Abstract
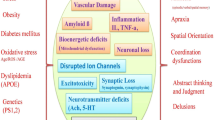
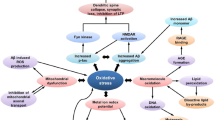
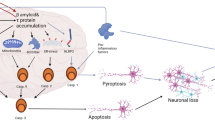
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a devastative neurodegenerative disorder with complex etiology. Apoptosis, a biological process that plays an essential role in normal physiology to oust a few cells and contribute to the normal growth, when impaired or influenced by various factors such as Bcl2, Bax, caspases, amyloid beta, tumor necrosis factor-α, amyloid precursor protein intracellular C-terminal domain, reactive oxygen species, perturbation of enzymes leads to deleterious neurodegenerative disorders like AD. There are diverse pathways that provoke manifold events in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to execute the process of cell death. This review summarizes the crucial apoptotic mechanisms occurring in both mitochondria and ER. It gives substantial summary of the diverse mechanisms studied in vivo and in vitro. A brief account on neuroprotection of several bioactive components, flavonoids and antioxidants of plants against apoptotic events of both mitochondria and ER in both in vitro and in vivo has been discussed. In light of this, the burgeoning need to develop animal models to study the efficacy of various therapeutic effects has been accentuated.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Obulesu M, Rao Dowlathabad Muralidhara (2010) Animal models of Alzheimer’s disease: an understanding of pathology and therapeutic avenues. Int J Neurosci 120:531–537
Wright JW, Harding JW (2010) The brain RAS and Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 223:326–333
Obulesu M, Venu R, Somashekhar R (2011) Lipid peroxidation in Alzheimer’s disease: emphasis on metal mediated neurotoxicity. Acta Neurol Scand 124:295–301
Obulesu M, Somashekhar R, Venu R (2011) Genetics of Alzheimer’s disease: apo E and presenilins instigated neurodegeneration. Int J Neurosci 121:229–236
Obulesu M, Rao Dowlathabad Muralidhara (2010) DNA damage and impairment of DNA repair in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neurosci 120:397–403
Magisetty O, Rao DM, Shamasundar NM (2009) Studies on genomic DNA stability in aluminium maltolate treated aged New Zealand rabbit: relevance to the Alzheimer’s animal model. J Clin Med Res 1:212–218
Obulesu M, Venu R, Somashekhar R (2011) Tau mediated neurodegeneration: an insight into Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Neurochem Res 36:1329–1335
Szewczyk B (2013) Zinc homeostasis and neurodegenerative disorders. Front Aging Neurosci 5:33
Obulesu M, Jhansilakshmi M (2014) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: an understanding of physiology and pathology. Int J Neurosci 124:227–235
Kataoka S, Tsuruo T (1996) Apoptosis. Oncologist 1:399–401
Rathmell JC, Lindsten T, Zong WX et al (2002) Deficiency in Bak and Bax perturbs thymic selection and lymphoid homeostasis. Nat Immunol 3:932–939
Zapala B, Kaczynski L, Kiec-wilk B et al (2010) Humanins, the neuroprotective and cytoprotective peptides with antiapoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties. Pharmacol Rep 62:767–777
Alvarez S, Blanco S, Fresno M et al (2011) TNF-α contributes to caspase-3 independent apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells: role of NFAT. PLoS One 6:e16100
Alberini CM (2009) Transcription factors in long-term memory and synaptic plasticity. Physiol Rev 89:121–145
Gatta V, Gatta D, Drago K et al (2011) Microarray analysis on human neuroblastoma cells exposed to aluminum, β(1-42)-amyloid or the β(1-42)-amyloid aluminum complex. PLoS One 6:e15965
Morrison BE, Majdzadeh N, D’mello SR (2007) Histone deacetylases: focus on the nervous system. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2258–2269
Konishi Y, Lehtinen M, Donovan N et al (2002) Cdc2 phosphorylation of BAD links the cell cycle to the cell death machinery. Mol Cell 9:1005–1016
Lee HP, Casadesus G, Zhu X et al (2009) All-trans retinoic acid as a novel therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 9:1615–1621
Radi E, Formichi P, Battisti C et al (2014) Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. J Alzheimers Dis 42:S125–S152
Menendez-Gonzalez M, Perez-Pinera P, Martinez-Rivera M et al (2011) Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease: rational basis in ongoing clinical trials. Curr Pharm Des 17:508–520
