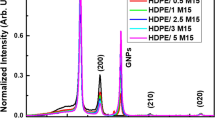
Filled compositions of polylactide (PLA) with a reduced graphene oxide (RGO) at various components ratios were obtained by two independent methods: the solid-phase mixing of components under the action of shear strains and the liquid-phase synthesis in a chloroform solution with ultrasonic stirring. The influence of the structure of formed composites on the complex of their properties was studied. The method of scanning electron microscopy showed the formation of aggregates of RGO nanoparticles during the synthesis of compositions in the liquid phase, leading to a decrease in their strength and electrical characteristics. A comparative study of the thermophysical characteristics of polylactide in the compositions obtained by the solid- and liquid-phase methods was carried out, the corresponding temperatures and heats of thermal transitions were determined, and the crystallinity of the compositions was calculated. The sharp drop observed in the crystallinity of PLA in the compositions synthesized in the solid phase was caused by amorphization of the polymer under the action of shear strains and by a decrease in the segmental mobility of macromolecules under these conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. J. Jem, J. F. van der Pol, and S. de Vos Microbial Lactic Acid, Its Polymer Poly(lactic acid) and their industrial Applications, Plastics from Bacteria: Natural Functions and Applications / Ed. G. G.-Q. Chen — Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 323-346 (2010).
D. A. Garlotta, “Literature review of poly(lactic acid),” J. Polym. Environ., 19, No. 2, 63-84 (2011).
T. Ghaffar, M. Irshad, Z. Anwar, T. Aqil, Z. Zulifqar, A. Tarig, M. Kamran, N. Ehsan, and S. Mehmood Recent trends in lactic acid biotechnology: A brief review on production to purification,” J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci., 7, No. 2, 222-229 (2014).
R. Mehta, V. Kumar, H. Bhunia, and S. N. Upadhyay, “Synthesis of poly(lactic acid): A Review,” J. Macromol. Sci., Polym. Rev., 45, No. 4, 325-349 (2005).
R. E. Drumright, P. R. Gruber, and D. E. Henton, “Polylactic acid technology,” Adv. Mater., 12, No. 23, 1841-1846 (2000).
W. Gao, The Chemistry of Grapheme Oxide, Graphene Oxide. Cham: Springer Int. Publ., 61-95 (2015).
Y. Fu, L. Liu, J. Zhang, and W. C. Hiscox, “Functionalized graphenes with polymer toughener as novel interface modifier for property-tailored polylactic acid/graphene nanocomposites,” Polym., 55, No. 24, 6381-6389 (2014).
S. Rogovina, S. Lomakin, S. Usachev, and M. Gasymov, O. Kuznetsova, N. Shilkina, V. Shevchenko, A. Shapagin, E. Prut, and A.Berlin, “The study of properties and structure of polylactide-graphite nanoplates compositions,” Hindawi Polym. Crystal., Article ID 4367582, 9 p. (2022).
B. Mortazavi, F. Hassouna, A. Laachachi, A. Rajabpour, S. Ahzi, D. Chapron, V. Toniazzo, and D. Ruch, “Experimental and multiscale modeling of thermal conductivity and elastic properties of PLA/expanded graphite polymer nanocomposites,” Thermochim. Acta, 552, 106-113 (2013).
Y. Gao, O.T. Picot, E. Bilotti, and T. Peijs, “Influence of filler size on the properties of poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/graphene nanoplatelet (GNP) nanocomposites,” Europ. Polym. J., 86, 117-131 (2017).
Y.-H. Lai, Y.-H. Chen, A. Pal, S.-H. Chou, S.-J. Chang, E.-W. Huan, Z.-H. Lin, and S.-Y. Chen, “Regulation of cell differentiation via synergistic self-powered stimulation and degradation behavior of a biodegradable composite piezoelectric scaffold for cartilage tissue,” Nano Energy. Part A, 90, 106545 (2021).
D. Esperanza, I. Naroa, R. Sylvie, and L.-M. Senentxu, “Cytocompatible scaffolds of poly(L-lactide)/reduced graphene oxide for tissue engineering,” J. Biomat. Sci. Polym., 32, No. 11, 1406-1419 (2021).
S. V. Usachev, S. M. Lomakin, E. V. Koverzanova, N. G. Shilkina, I. I. Levina, E. V. Prut, S. Z. Rogovina, and A. A. Berlin, “Thermal degradation of various types of polylactides research. The effect of reduced graphite oxide on the composition of the PLA4042D,” Thermochim. Acta, 712, 179227 (2022).
M. Moniruzzaman and K. I. Winey, “Polymer nanocomposites containing carbon nanotubes,” Macromolecules, 39, 5194-5205 (2006).
