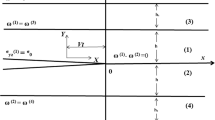
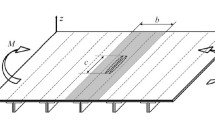
Crack penetration through the bimaterial interface of two polymers is investigated numerically. Due to the practical importance of the problem, a crack in a three-layer pipe consisting of a main and two, inner and outer, protective layers is analyzed in this paper. The prime aim is to formulate the conditions under which the crack stays arrested at the interface between the protective layer and the main pipe or penetrates into the interface and causes failure of the main pipe and consequently of the entire pipe system. The crack tip stress field is described by using a generalized stress intensity factor for cases where the crack touches the interface and the stress singularity exponent differs from 1/2. In the case of short-term applications, the stress state on the interface is given simply by a combination of the elastic properties of materials of the main pipe and the protective layers. In long-term applications, the time-dependent properties of the materials can significantly influence the stress state of the interface and can lead to considerable changes in failure conditions. The results presented here may contribute to a more accurate estimation of the residual lifetime of multilayer pipes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. H. England, “A crack between dissimilar media,” J. Appl. Mech., 32, 400–402 (1965).
F. Erdogan, “Stress distribution in a nonhomogeneous elastic plane with cracks,” J. Appl. Mech., 30, 232–236 (1963).
D. B. Bogy, “On the plane elastostatic problem of a loaded crack terminating at a material interface,” J. Appl. Mech., 38, 911–918 (1971).
S. A. Meguid, M. Tan, and Z. H. Zhu, “Analysis of crack perpendicular to bimaterial interface using a novel finite element,” Int. J. Fract., 75, 1–25 (1995).
T. L. Anderson, Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, CRC Press Inc. (1995).
K. Y. Lin and J. W. Mar, “Finite element analysis of stress intensity factors for cracks at a bi-material interface,” Int. J. Fract., 12, No. 4, 521–531 (1976).
Z. Q. Qian and A. R. Akisanya, “Wedge corner stress behaviour of bonded dissimilar materials,” Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech., 32, 209–222 (1999).
Z. Knésl, A. Knápek, and K. Bednář, “Evaluation of the critical stress in bonded materials with a crack perpendicular to the interface,” in: Surface Modification Technologies XI, The Institute of Materials, London (1998).
L. Náhlík, Z. Knésl, and J. Klusák, “Crack initiation criteria for singular stress concentrations. Part III: An application to a crack touching a bimaterial interface,” Eng. Mech., 15, 99–114 (2008).
J. Dundurs, in: T. Mura, (ed.), Mathematics of Dislocation, ASME, New York (1969), pp. 70–115.
J. Hessel, “Mindesbendsdauer von erdverlegten Rohen aus Polyethylen ohne Sandeinbettung,” 3R International, 4, 178–184 (2001).
L. E. Janson, Plastics Pipes for Water Supply and Sewage Disposal, Borealis, Stockholm (1999).
Z. Knésl, J. Klusák, and L. Náhlík, “Crack initiation criteria for singular stress concentrations. Part I: A universal assessment of singular stress concentrations,” Eng. Mech., 14, 399–408 (2007).
P. Hutař, L. Náhlík, L. Šestáková, M. Ševčík, Z. Knésl, and E. Nezbedová, “A fracture mechanics assessment of surface cracks existing in protective layers of multi-layer composite pipes,” Compos. Struct., 92, 1120–1125 (2010).
L. Náhlík, L. Šestáková, and P. Hutař, “Estimation of apparent fracture toughness of ceramic laminates,” Comput. Mater. Sci., 46, No. 3, 614–620 (2009).
L. Náhlík, L. Šestáková, P. Hutař, and R. Bermejo, “Prediction of crack propagation in layered ceramics with strong interfaces,” Eng. Fract. Mech., 77, 2192–2199 (2009).
G. C. Sih, “Strain-energy-density factor applied to mixed mode crack problems,” Int. J. Fract., 10, No. 3, 305–321 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 47, No. 2, pp. 289–300, March-April, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zouhar, M., Hutař, P., Náhlík, L. et al. Effect of time-dependent material properties on the crack behavior in the interface of two polymeric materials. Mech Compos Mater 47, 203–210 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-011-9198-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-011-9198-6