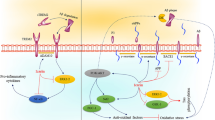
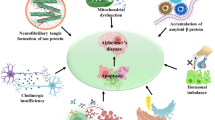
Abstract
Modulation of cell signaling pathways is the key area of research towards the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Altered Nrf2-Keap1-ARE (Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2-Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1-Antioxidant responsive element) and SIRT1 (Sirtuin 1) cell signaling pathways are considered to play major role in the etiology and pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Strikingly, betanin, a betanidin 5-O-β-D-glucoside compound is reported to show commendable anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects in several disease studies including AD and PD. The present review discusses the pre-clinical studies demonstrating the neuroprotective effects of betanin by virtue of its potential to ameliorate oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, abnormal protein aggregation and cell death. It highlights the direct linkage between the neuroprotective abilities of betanin and upregulation of the Nrf2-Keap1-ARE and SIRT1 signaling pathways. The review further hypothesizes the involvement of the betanin-Nrf2-ARE route in the inhibition of beta-amyloid aggregation through beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), one of the pivotal hallmarks of AD. The present review hereby for the first time elaborately discusses the reported neuroprotective abilities of betanin and decodes the Nrf2 and SIRT1 modulating potential of betanin as a primary mechanism of action behind, hence highlighting it as a novel drug candidate for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases in the near future.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abedimanesh N, Asghari S, Mohammadnejad K, Daneshvar Z, Rahmani S, Shokoohi S, Farzaneh AH, Hosseini SH, Jafari Anarkooli I, Noubarani M, Andalib S, Eskandari MR, Motlagh B (2021) The anti-diabetic effects of betanin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through modulating AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Nutr Metab 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-021-00621-9
Ahmadi H, Nayeri Z, Minuchehr Z, Sabouni F, Mohammadi MI (2020) Betanin purification from red beetroots and evaluation of its anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activity on LPS-activated microglial cells. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0233088
Ahmed SMU, Luo L, Namani A, Wang XJ, Tang X (2017) Nrf2 signaling pathway: pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta - Mol Basis Dis 1863:585–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.005
Albasher G, Alsaleh AS, Alkubaisi N, Alfarraj S, Alkahtani S, Farhood M, Alotibi N, Almeer R (2020) Red beetroot extract abrogates chlorpyrifos-induced cortical damage in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2963020
Alghazwi M, Smid S, Musgrave I, Zhang W (2019) In vitro studies of the neuroprotective activities of astaxanthin and fucoxanthin against amyloid beta (Aβ 1–42) toxicity and aggregation. Neurochem Int 124:215–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2019.01.010
Amjadi S, Ghorbani M, Hamishehkar H, Roufegarinejad L (2018) Improvement in the stability of betanin by liposomal nanocarriers: Its application in gummy candy as a food model. Food Chem 256:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FOODCHEM.2018.02.114
Amjadi S, Mesgari Abbasi M, Shokouhi B, Ghorbani M, Hamishehkar H (2019) Enhancement of therapeutic efficacy of betanin for diabetes treatment by liposomal nanocarriers. J Funct Foods 59:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.05.015
Araujo JA, Zhang M, Yin F (2012) Heme oxygenase-1, oxidation, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Front Pharmacol 3 JUL:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2012.00119
Armstrong RA (2013) What causes Alzheimer’s disease? Folia Neuropathol 51:169–188. https://doi.org/10.5114/fn.2013.37702
Bahn G, Park JS, Yun UJ, Lee YJ, Choi Y, Park JS, Baek SH, Choi BY, Cho YS, Kim HK, Han J, Sul JH, Baik SH, Lim J, Wakabayashi N, Bae SH, Han JW, Arumugam TV, Mattson MP, Jo DG (2019) NRF2/ARE pathway negatively regulates BACE1 expression and ameliorates cognitive deficits in mouse Alzheimer’s models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:12516–12523. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1819541116
Baião D dos S, da Silva DVT, Paschoalin VMF (2020) Beetroot, a remarkable vegetable: Its nitrate and phytochemical contents can be adjusted in novel formulations to benefit health and support cardiovascular disease therapies. Antioxidants 9:1–36. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9100960
