Abstract
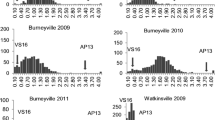
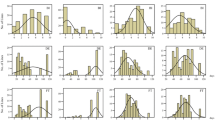
The genotypic correlation between line per se and testcross performance is an important quantitative genetic parameter in the design of hybrid breeding programs. The main goal of this survey was to study the association of line per se and testcross performance at the phenotypic and molecular levels by applying multiple-line cross quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping. We used experimental data from line per se and testcross performance of three segregating sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) populations. The segregating progenies were genotyped with 481 single nucleotide polymorphism and 40 simple sequence repeat markers and evaluated in field trials for beet yield as well as potassium and sodium content. We observed a decrease in the genotypic correlations between testcross and line per se performance with increasing complexity of the analyzed trait. This picture was also reflected at a molecular level by the presence of overlapping QTLs. A more detailed analysis of the forces causing low genotypic correlation between line per se and testcross performance could not rule out a possible relevance of epistasis and suggested the presence of masking dominance effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali F, Zahid KR, Shah F, Gul R, Pan Q, Hira, Mustafa G, Jamal Y, Khan H, Ullah H (2013) Heterosis and early generation testing is a pivotal method for production of hybrid. Aust J Crop Sci 7:1728–1736
Bekavac G, Purar B, Jocković D (2008) Relationships between line per se and testcross performance for agronomic traits in two broad-based populations of maize. Euphytica 162:363–369
Bolduan C, Miedaner T, Utz HF, Dhillon BS, Melchinger AE (2010) Genetic variation in testcrosses and relationship between line per se and testcross performance for resistance to Gibberella Ear Rot in maize. Crop Sci 50:1691–1696
Bosemark NO (1993) Genetics and breeding. In: Cook DA, Scott RK (eds) The sugar beet crop. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 67–119
Bosemark NO (2006) Genetics and breeding, Chapter 4. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 50–88
Cochran WG, Cox GM (1957) Experimental designs, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Cooper M, DeLacy IH (1994) Relationships among analytical methods used to study genotypic variation and genotype-by-environment interaction in plant breeding multi-environment experiments. Theor Appl Genet 88:561–572
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142:285–294
Draycott AP (2006) Sugar beet, 1st edn. Blackwell, Oxford
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4th edn. Longman Group, London
Falke KC, Wilde P, Wortmann H, Müller BU, Möhring J, Piepho H-P, Miedaner T (2010) Correlation between per se and testcross performance in rye (Secale cereale L.) introgression lines estimated with a bivariate mixed linear model. Crop Sci 50:1863–1873
Geiger HH, Gordillo GA, Koch S (2013) Genetic correlations among haploids, doubled haploids, and testcrosses in maize. Crop Sci 53:2313–2320
Grieder C, Dhillon BS, Schipprack W, Melchinger AE (2012a) Breeding maize as biogas substrate in Central Europe: I. Quantitative-genetic parameters for testcross performance. Theor Appl Genet 124:971–980
Grieder C, Dhillon BS, Schipprack W, Melchinger AE (2012b) Breeding maize as biogas substrate in Central Europe: II. Quantitative-genetic parameters for inbred lines and correlations with testcross performance. Theor Appl Genet 124:981–988
Hallauer AR, Miranda JB (1988) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding, 2nd edn. Iowa State Univ. Press, Ames, IA
Holland JB, Portyanko VA, Hoffman DL, Lee M (2002) Genomic regions controlling vernalization and photoperiod responses in oat. Theor Appl Genet 105:113–126
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Jannink JL (2007) Identifying quantitative trait locus by genetic background interactions in association studies. Genetics 176:553–561
Kebede AZ, Melchinger AE, Cairns JE, Araus LJ, Makumbi D, Atlin GN (2013) Relationship of line per se and testcross performance for grain yield of tropical maize in drought and well-watered trials. Crop Sci 53:1228–1236
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritabilitiy on a progeny mean basis. Crop Sci 25:192–194
Kosambi D (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Botstein S (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Li J, Lühmann A-K, Weißleder K, Stich B (2011) Genome-wide distribution of genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in elite sugar beet germplasm. BMC Genom 12:484
Liu BH, Knapp SJ, Birkes D (1997) Sampling distributions, biases, variances, and confidence intervals for genetic correlations. Theor Appl Genet 94:8–19
Liu W, Reif JC, Ranc N, Della Porta G, Würschum T (2012) Comparison of biometrical approaches for QTL detection in multiple segregating families. Theor Appl Genet 125:987–998
Liu W, Maurer HP, Reif JC, Melchinger AE, Utz HF, Tucker MR, Ranc N, Della Porta G, Würschum T (2013) Optimum design of family structure and allocation of resources in association mapping with lines from multiple crosses. Heredity 110:71–79
Löffler M, Kessel B, Ouzunova M, Miedaner T (2011) Covariation between line and testcross performance for reduced mycotoxin concentrations in European maize after silk channel inoculation of two Fusarium species. Theor Appl Genet 122:925–934
Longin CFH, Mühleisen J, Maurer HP, Zhang H, Gowda M, Reif JC (2012) Hybrid breeding in autogamous cereals. Theor Appl Genet 125:1087–1096
Lübberstedt T, Melchinger AE, Fähr S, Klein D, Dally A, Westhoff P (1998) QTL mapping in testcrosses of flint lines of maize: III. Comparison across populations for forage traits. Crop Sci 38:1278–1289
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998) Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
