Abstract
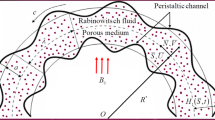
The main objective of this paper is to investigate boundary layer character of the velocity in peristaltic flow of a Sisko fluid in a curved channel under the influence of strong imposed radial magnetic field. The Sisko fluid model falls in the category of generalized Newtonian fluid models. The constitutive equation of Sisko model is described in terms of three material constants namely; power-law index (n), infinite shear rate viscosity (a) and consistency index (b). This model is capable of predicting shear-thinning and shear-thickening effects for n < 1 and n > 1, respectively. The equation governing the flow is first derived under the assumptions of long wavelength and low Reynolds number, and then made dimensionless by defining appropriate parameters. In dimensionless form it contains three dimensionless parameters namely; generalized ratio of infinite-shear rate viscosity to consistency index, power-law index and Hartmann number characterizing strength of the imposed magnetic field. It is found that the governing equation of flow becomes singular for large values of Hartmann number. Asymptotic solutions representing flow velocity at large values of Hartmann number are reported for two specific values of power-law index (namely n = 1 and n = 1/2) using singular perturbation technique. The flow velocity in either case exhibits qualitatively similar behavior. In fact, it exhibits boundary layer character i.e., it varies sharply in thin layer near the walls and varies linearly over rest of the cross-sections. This is contrary to what that is observed for flow velocity in straight channel (where except in thin layer near the channel walls the velocity over rest of the cross-section is uniform). The estimates of boundary layer thickness at upper and lower walls in either case are different. Moreover, the boundary layer thickness in either case is found to be inversely proportional to the Hartmann number.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taber LA, Zhang J, Perucchio R (2006) Computational model for the transition from peristaltic to pulsatile flow in the embryonic heart tube. ASME J Biomech Eng 129:441–449
Jackman WS, Lougheed W, Marliss EB, Zinman B, Albisser AM (1980) For insulin infusion: a miniature precision peristaltic pump and silicone rubber reservoir. Diabetes Care 3:322–331
Tripathi D, Anwar Beg O (2014) A study on peristaltic flow of nanofluids: application in drug delivery systems. Int J Heat Mass Transf 70:61–70
Fung YC, Yih CS (1968) Peristaltic transport. Trans ASME J Appl Mech 33:669–675
Shapiro AH, Jaffrin MY, Weinberg SL (1969) Peristaltic pumping with long wavelength at low Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 37:799–825
Lykoudis P, Roos R (1970) The fluid mechanics of the ureter from a lubrication theory point of view. J Fluid Mech 43:661–674
Pozrikidis C (1987) A study of peristaltic flow. J Fluid Mech 180:515–527
Takabatake S, Ayukawa K, Mori A (1988) Peristaltic pumping in circular cylindrical tubes: a numerical study of fluid transport and its efficiency. J Fluid Mech 193:267–283
Böhme G, Friedrich R (1983) Peristaltic flow of viscoelastic liquids. J Fluid Mech 128:109–122
Srivastava LM, Srivastava VP (1984) Peristaltic transport of blood: casson model II. J Biomech 17:821–829
Siddiqui AM, Schwarz WH (1994) Peristaltic flow of second order fluid in tubes. J Non Newton Fluid Mech 53:257–284
Mekheimer KhS, El-Shehawey EF, Alaw AM (1998) Peristaltic motion of a particle fluid suspension in a planar channel. Int J Theor Phys 37:2895–2920
Hayat T, Wang Y, Siddiqui AM, Hutter K, Asghar S (2002) Peristaltic transport of a third order fluid in a circular cylindrical tube. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 12:1691–1706
Hayat T, Afsar A, Ali N (2008) Peristaltic transport of a Johnson–Segalman fluid in an asymmetric channel. Math Compt Model 47:380–400
Hayat T, Ali N (2007) A mathematical description of peristaltic hydromagnetic flow in a tube. Appl Math Comput 188:1491–1502
Ali N, Hayat T (2007) Peristaltic motion of a Carreau fluid in an asymmetric channel. Appl Math Comput 193:535–552
Wang Y, Hayat T, Hutter K (2007) Peristaltic flow of a Johnson–Segalman fluid through a deformable tube. Theor Comput Fluid Dyn 21:369–380