Bhattacharjee N, Borah A (2016) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are the underlying events of dopaminergic neurodegeneration in homocysteine rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 101:48–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2016.10.001
Bhattacharjee P, Öhrfelt A, Lashley T, Blennow K, Brinkmalm A, Zetterberg H (2019) Mass spectrometric analysis of lewy body-enriched α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease. J Proteome Res 18:2109–2120. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00982
Blandini F, Armentero MT (2014) Dopamine receptor agonists for Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 23:387–410. https://doi.org/10.1517/13543784.2014.869209
Cucullo L, Mcallister MS, Kight K, Krizanac-Bengez L, Marroni M, Mayberg MR, Stanness KA, Janigro D (2002) A new dynamic in vitro model for the multidimensional study of astrocyte-endothelial cell interactions at the blood-brain barrier a a a a. Brain Res 951:243–254
Dehouck B, Fenart L, Dehouck MP, Pierce A, Torpier G, Cecchelli R (1997) A new function for the LDL receptor: transcytosis of LDL across the blood-brain barrier. J Cell Biol 138:877–889. https://doi.org/10.1083/JCB.138.4.877
Deture MA, Dickson DW (2019) The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 14:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-019-0333-5
Devadiga D, Ahipa TN (2020) Betanin: a red-violet pigment - chemistry and applications. Chem Technol Nat Synth Dye Pigment. https://doi.org/10.5772/INTECHOPEN.88939
Dexter DT, Jenner P (2013) Parkinson disease: from pathology to molecular disease mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med 62:132–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.018
Dezsi L, Vecsei L (2017) Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors in Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurol Disord - Drug Targets 16:425–439. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527316666170124165222
Dhage PA, Sharbidre AA, Dakua SP, Balakrishnan S (2021) Leveraging hallmark Alzheimer’s molecular targets using phytoconstituents: current perspective and emerging trends. Biomed Pharmacother 139:111634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111634
Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP (2008) JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 27:6245–6251. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.301
Dechant JE(2021) Complications of parenteral administration of drugs. Complications in Equine Surgery10–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119190332.ch2
El Shaffei I, Abdel-Latif GA, Farag DB, Schaalan M, Salama RM (2021) Ameliorative effect of betanin on experimental cisplatin-induced liver injury; the novel impact of miRNA-34a on the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22753
Esatbeyoglu T, Wagner AE, Motafakkerazad R, Nakajima Y, Matsugo S, Rimbach G (2014) Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of betanin: electron spin resonance spectroscopy studies and studies in cultured cells. Food Chem Toxicol 73:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.08.007
Esatbeyoglu T, Wagner AE, Schini-Kerth VB, Rimbach G (2015) Betanin–a food colorant with biological activity. Mol Nutr Food Res 59:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/MNFR.201400484
Fagiani F, Lanni C, Racchi M, Govoni S (2021) (Dys)regulation of synaptic activity and neurotransmitter release by β-amyloid: a look beyond Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2021.635880
Ferreira-Vieira TH, Guimaraes IM, Silva FR, Ribeiro FM (2016) Alzheimer’s disease: targeting the cholinergic system. Curr Neuropharmacol 14:101–115. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159x13666150716165726
Fracassi A, Marcatti M, Zolochevska O, Tabor N, Woltjer R, Moreno S, Taglialatela G (2021) Oxidative damage and antioxidant response in frontal cortex of demented and nondemented individuals with alzheimer’s neuropathology. J Neurosci 41:538–554. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0295-20.2020
García-Ayllón MS, Riba-Llena I, Serra-Basante C, Alom J, Boopathy R, Sáez-Valero J (2010) Altered levels of acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer plasma. PLoS One 5. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008701
Gee JM, Dupont MS, Rhodes MJC, Johnson IT (1998) Quercetin glucosides interact with the intestinal glucose transport pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 25:19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(98)00020-3
Giridharan S, Srinivasan M (2018) Mechanisms of NF-κB p65 and strategies for therapeutic manipulation. J Inflamm Res 11:407–419. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S140188