Mackay IJ, Gibson JP, Caligari PDS (1999) The genetics of selfing with concurrent backcrossing in breeding hybrid sugar beet (Beta vulgaris altissima L.). Theor Appl Genet 98:1156–1162
Miedaner T, Schwegler DD, Wilde P, Reif JC (2013) Association between line per se and testcross performance for eight agronomic and quality traits in winter rye. Theor Appl Genet. doi:10.1007/s00122-013-2198-2
Mihaljevic R, Schön CC, Utz HF, Melchinger AE (2005) Correlation and QTL correspondence between line per se and testcross performance for agronomic traits in four populations of European maize. Crop Sci 45:114–122
Peng B, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Tan W, Wang D, Shi Y, Sun B, Song Y, Wang T, Li Y (2013) Correlations and comparisons of quantitative trait loci with family per se and testcross performance for grain yield and related traits in maize. Theor Appl Genet 126:773–789
Presterl T, Seitz G, Schmidt W, Geiger HH (2002) Improving nitrogen-use efficiency in European maize—comparison between line per se and testcross performance under high and low soil nitrogen. Maydica 47:83–91
Qi H, Huang J, Zheng Q, Huang Y, Shao R, Zhu L, Zhang Z, Qiu F, Zhou G, Zheng Y, Yue B (2013) Identification of combining ability loci for five yield-related traits in maize using a set of testcrosses with introgression lines. Theor Appl Genet 126:369–377
Rauf S, Sadaqat HA, Khan IA (2008) Effect of moisture regimes on combining ability variations of seedling traits in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Can J Plant Sci 88:323–329
R Development Core Team (2010) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.R-project.org
Reddy Y, Ravi D, Reddy Ch, Prasad KVSV, Zaidi PH, Vinyan MT, Blümmel M (2013) A note on the correlations between maize grain and maize stover quantitative and qualitative traits and the implications for whole maize plant optimization. Field Crops Res 153:63–69
Rehman R, Arshad M, Khan MA, Mohmand AS, Shabbir G, Shah MKN (2012) Using multivariate analysis for selecting desirable hybrids in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Pak J Bot 44:1715–1720
Reif JC, Liu W, Gowda M, Maurer HP, Möhring J, Fischer S, Schechert A, Würschum T (2010) Genetic basis of agronomically important traits in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) investigated with joint linkage association mapping. Theor Appl Genet 8:1489–1495
Robertson LA, Kleinschmidt CE, White DG, Payne GA, Maragos CM, Holland JB (2006) Heritabilities and correlations of Fusarium ear rot resistance and fumonisin contamination resistance in two maize populations. Crop Sci 46:353–361
Sala RG, Andrade FH, Cerono JC (2012) Quantitative trait loci associated with grain moisture at harvest for line per se and testcross performance in maize: a meta analysis. Euphytica 185:429–440
SAS Institute (2008) SAS/STAT 9.2 user’s guide. SAS Inst., Cary, NC
Schnell FW (1961) On some aspects of reciprocal recurrent selection. Euphytica 10:24–30
Schön CC, Utz HF, Groh S, Truberg B, Openshaw S, Melchinger AE (2004) Quantitative trait locus mapping based on resampling in a vast maize testcross experiment and its relevance to quantitative genetics for complex traits. Genetics 167:485–498
Schwegler DD, Liu W, Gowda M, Würschum T, Schulz B, Reif JC (2013) Multiple-line cross quantitative trait locus mapping in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Mol Breed 31:279–287
Searle SR (1971) Linear models. Wiley, New York
Smith OS (1986) Covariance between line per se and testcross performance. Crop Sci 26:540–543
Strigens A, Grieder C, Hausmann BIG, Melchinger AE (2012) Genetic variation among inbred lines and testcrosses of maize for early growth parameters and their relationship to final dry matter yield. Crop Sci 52:1084–1092
Tomerius A-M, Miedaner T, Geiger HH (2008) A model calculation approach towards the optimization of a standard scheme of seed-parent line development in hybrid rye breeding. Plant Breed 127:433–440
Utz HF, Melchinger AE, Schön CC (2000) Bias and sampling error of the estimated proportion of genotypic variance explained by quantitative trait loci determined from experimental data in maize using cross validation and validation with independent samples. Genetics 154:1839–1849
van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap 3.0: software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International BV, Wageningen
Wricke G, Weber WE (1986) Quantitative genetics and selection in plant breeding. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin
Würschum T, Maurer HP, Kraft T, Janssen G, Nilsson C, Reif JC (2011) Genome-wide association mapping of agronomic traits in sugar beet. Theor Appl Genet 123:1121–1131
Zang Y, Li Y, Wang Y, Peng B, Liu C, Liu Z, Tan W, Wang D, Shi Y, Sun B, Song Y, Wang T, Li Y (2011) Correlations and QTL detection in maize family per se and testcross progenies for plant height and ear height. Plant Breed 130:617–624
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted within the Biometric and Bioinformatic Tools for Genomic-based Plant Breeding project of the GABI-FUTURE initiative. D.D. Schwegler was supported by DFG within the project “Genetische Architektur der Eigen- versus Testkreuzungsleistung für wichtige agronomische Merkmale beim Roggen” (Grant ID:MI 519/1-1). M. Gowda was supported by BMBF within the HYWHEAT project (Grant ID: FKZ0315945D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwegler, D.D., Gowda, M., Schulz, B. et al. Genotypic correlations and QTL correspondence between line per se and testcross performance in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) for the three agronomic traits beet yield, potassium content, and sodium content. Mol Breeding 34, 205–215 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0030-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-014-0030-6