Lauterbach EC, Victoroff J, Coburn KL et al (2010) Mendez, Psychopharmacological neuroprotection in neurodegenerative disease: assessing the preclinical data. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 22:8–18
Friedlander RM (2003) Apoptosis and caspases in neurodegenerative diseases. N Engl J Med 348:1365–1375
Zhang JH, Zhang Y, Herman B (2003) Caspases, apoptosis and aging. Ageing Res Rev 2:357–366
Le Bras M, Rouy I, Brenner C (2006) The modulation of inter-organelle cross-talk to control apoptosis. Med Chem 2:1–12
El-Guendy N, Rangnekar VM (2003) Apoptosis by Par-4 in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Cell Res 283:51–66
Kim R (2005) Unknotting the roles of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL in cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 333:336–343
Hengartner MO, Bryant JA (2000) Apoptotic cell death: from worms to wombats… but what about the weeds? Symp Soc Exp Biol 52:1–12
Jahanshahi M, Nickmahzar EG, Babakordi F (2013) The effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on scopolamine-induced apoptosis in the hippocampus of rats. Anat Sci Int 88:217–222
Malik M, Fenko MD, Sheikh AM et al (2011) A novel approach for characterization of cathepsin D protease and its effect on tau and β-amyloid proteins. Neurochem Res 36:754–760
Vasileiou E, Montero RM, Turner CM et al (2010) P2X7 receptor at the heart of disease. Hippocratia 14:155–163
Morelli A, Chiozzi P, Chiesa A et al (2003) Extracellular ATP causes ROCK 1-dependent bleb formation in P2X7-transfected HEK293 cells. Mol Biol Cell 14:2655–2664
North A (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82:1013–1067
Chen CH, Zhou W, Liu S et al (2011) Increased NF-κB signalling up-regulates BACE1 expression and its therapeutic potential in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18:1–14
Kell DB (2010) Towards a unifying, systems biology understanding of large-scale cellular death and destruction caused by poorly liganded iron: parkinson’s, Huntington’s, Alzheimer’s, prions, bactericides, chemical toxicology and others as examples. Arch Toxicol 84:825–889
Maestre C, Delgado-Esteban M, Gomez-Sanchez JC et al (2008) Cdk5 phosphorylates Cdh1 and modulates cyclin B1 stability in excitotoxicity. EMBO J 27:2736–2745
Siegel RM (2006) Caspases at the crossroads of immune-cell life and death. Nat Rev Immunol 6:308–317
Shi Y (2004) Caspase activation: revisiting the induced proximity model. Cell 117:855–858
Shi Y (2002) Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell 9:459–470
Sun X, Wu B, Zhang Z et al (2011) Regulator of calcineurin 1 (RCAN1) facilitates neuronal apoptosis through caspase 3 activation. J Biol Chem 286:9049–9062
Eckert A, Marques CA, Keil U et al (2003) Increased apoptotic cell death in sporadic and genetic Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:604–609
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K et al (2006) Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311:847–851
Li C, Zhao R, Gao K et al (2010) Astrocytes: implications for neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 8:67–80
Kim JK, Kim SH, Cho HY et al (2010) GD3 accumulation in cell surface lipid rafts prior to mitochondrial targeting contributes to amyloid-β-induced apoptosis. J Korean Med Sci 25:1492–1498
Simon D, Medina M, Avila J et al (2011) Overcoming cell death and tau phosphorylation mediated by PI3KInhibition: a cell assay to measure neuroprotection. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10:208–214
Copani A, Melchiorri D, Caricasole A et al (2002) β-Amyloid induced synthesis of the ganglioside GD3 is a requisite for cell cycle reactivation and apoptosis in neurons. J Neurosci 22:3963–3968
Tillement L, Lecanu L, Papadopoulos V (2011) Further evidence on mitochondrial targeting of β-amyloid and specificity of β-amyloid-induced mitotoxicity in neurons. Neurodegener Dis 8:331–344
Gamba P, Leonarduzzi G, Tamagno E et al (2011) Interaction between 24-hydroxycholesterol, oxidative stress and amyloid-β in amplifying neuronal damage in Alzheimer’s disease: three partners in crime. Aging Cell 10:403–417
Ermak G, Morgan TE, Davies KJ (2001) Chronic overexpression of the calcineurin inhibitory gene DSCR1 (Adapt78) is associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 276:38787–38794
Ohtsuka T, Ryu H, Minamishima YA et al (2004) ASC is a Bax adaptor and regulates the p53-Bax mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Nat Cell Biol 6:121–128