Goldstein DS, Sullivan P, Holmes C, Kopin IJ, Basile MJ, Mash DC (2011) Catechols in post-mortem brain of patients with Parkinson disease. Eur J Neurol 18:703–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03246.x
Gómez-Benito M, Granado N, García-Sanz P, Michel A, Dumoulin M, Moratalla R (2020) Modeling Parkinson’s disease with the alpha-synuclein protein. Front Pharmacol 11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00356
González-Ponce HA, Martínez-Saldaña MC, Tepper PG, Quax WJ, Buist-Homan M, Faber KN, Moshage H (2020) Betacyanins, major components in Opuntia red-purple fruits, protect against acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Food Res Int 137:109461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109461
Guo JD, Zhao X, Li Y, Li GR, Liu XL (2018) Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease (Review). Int J Mol Med 41:1817–1825. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3406
Hadipour E, Fereidoni M, Tayarani-Najaran Z (2020a) Betanin attenuates oxidative stress induced by 6-OHDA in PC12 cells via SAPK/JNK and PI3 K pathways. 45: 395–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02927-w
Hadipour E, Taleghani A, Tayarani-Najaran N, Tayarani-Najaran Z (2020b) Biological effects of red beetroot and betalains: a review. Phyther Res 34:1847–1867. https://doi.org/10.1002/PTR.6653
Han J, Zhang Z, Yang S, Wang J, Yang X, Tan D (2014) Betanin attenuates paraquat-induced liver toxicity through a mitochondrial pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 70:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2014.04.038
Han J, Ma D, Zhang M, Yang X, Tan D (2015) Natural antioxidant betanin protects rats from paraquat-induced acute lung injury interstitial pneumonia. Biomed Res Int 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/608174
Hu YR, Ma H, Zou ZY, He K, Xiao YB, Wang Y, Feng M, Ye XL, Li XG (2017) Activation of Akt and JNK/Nrf2/NQO1 pathway contributes to the protective effect of coptisine against AAPH-induced oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 85:313–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.031
Huang AS, Elbe JHV (1987) Effect of pH on the degradation and regeneration of betanine. J Food Sci 52:1689–1693. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1987.tb05907.x
Huang K, Gao X, Wei W (2017) The crosstalk between Sirt1 and Keap1/Nrf2/ARE anti-oxidative pathway forms a positive feedback loop to inhibit FN and TGF-β1 expressions in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Cell Res 361:63–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.09.042
Imamura T, Koga H, Higashimura Y Isozumi N, Matsumoto K, Ohki S, Mori M (2021) Red-beet betalain pigments inhibit amyloid-β aggregation and toxicity in amyloid-β expressing Caenorhabditis elegans. bioRxiv 2020.12.23.424246. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.23.424246
Kaakkola S (2010) Problems with the present inhibitors and a relevance of new and improved COMT inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-381326-8.00009-0 (Elsevier Inc)
Kanner J, Harel S, Granit R (2001) Betalains - a new class of dietary cationized antioxidants. J Agric Food Chem 49:5178–5185. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010456f
Krajka-Kuźniak V, Paluszczak J, Szaefer H, Baer-Dubowska W (2013) Betanin, a beetroot component, induces nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor 2-mediated expression of detoxifying/antioxidant enzymes in human liver cell lines. Br J Nutr 110:2138–2149. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513001645
Kwankaew N, Okuda H, Aye-Mon A, Ishikawa T, Hori K, Sonthi P, Kozakai Y, Ozaki N (2021) Antihypersensitivity effect of betanin (red beetroot extract) via modulation of microglial activation in a mouse model of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain (united Kingdom) 25:1788–1803. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.1790
Lee JH, Son CW, Kim MY, Kim MH, Kim HR, Kwak ES, Kim S, Kim MR (2009) Red beet (Beta vulgaris L.) leaf supplementation improves antioxidant status in C57BL/6J mice fed high fat high cholesterol diet. Nutr Res Pract 3:114. https://doi.org/10.4162/NRP.2009.3.2.114
Liu J, Huang D, Xu J, Tong J, Wang Z, Huang L, Yang Y, Bai X, Wang P, Suo H, Ma Y, Yu M, Fei J, Huang F (2015) Tiagabine protects dopaminergic neurons against neurotoxins by inhibiting microglial activation. Sci Rep 5:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep15720. (2015 51)
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z, Li W, Hu J, Lu C, Liu Y (2020) PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis 11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02998-6
