Japonica and Javanica (73–91) - Blue colored;; Aus (92–96)- Pink colored. For complete list of the rice genotypes (1–96) refer Supl Table 1. (JPEG 1645 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 57 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOC 46 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
(DOC 39 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
(DOC 39 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
(DOC 51 kb)
Supplementary Table 6
(DOC 59 kb)
Supplementary Table 7
(DOC 29 kb)
Supplementary Table 8
(DOC 30 kb)
Supplementary Table 9
(DOC 44 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deborah, D.A., Vemireddy, L.R., Roja, V. et al. Molecular dissection of QTL governing grain size traits employing association and linkage mapping in Basmati rice. Mol Breeding 37, 77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0678-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-017-0678-9