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Ladenheim B et al (2005) Cadet, Calcineurin/NFAT-induced up-regulation of the Fas ligand/Fas death pathway is involved in methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:868–873
Viviani B, Bartesaghi S, Corsini E et al (2004) Cytokines role in neurodegenerative events. Toxicol Lett 149:85–89
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K, Scheurich P (2003) Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ 10:45–65
Figiel I, Dzwonek K (2007) TNF alpha and TNF receptor 1 expression in the mixed neuronal-glial cultures of hippocampal dentate gyrus exposed to glutamate or trimethyltin. Brain Res 1131:17–28
Lambertsen KL, Clausen BH, Fenger C et al (2007) Microglia and macrophages express tumor necrosis factor receptor p75 following middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Neuroscience 144:934–949
Ye L, Huang Y, Zhao L et al (2013) IL-1β and TNF-α induce neurotoxicity through glutamate production: a potential role for neuronal glutaminase. J Neurochem 125:897–908
DeChiara TM, Vejsada R, Poueymirou WT et al (1995) Mice lacking the CNTF receptor, unlike mice lacking CNTF, exhibit profound motor neuron deficits at birth. Cell 83:313–322
Bianco F, Pravettoni E, Colombo A et al (2005) Astrocyte derived ATP induces vesicle shedding and IL-1 release from microglia. J Immunol 174:7268–7277
Chang KA, Su YH (2010) Possible roles of amyloid intracellular domain of amyloid precursor protein. BMB rep 43:656–663
Nakaya T, Suzuki T (2006) Role of APP phosphorylation in FE65-dependent gene transactivation mediated by AICD. Genes Cells 11:633–645
Nakayama K, Ohkawara T, Hiratochi M et al (2008) The intracellular domain of amyloid precursor protein induces neuron-specific apoptosis. Neurosci Lett 444:127–131
Ozaki T, Li Y, Kiruchi H et al (2006) The intracellular domain of the amyloid precursor protein (AICD) enhances the p53-mediated apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:57–63
Xu Y, Kim HS, Joo Y et al (2007) Intracellular domains of amyloid precursor-like protein 2 interact with CP2 transcription factor in the nucleus and induce glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta expression. Cell Death Differ 14:79–91
Vazquez MC, Vargas LM, Inestrosa NC et al (2009) c-Abl modulates AICD dependent cellular responses: transcriptional induction and apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 220:136–143
Saraiva LM, da Silva GSS, Galina A et al (2010) Amyloid-β triggers the release of neuronal hexokinase 1 from mitochondria. PLoS One 5:e15230
Vander Heiden MG, Plas DR, Rathmell JC et al (2001) Growth factors can influence cell growth and survival through effects on glucose metabolism. Mol Cell Biol 21:5899–5912
YamamotoY Takase K, Kishino J et al (2011) Proteomic identification of protein targets for 15-Deoxy-D12,14-Prostaglandin J2 in neuronal plasma membrane. PLoS One 6:e17552
Tsai FM, Shyu RY, Lin SC et al (2009) Induction of apoptosis by the retinoid inducible growth regulator RIG1 depends on the NC motif in HtTA cervical cancer cells. BMC Cell Biol 10:15
Ueki S, Mahemuti G, Oyamada H et al (2008) Retinoic acids are potent inhibitors of spontaneous human eosinophil apoptosis. J Immunol 181:7689–7698
Farooqui AA, Antony P, Ong WY et al (2004) Retinoic acid-mediated phospholipase A2 signaling in the nucleus. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 45:179–195
Mattson MP (2004) Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 430:631–639
Moreira PI, Smith MA, Zhu X et al (2005) Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1043:545–552
Rao RV, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE (2004) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program. Cell Death Differ 11:372–380
Lindholm D, Wootz H, Korhonen L (2006) ER stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Death Differ 13:385–392
Verkhratsky A (2005) Physiology and pathophysiology of the calcium store in the endoplasmic reticulum of neurons. Physiol Rev 85:201–279
LaFerla F (2002) Calcium dyshomeostasis and intracellular signalling in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:862–872
Katayama T, Imaizumi K, Manabe T et al (2004) Tohyama, Induction of neuronal death by ER stress in Alzheimer’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 28:67–78
Hitomi J, Katayama T, Eguchi Y et al (2004) Involvement of caspase-4 in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and Abeta-induced cell death. J Cell Biol 165:347–356