Marucci G, Buccioni M, Ben DD, Lambertucci C, Volpini R, Amenta F (2021) Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 190:108352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108352
McAllister MS, Krizanac-Bengez L, Macchia F, Naftalin RJ, Pedley KC, Mayberg MR, Marroni M, Leaman S, Stanness KA, Janigro D (2001) Mechanisms of glucose transport at the blood-brain barrier: an in vitro study. Brain Res 904:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02418-0
Minh Hung H, Nguyen MT, Tran PT, Truong VK, Chapman J, Quynh Anh LH, Derreumaux P, Vu VV, Ngo ST (2020) Impact of the astaxanthin, betanin, and EGCG compounds on small oligomers of amyloid Aβ40Peptide. J Chem Inf Model 60:1399–1408. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.JCIM.9B01074/SUPPL_FILE/CI9B01074_SI_001.PDF
Misrani A, Tabassum S, Yang L (2021) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 13:1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.617588
Motawi TK, Ahmed SA, El-Boghdady NA, Metwally NS, Nasr NN (2019) Impact of betanin against paracetamol and diclofenac induced hepato-renal damage in rats. 25: 86–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750X.2019.1697365
Muddapu VR, Dharshini SAP, Chakravarthy VS, Gromiha MM (2020) Neurodegenerative diseases – is metabolic deficiency the root cause? Front Neurosci 14:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00213
Mukherjee S, Perez KA, Lago LC, Klatt S, McLean CA, Birchall IE, Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Roberts BR (2021) Quantification of N-terminal amyloid-β isoforms reveals isomers are the most abundant form of the amyloid-β peptide in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Commun 3:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/braincomms/fcab028
Nichols E, Steinmetz JD, Vollset SE, Fukutaki K, Chalek J, Abd-Allah F, Abdoli A, Abualhasan A, Abu-Gharbieh E, Akram TT, Al Hamad H, Alahdab F, Alanezi FM, Alipour V, Almustanyir S, Amu H, Ansari I, Arabloo J, Ashraf T, Astell-Burt T, Ayano G, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Baig AA, Barnett A, Barrow A, Baune BT, Béjot Y, Bezabhe WMM, Bezabih YM, Bhagavathula AS, Bhaskar S, Bhattacharyya K, Bijani A, Biswas A, Bolla SR, Boloor A, Brayne C, Brenner H, Burkart K, Burns RA, Cámera LA, Cao C, Carvalho F, Castro-de-Araujo LFS, Catalá-López F, Cerin E, Chavan PP, Cherbuin N, Chu DT, Costa VM, Couto RAS, Dadras O, Dai X, Dandona L, Dandona R, De la Cruz-Góngora V, Dhamnetiya D, Dias da Silva D, Diaz D, Douiri A, Edvardsson D, Ekholuenetale M, El Sayed I, El-Jaafary SI, Eskandari K, Eskandarieh S, Esmaeilnejad S, Fares J, Faro A, Farooque U, Feigin VL, Feng X, Fereshtehnejad SM, Fernandes E, Ferrara P, Filip I, Fillit H, Fischer F, Gaidhane S, Galluzzo L, Ghashghaee A, Ghith N, Gialluisi A, Gilani SA, Glavan IR, Gnedovskaya EV, Golechha M, Gupta R, Gupta VB, Gupta VK, Haider MR, Hall BJ, Hamidi S, Hanif A, Hankey GJ, Haque S, Hartono RK, Hasaballah AI, Hasan MT, Hassan A, Hay SI, Hayat K, Hegazy MI, Heidari G, Heidari-Soureshjani R, Herteliu C, Househ M, Hussain R, Hwang BF, Iacoviello L, Iavicoli I, Ilesanmi OS, Ilic IM, Ilic MD, Irvani SSN, Iso H, Iwagami M, Jabbarinejad R, Jacob L, Jain V, Jayapal SK, Jayawardena R, Jha RP, Jonas JB, Joseph N, Kalani R, Kandel A, Kandel H, Karch A, Kasa AS, Kassie GM, Keshavarz P, Khan MA, Khatib MN, Khoja TAM, Khubchandani J, Kim MS, Kim YJ, Kisa A, Kisa S, Kivimäki M, Koroshetz WJ, Koyanagi A, Kumar GA, Kumar M, Lak HM, Leonardi M, Li B, Lim SS, Liu X, Liu Y, Logroscino G, Lorkowski S, Lucchetti G, Lutzky Saute R, Magnani FG, Malik AA, Massano J, Mehndiratta MM, Menezes RG, Meretoja A, Mohajer B, Mohamed Ibrahim N, Mohammad Y, Mohammed A, Mokdad AH, Mondello S, Moni MAA, Moniruzzaman M, Mossie TB, Nagel G, Naveed M, Nayak VC, Neupane Kandel S, Nguyen TH, Oancea B, Otstavnov N, Otstavnov SS, Owolabi MO, Panda-Jonas S, Pashazadeh Kan F, Pasovic M, Patel UK, Pathak M, Peres MFP, Perianayagam A, Peterson CB, Phillips MR, Pinheiro M, Piradov MA, Pond CD, Potashman MH, Pottoo FH, Prada SI, Radfar A, Raggi A, Rahim F, Rahman M, Ram P, Ranasinghe P, Rawaf DL, Rawaf S, Rezaei N, Rezapour A, Robinson SR, Romoli M, Roshandel G, Sahathevan R, Sahebkar A, Sahraian MA, Sathian B, Sattin D, Sawhney M, Saylan M, Schiavolin S, Seylani A, Sha F, Shaikh MA, Shaji KS, Shannawaz M, Shetty JK, Shigematsu M, Shin JI, Shiri R, Silva DAS, Silva JP, Silva R, Singh JA, Skryabin VY, Skryabina AA, Smith AE, Soshnikov S, Spurlock EE, Stein DJ, Sun J, Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Thakur B, Timalsina B, Tovani-Palone MR, Tran BX, Tsegaye GW, Valadan Tahbaz S, Valdez PR, Venketasubramanian N, Vlassov V, Vu GT, Vu LG, Wang YP, Wimo A, Winkler AS, Yadav L, Yahyazadeh Jabbari SH, Yamagishi K, Yang L, Yano Y, Yonemoto N, Yu C, Yunusa I, Zadey S, Zastrozhin MS, Zastrozhina A, Zhang ZJ, Murray CJL, Vos T (2022) Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Public Heal 7:e105–e125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00249-8
