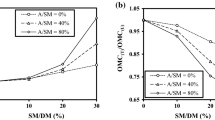
The effects of weathering on the physical and mechanical properties of polypropylene (PP)/wood flour (WF) composites with and without nanoclay were investigated. The composites were placed in a xenon-arc weatherometer chamber, and then their color changes, flexural strength (MOR) and modulus (MOE), and water uptake were evaluated during 1800 h of their accelerated weathering. The study showed that the water uptake and thickness swelling of the composite increased and their MOR and MOE decreased with weathering time, but the addition of nanoclay diminished these effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. M. Rowell, A. R. Sandi, D. F. Gatenholm, and R. E. Jacobson, “Utilization of natural fibers in plastic composites: Problem and opportunities in lignocellulosic composites,” J. Compos., 18, 23-51 (1997).
A. K. Bledzki and J. Gassan, “Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibers,” J. Polym. Sci., 24, 221-274 (1999).
K. Oksman and M. Sain, Wood-Polymer Composites, Woodhead Publishing Ltd, Great Abington, Cambridge, UK, 2008, 366.
J. L. Lopez, M. Sain, and P. Gooper, “Performance of natural fiber plastic composites under stress for application: effect of moisture, temperature and ultraviolet light exposure,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 99, No. 5, 2570-2577 (2005).
F. Mantiam and M. Morreale, “Accelerated weathering of polypropylene/wood flour composites,” Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 93, 1252-1258 (2008).
M. Stark, L. Matuana, and M. Clemons, “Effect of processing method on surface and weathering characteristics of wood–flour/HDPE composites,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 93, 1021-1030 (2004).
M. Stark and H. Nicole, “Effect of weathering cycle and manufactured method on performance of wood flour and high density polyethylene composites,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 100, 3131-3140 (2006).
J. Fabiyai, A.G. Mcdonald, M. Wolcott, and P. Griffith, “Wood plastic composites weathering: visual appearance and chemical changes,” J. Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 93, 1405-1414 (2008).
P. Darabi, J. Gril, M. F. Thevenon, A. N. Karimi, and M. Azadfalah, “Evaluation of high density polyethylene composite filled with bagasse after accelerated weathering followed by biodegradation,” Biores, 7, No. 4, 5285-5267 (2012).
K. C. Hung, Y. L. Chen, and J. H. Wu, “Natural weathering properties of acetylated bamboo plastic, composites,” Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 97, No. 9, 1680-1685 (2012).
C. Homkhiew, T. Ratanawilai, and W. Thongruang, “Effects of natural weathering on the properties of recycled polypropylene composites reinforced with wood flour,” Ind. Crop. Prod., 56, 52-59 (2014).
J. Fabiyi and A. G. McDonald, “Weathering performance of delignified pine-based polyvinyl chloride composites,” J. Reinf. Plas. Compos., 32, No. 8, 547-563 (2013).
L. Wei, A. G. McDonald, C. Freitag, and J. Morrell, “Effects of wood fiber esterification on properties, weatherability and biodurability of wood plastic composites,” Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 98, 1348-1361 (2013).
K. Chaochanchaikul and N. Sombatsompop, “Stabilizations of molecular structures and mechanical properties of PVC and wood/PVC composites by tinuvin and TiO2 stabilizers,” Polym. Eng. Sci., 51, No. 7, 1354-1365 (2011).
N. M. Stark and L. M. Matuana, “Influence of photostabilizers on wood flour-HDPE composites exposed to xenon-arc radiation with and without water spray,” Polym. Degrad. Stab. 91, No. 12, 3048-3056 (2006).
N. M. Stark and S. A. Mueller, “Improving the color stability of wood-plastic composites through fiber pre-treatment,” Wood Fiber Sci., 40, No. 2, 271-278 (2008).
S. C. Tjong, “Structural and mechanical properties of polymer nanocomposites; a review,” J. Mater. Sci. Eng., 53, 73-197 (2006).
V. Viswanathan, T. Laha, K. Balani, A. Agarwal, and S. Seal, “Challenges and advances in nanocomposite processing techniques; a review,” J. Mater. Sci. Eng., 54, 121-285 (2006).
L. A. Utracki, M. Sepehr, and E. Boccaleri, “Synthetic layered nanoparticles for polymeric nanocomposites (PNCs); a review,” J. Polym. Adv. Technol., 18, 1-37 (2007).
Y. Zhao, K. Wang, F. Zhu, P. Xue, and M. Jia, “Properties of poly (vinylchloride)/wood flour/montmorillonite composites: effects of coupling agents and layered silicate,” Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 91, 2874-2883 (2006).
Q. Wu, Y. Lei, C. M. Clemons, F. Yao, Y. Xu, and K. Lian, “Properties of HDPE/clay/wood nanocomposites,” J. Plas. Technol., 27, 108-115 (2007).
Y. Lei, Q. Wu, C. M. Clemons, F. Yao, and Y. Xu, “Influence of nanoclay on properties of HDPE/wood composites,” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 18, 1425-1433 (2007).
G. Han, Y. Lei, Q. Wu, Y. Kojima, and S. Suzuki, “Bamboo–fiber filled high density polyethylene composites; effect of coupling treatment and nanoclay,” J. Polym. Envi., 21, 1567-1582 (2008).
M. Hetzer and D. Kee, “Wood/polymer/nanoclay composites, environmentally friendly sustainable technology; a review,” J. Chem. Eng., 16, 1016-1027 (2008).
A. Hemmasi, H. Khademieslam, M. Talaiepoor, I. Ghasemi, and B. Kord, “Effect of nanoclay on the mechanical and morphological properties of wood polymer nanocomposites,” J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., 29, No. 7, 964-971 (2010).
B. Kord, A. Hemmasi, and I. Ghasemi, “Properties of PP/wood flour/ organomodified montmorillonite nanocomposites,” Wood Sci. Technol., 45, 111-119, (2010).
T. O. Kumanayaka, R. Parthasarathy, and M. Jollands, “Accelerating effect of montmorillonite on oxidative degradation of polyethylene nanocomposites,” Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 95, No. 4, 672-676 (2010).
A. Eshraghi, H. Khademieslam, I. Ghasemi, and M. Talaiepoor, “Effect of weathering on the properties of hybrid composite based on polyethylene, wood flour, and nanoclay,” Bioresour, 8, No. 1, 201-210 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 53, No. 2, pp. 383-394 , March-April, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kord, B., Malekian, B. & Ayrilmis, N. Weathering Performance of Montmorillonite/Wood Flour-Based Polypropylene Nanocomposites. Mech Compos Mater 53, 271–278 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-017-9660-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-017-9660-1