Choi JH, Choi AY, Yoon H et al (2010) Baicalein protects HT22 murine hippocampal neuronal cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis through inhibition of reactive oxygen species production and CHOP induction. Exp Mol Med 42:811–822
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11:381–389
Shimoke K, Sasaya H, Ikeguchi T (2011) Analysis of the role of nerve growth factor in promoting cell survival during endoplasmic reticulum stress in PC12 cells. Methods Enzymol 490:53–70
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM et al (2006) Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep 7:880–885
Kim I, Xu W, Reed JC (2008) Cell death and endoplasmic reticulum stress: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:1013–1030
Parvathinani LK, Tertysnikova S, Greco CR et al (2003) P2X7 mediates superoxide production in primary microglia and is up-regulated in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem 278:13309–13317
Luciano F, Zhai D, Zhu X et al (2005) Cytoprotective peptide humanin binds and inhibits proapoptotic Bcl-2/Bax family protein BimEL. J Biol Chem 280:15825–15835
Kariya S, Hirano M, Nagai Y et al (2003) Humanin attenuates apoptosis induced by DRPLA proteins with expanded polyglutamine stretches. J Mol Neurosci 25:165–169
Sponne I, Fifre A, Koziel V et al (2004) Humanin rescues cortical neurons from prion-peptide induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Neurosci 25:95–102
Hashimoto Y, Niikura T, Chiba T et al (2003) The cytoplasmic domain of Alzheimer’s amyloid-β protein precursor causes sustained apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1/c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase-mediated neurotoxic signal via dimerization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:889–902
Hashimoto Y, Kurita M, Aiso S et al (2009) Humanin inhibits neuronal cell death by interacting with a cytokine receptor complex or complexes involving CNTF receptor α/WSX-1/gp130. Mol Biol Cell 20:2864–2873
Niikura T, Hashimoto Y, Tajima H et al (2003) A tripartite motif protein TRIM11 binds and destabilizes humanin, a neuroprotective peptide against Alzheimer’s disease relevant insults. Eur J Neurosci 17:1150–1158
Pislar AH, Kos J (2013) C-terminal peptide of γ-enolase impairs amyloid-β-induced apoptosis through p75NTR signaling. Neuromolecular Med 15:623–635
Kim IK, Lee KJ, Rhee S et al (2013) Protective effects of peroxiredoxin 6 overexpression on amyloid β-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Free Radic Res 47:836–846
Le Y, Gong W, Tiffany HL (2001) Amyloid β42 activates a G-protein-coupled chemoattractant receptor, FPR-like-1. J Neurosci 21:RC123
Ramirez C, Tercero I, Pineda A et al (2011) Simvastatin is the statin that most efficiently protects against kainate-induced excitotoxicity and memory impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 24:161–174
Li X, Darzynkiewicz Z (2000) Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase measured in situ in individual cells: relationship to DNA fragmentation and cell cycle position during apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 255:125–132
Song J, Park KA, Lee WT et al (2014) Apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1 (ASK1): potential as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Sci 15:2119–2129
Mishra M, Heese K et al (2010) P60TRP interferes with the GPCR/secretase pathway to mediate neuronal survival and synaptogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 15:2462–2477
Hoarau JJ, Krejbich-Trotot MC, Jaffar-Bandjee T et al (2010) Activation and control of CNS innate immune responses in health and diseases: a balancing act finely tuned by neuroimmune regulators (NIReg). CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10:25–43
Ha S, Furukawa R, Fechheimer M (2011) Association of AICD and Fe65 with Hirano bodies reduces transcriptional activation and initiation of apoptosis. Neurobiol Aging 32:2287–2298
Oules B, Del Prete D, Greco B et al (2012) Ryanodine receptor blockade reduces amyloid-β load and memory impairments in Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J Neurosci 32:11820–11834
Chang WH, Chen CH, Gau RJ et al (2002) Effect of baicalein on apoptosis of the human Hep G2 cell line was induced by mitochondrial dysfunction. Planta Med 8:302–306
Wang J, Yu Y, Hashimoto F et al (2004) Baicalein induces apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway in HL-60 cells. Int J Mol Med 14:627–632