Obulesu M, Lakshmi MJ (2014) Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease: an understanding of the physiology, pathology and therapeutic avenues. Neurochem Res 39:2301–2312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1454-4
Osama A, Zhang J, Yao J, Yao X, Fang J (2020) Nrf2: a dark horse in Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Ageing Res Rev 64:101206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101206
Ou Z, Pan J, Tang S, Duan D, Yu D, Nong H, Wang Z (2021) Global trends in the incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability of Parkinson’s disease in 204 countries/territories from 1990 to 2019. Front Public Heal 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.776847
Pain S, Deguil J, Belin J, Barraud P, Ragot S, Houeto JL (2020) Regulation of protein synthesis and apoptosis in lymphocytes of parkinson patients: the effect of dopaminergic treatment. Neurodegener Dis 19:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505750
Patching SG (2017) Glucose transporters at the blood-brain barrier: function, regulation and gateways for drug delivery. Mol Neurobiol 54:1046–1077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9672-6
Paul R, Choudhury A, Kumar S, Giri A, Sandhir R, Borah A (2017) Cholesterol contributes to dopamineneuronal loss in MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: involvement of mitochondrial dysfunctions and oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 12:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171285
Percário S, Da Silva Barbosa A, Varela ELP, Gomes ARQ, Ferreira MES, De Nazaré Araújo Moreira T, Dolabela MF (2020) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease: potential benefits of antioxidant supplementation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2360872
Porcellotti S, Fanelli F, Fracassi A, Sepe S, Cecconi F, Bernardi C, Cimini A, Cerù MP, Moreno S (2015) Oxidative stress during the progression of β-amyloid pathology in the neocortex of the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/967203
Pulgar VM (2019) Transcytosis to cross the blood brain barrier, new advancements and challenges. Front Neurosci 13:1019. https://doi.org/10.3389/FNINS.2018.01019/BIBTEX
Rahimi P, Mesbah-Namin SA, Ostadrahimi A, Abedimanesh S, Separham A, Asghary Jafarabadi M (2019) Effects of betalains on atherogenic risk factors in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Food Funct 10:8286–8297. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo02020a
Ren Z, He H, Zuo Z, Xu Z, Wei Z, Deng J (2019) The role of different SIRT1-mediated signaling pathways in toxic injury. Cell Mol Biol Lett 24:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0158-9
Rinne JO, Kaasinen V, Järvenpää T, Någren K, Roivainen A, Yu M, Oikonen V, Kurki T (2003) Brain acetylcholinesterase activity in mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:113–115. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.74.1.113
Saha S, Buttari B, Profumo E, Tucci P, Saso L (2022) A perspective on Nrf2 signaling pathway for neuroinflammation: a potential therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Front Cell Neurosci 15:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.787258
Sharma K (2019) Cholinesterase inhibitors as Alzheimer’s therapeutics (Review). Mol Med Rep 20:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10374
Shinotoh H, Namba H, Fukushi K, Nagatsuka SI, Tanaka N, Aotsuka A, Tanada S, Irie T (2000) Brain acetylcholinesterase activity in Alzheimer disease measured by positron emission tomography. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 14:114–118. https://doi.org/10.1097/00002093-200000001-00017
Shunan D, Yu M, Guan H, Zhou Y (2021) Neuroprotective effect of Betalain against AlCl3-induced Alzheimer’s disease in Sprague Dawley Rats via putative modulation of oxidative stress and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 137:111369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111369
Silva MVF, Loures CDMG, Alves LCV, De Souza LC, Borges KBG, Carvalho MDG (2019) Alzheimer’s disease: risk factors and potentially protective measures. J Biomed Sci 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12929-019-0524-Y