H. B. Zhang, W. G. Zheng, Q. Yan, J. W. Wang, Z. H. Lu et al., “Electrically conductive polyethylene terephthalate/graphene nanocomposites prepared by melt compounding,” Polymers, 51, 1191-1196 (2010).
S. Z. Rogovina, K. V. Aleksanyan, A. A. Loginova, N. E. Ivanushkina, L. V. Vladimirov, E. V. Prut, and A. A. Berlin, “Influence of PEG on mechanical properties and biodegradation of composites based on PLA and starch,” Starch/Staerke., 70, (2018).https://doi.org/10.002/star.201700268
S. Z. Rogovina, E. V. Prut, K. V. Aleksanyan, V. G. Krashininnikov, E. O. Perepelitsyna, D. P. Shaskin, N. E. Ivanushkina, and A. A. Berlin, “Production and investigation of structure and properties of polyethуlene-polylactide composites,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 136, No. 22, 47598. (2019); https:// doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47598
S. Z. Rogovina, L. A. Zhorina, A. K. Gatin, E. V. Prut, O. P. Kuznetsova, A. R. Yakhina, A. A. Olkhov, N. A. Samoylov, M. V. Grishin, A. L. Iordanskii, and A. A. Berlin, “Biodegradable polylactide-poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) compositions obtained via blending under shear deformations and electrospinning: characterization and environmental application,” Polymers, 12, 1088 (2020); doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051088
A. A. Arbuzov, V. E. Muradyan, B. P. Tarasov, E. A. Sokolov, and S. D. Babenko, “Epoxy composites with thermally reduced graphite oxide and their properties,” Zh. Physical Chemistry, 90, No. 5, 663-667 (2016).
A. A. Arbuzov, V. E. Muradyan, and B. P. Tarasov, “Synthesis of graphene-like materials by reduction of graphite oxide,” Izv. RAS Ser. Chem., No. 9, 1962-1966 (2013).
M. Alexandre and P. Dubois, “Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites: preparation, properties and uses of a new class of materials,” Mater. sci. Eng. R. Rep., 28, 1-63 (2000).
T. D. Fornes and D. R. Paul, “Modeling properties on nylon 6/clay nano-composites using composite theories,” Polym., 44, 4993-5013 (2003).
L. Gong, I. A. Kinloch, R. J. Young, I. Riaz, R. Jalil, and K. S. Novoselov, “Interfacial stress transfer in a graphene monolayer nanocomposite,” Adv. Mater., 22, 2694-2697 (2010).
D. W. Schaefer and R. S. Justice, “How nano are nanocomposites,” Macromol., 40, 8501-8517 (2007).
D. R. Dreyer, S. Park, C. W. Bielawski, and R. S. Ruoff, “The chemistry of graphene oxide, Chem. Soc. Rev., 39, 228-240 (2010).
H. C. Schniepp, J. L. Li, M. J. McAllister, H. Sai, M. Herrera-Alonso, D. H. Adamson, et al., “Functionalized single graphene sheets derived from splitting graphite oxide,” J. Phys. Chem. B, 110, No. 17, 8535-8539 (2006).
S. Z. Rogovina, Chemical modification of natural polysaccharides of cellulose, chitin and chitosan in the solid phase under the action of shear deformations, Dis. ... Dr. chem. Sciences. ISPM RAS. - M., 232 p. (2003).
T. Batakliev, V. Georgiev, C. Kalupgian, P. A. R. Musoz, H. Ribeiro, G. J. M. Fechine, R. J. E. Andrade, E. Ivanov, and R. Kotsilkova, “Physico-chemical characterization of PLA-based composites holding carbon nanofillers,” Appl. Compos. Mat., 28, 1175-1192 (2021).
V. Goodarzi, M. Fasihib, H. Garmabi, M. Ohshima., K. Taki, and M. R. Saeb, “Microstructure, mechanical and electrical characterizations of bimodal and nanocellular polypropylene/graphene nanoplatelet composite foams,” Mater. Today Comm., 25, 101447 (2020).
Y. A. Balogun and R. C. Buchanan, “Enhanced percolative properties from solubility dispersion of filler phase in conducting polymer composites (CPCs),” Compos. Sci. Technol., 892-900 (2010).
E. Fischer, H. Sterzel, and G. Wegner, “Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions,” Colloid Polym. Sci., 521, 980-990 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 58, No. 6, pp. 1207-1224, November-December, 2022. Russian DOI: https://doi.org/10.22364/mkm.58.6.07.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rogovina, S.Z., Gasymov, M.M., Lomakin, S.M. et al. Influence of the Method of Obtaining Filled Polymer Nanocomposites of Polylactide Reduced Graphene Oxide on Their Properties and Structure. Mech Compos Mater 58, 845–856 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-023-10073-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-023-10073-2