Tripathi D, Anwar Beg O (2014) Peristaltic propulsion of generalized Burgers’ fluids through a non-uniform porous medium: a study of chyme dynamics through the intestine. Math Biosci 248:67–77
Tripathi D, Anwar Bég O (2014) A study on peristaltic flow of nanofluids: application in drug delivery systems. Int J Heat Mass Transf 70:61–70
Akram S, Nadeem S (2013) Influence of induced magnetic field and heat transfer on the peristaltic motion of a Jeffrey fluid in an asymmetric channel: closed form solutions. J Magn Magn Mater 328:11–20
Hayat T, Ali N, Asghar S (2007) Hall effects on peristaltic flow of a Maxwell fluid in a porous medium. Phys Lett A 363:397–403
Kothandapani M, Srinivas S (2008) On the influence of wall properties in the MHD peristaltic transport with heat transfer and porous medium. Phys Lett A 372:4586–4591
Srinivas S, Kothandapani M (2009) The influence of heat and mass transfer on MHD peristaltic flow through a porous space with compliant walls. Appl Math Comput 213:197–208
Sato H, Kawai T, Fujita T, Okabe M (2000) Two dimensional peristaltic flow in curved channels. Trans Jpn Soc Mech Eng B 66:679–685
Ali N, Sajid M, Hayat T (2010) Long wavelength flow analysis in a curved channel. Z Naturforsch 65a:191–196
Ali N, Sajid M, Javed T, Abbas Z (2010) Heat transfer analysis of peristaltic flow in a curved channel. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:3319–3325
Ali N, Sajid M, Abbas Z, Javed T (2010) Non-Newtonian fluid flow induced by peristaltic waves in a curved channel. Eur J Mech B/Fluids 29:3511–3521
Hayat T, Javed M, Hendi A (2011) Peristaltic transport of viscous fluid in a curved channel with compliant walls. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:1615–1621
Hayat T, Noreen S, Alsaedi A (2012) Effect of an induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of non-Newtonian fluid in a curved channel. J Mech Med Biol 12:1250058–1250084
Abbasi FM, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2015) Numerical analysis for MHD peristaltic transport of Carreau–Yasuda fluid in a curved channel with Hall effects. J Magn Magn Mater 382:104–110
Hina S, Hayat T, Mustafa M, Aldossary OM, Asghar S (2012) Effect of wall properties on the peristaltic flow of a third grade fluid in a curved channel. J Mech Med Biol 12:1–16
Hina S, Hayat T, Asghar S (2012) Heat and mass transfer effects on the peristaltic flow of Johnson–Segalman fluid in a curved channel with compliant walls. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:3511–3521
Hina S, Mustafa M, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2013) Peristaltic flow of pseudo plastic fluid in a curved channel with wall properties. ASME J Appl Mech 80:024501–024507
Narla VK, Prasad KM, Ramanamurthy JV (2013) Peristaltic motion of viscoelastic fluid with fractional second grade model in curved channels. Chin J Eng 2013:582390–582397
Ramanamurthy JV, Prasad KM, Narla VK (2013) Unsteady peristaltic transport in curved channels. Phys Fluids 25:091903–091920
Kalantari A, Sadeghy K, Sadeqi S (2013) Peristaltic flow of non-Newtonian fluids through curved channels: a numerical study. Ann Trans Nordic Rheol Soc 21:163–170
Asghar S, Minhas T, Ali A (2014) Existence of a Hartmann layer in the peristalsis of Sisko fluid. Chin Phys B 24:054702–0547027
Barnes HA, Hutton JF, Watters K (1993) An introduction to rheology. Elsevier Science Publishers B.V, Amsterdam
Bush AW (1994) Perturbation methods for engineers and scientists, vol 12. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Dyke MV (1964) Perturbation methods in fluid mechanics. Academic Press, New York
Wang Y, Hayat T, Ali N, Oberlack M (2008) Magnetohydrodynamic peristaltic motion of a Sisko fluid in a symmetric or asymmetric channel. Phys A 387:347–362
Acknowledgments
The second author is grateful to the Higher Education Commission (HEC) Pakistan for award of indigenous scholarship for his Ph.D. studies. We further thank the anonymous reviewer for his useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, N., Javid, K., Sajid, M. et al. New concept about existence of Hartmann boundary layer in peristalsis through curved channel-asymptotic solution. Meccanica 51, 1783–1795 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0346-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0346-2