Sutariya B, Taneja N, Badgujar L, Saraf M (2017) Modulatory effect of betanin on high glucose induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal proximal tubular cells. Biomed Pharmacother 89:18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.006
Taylor JM, Main BS, Crack PJ (2013) Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress: co-conspirators in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 62:803–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.12.016
Tesoriere L, Allegra M, Butera D, Livrea MA (2004) Absorption, excretion, and distribution of dietary antioxidant betalains in LDLs: potential health effects of betalains in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 80:941–945. https://doi.org/10.1093/AJCN/80.4.941
Thong-asa W, Prasartsri S, Klomkleaw N, Thongwan N (2020) The neuroprotective effect of betanin in trimethyltin-induced neurodegeneration in mice. Metab Brain Dis 35(8):1395–1405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00615-1
Thong-asa W, Jedsadavitayakol S, Jutarattananon S (2021) Benefits of betanin in rotenone-induced Parkinson mice. Metab Brain Dis 36(8):2567–2577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00826-0
Tönnies E, Trushina E (2017) oxidative stress, synaptic dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis 57:1105–1121. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-161088
Toth S, Jonecova Z, Maretta M, Curgali K, Kalpakidis T, Pribula M, Kusnier M, Fagova Z, Fedotova J, La Rocca G, Rodrigo L, Caprnda M, Zulli A, Ciccocioppo R, Mechirova E, Kruzliak P (2019) The effect of Betanin parenteral pretreatment on Jejunal and pulmonary tissue histological architecture and inflammatory response after Jejunal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Mol Pathol 110:104292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104292
Tufekci KU, Civi Bayin E, Genc S, Genc K (2011) The Nrf2/ARE pathway: a promising target to counteract mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis 2011. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/314082
Turner PV, Brabb T, Pekow C, Vasbinder MA (2011) Administration of substances to laboratory animals: routes of administration and factors to consider. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 50:600–613
Vieira Teixeira Da Silva D, D' Avila Pereira A, Teles Boaventura G, Stefan De Almeida Ribeiro R, Vericimo MA, Eponina De Carvalho-Pinto C, Dos D, Baião S, Mere E, Aguila D, Flosi Paschoalin VM (2019) Short-term betanin intake reduces oxidative stress in wistar rats. Nutrients 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11091978
Vieira Teixeira Da Silva D, Dos D, Baião S, Ferreira F, Margaret V, Paschoalin F (2020) Betanin as a multipath oxidative stress and inflammation modulator: a beetroot pigment with protective effects on cardiovascular disease pathogenesis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 62(2):539-554. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1822277
von Elbe JH, Maing I-Y, Amundson CH (1974) Color Stability of Betanin. J Food Sci 39:334–337. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1974.tb02888.x
Wang W, Zhao H, Chen B (2020) DJ-1 protects retinal pericytes against high glucose-induced oxidative stress through the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Sci Rep 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59408-2
Witt PAL, Fahn S (2016) Levodopa therapy for Parkinson disease: a look backward and forward. Neurology 86:S3–S12. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002509
Yang H, Zhang W, Pan H, Feldser HG, Lainez E, Miller C, Leung S, Zhong Z, Zhao H, Sweitzer S, Considine T, Riera T, Suri V, White B, Ellis JL, Vlasuk GP, Loh C (2012) SIRT1 activators suppress inflammatory responses through promotion of p65 deacetylation and inhibition of NF-κB activity. PLoS ONE 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The idea of the review was conceived by BanashreeChetiaPhukan, Rubina Roy, and Anupom Borah. Literature search, original manuscript preparation, and core concept and novel hypothesis presentation was performed by BanashreeChetiaPhukan and RubinaRoy. Figures were prepared by Rubina Roy. The manuscript was reviewed and edited by Rajib Paul, MuhammedKhairujjamanMazumder, JoyobratoNath, Pallab Bhattacharya, and Anupom Borah. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics declarations
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Phukan, B.C., Roy, R., Paul, R. et al. Traversing through the cell signaling pathways of neuroprotection by betanin: therapeutic relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Metab Brain Dis 38, 805–817 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01177-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01177-8