Pidgeon GP, Kandouz M, Meram A et al (2002) Mechanisms controlling cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis after 12-lipoxygenase inhibition in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 62:2721–2727
Lin HY, Shen SC, Lin CW et al (2007) Baicalein inhibition of hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via ROS-dependent heme oxygenase 1 gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1073–1086
Li WW, Gao XM, Wang XM et al (2011) Icariin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity through inhibition of phosphorylation of JNK/p38 MAPK and p53 activity. Mutat Res 708:1–10
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng ZH et al (2011) Troxerutin protects against high cholesterol-induced cognitive deficits in mice. Brain 134:783–797
Anekonda TS (2006) Resveratrol—a boon for treating Alzheimer’s disease? Brain Res Rev 52:316–326
Lavu S, Boss O, Elliott PJ et al (2008) Sirtuins-novel therapeutic targets to treat age-associated diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:841–853
Julien C, Tremblay C, Emond V et al (2009) Sirtuin 1 reduction parallels the accumulation of tau in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:48–58
Anekonda TS, Wadsworth TL, Sabin R et al (2011) Phytic acid as a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s pathology: evidence from animal and in vitro models. J Alzheimers Dis 23:21–35
Qin W, Yang T, Ho L et al (2006) Neuronal SIRT1 activation as a novel mechanism underlying the prevention of Alzheimer disease amyloid neuropathology by calorie restriction. J Biol Chem 281:21745–21754
Azmi NH, Azmi N, Ismail MU et al (2013) Ethyl acetate extract of germinated brown rice attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: role of anti-apoptotic, pro-survival and antioxidant genes. BMC Complement Altern Med 13:177
Hong SY, Jeong WS, Jun M (2012) Protective effects of the key compounds isolated from Corni fructus against β-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in PC 12 cells. Molecules 17:10831–10845
Virmani A, Pinto L, Binienda Z et al (2013) Food, nutrigenomics, and neurodegeneration—neuroprotection by what you eat! Mol Neurobiol 48:353–362
Qin W, Zhao W, Ho L et al (2008) Regulation of forkhead transcription factor FoxO3a contributes to calorie restriction-induced prevention of Alzheimer’s disease-type amyloid neuropathology and spatial memory deterioration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1147:335–347
Zhou Y, Qu ZQ, Zeng YS et al (2011) Neuroprotective effect of preadministration with Ganoderma lucidum spore on rat hippocampus. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:673–680
Lee C, Park GH, Lee SR et al (2013) Attenuation of β-amyloid-induced oxidative cell death by sulforaphane via activation of NF-E2-related factor 2. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:313510
Chen X, Zhang J, Chen C (2011) Endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol protects neurons against β-amyloid insults. Neuroscience 178:159–168
Sakai K, Yamada M (2013) Aβ immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Nerve 65:461–468
Geng J, Li M, Wu L et al (2012) Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based H2O2 responsive controlled-release system used for Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Adv Healthc Mater 1:332–336
Sureda FX, Junyent F, Verdaguer E et al (2011) Antiapoptotic drugs: a therapeutic strategy for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Pharm Des 17:230–245
Cavallucci V, D’Amelio M (2011) Matter of life and death: the pharmacological approaches targeting apoptosis in brain diseases. Curr Pharm Des 17:215–229
Cui B, Li K (2013) Chronic noise exposure and Alzheimer disease: Is there an etiological association? Med Hypotheses 81:623–626
Zhang H, Wu S, Xing D (2011) YAP accelerates Aβ(25–35)-induced apoptosis through upregulation of Bax expression by interaction with p73. Apoptosis 16:808–821
Hong YK, Park SH, Lee S et al (2011) Neuroprotective effect of SuHeXiang Wan in Drosophila models of Alzheimer’s disease. J Ethnopharmacol 134:1028–1032
Obulesu M, Rao Dowlathabad Muralidhara (2011) Effect of plant extracts on Alzheimer’s disease: an insight into therapeutic avenues. J Neurosci Rural Pract 2:56–61
Obulesu M, Dowlathabad MR, Bramhachari PV (2011) Carotenoids and Alzheimer’s disease: an insight into therapeutic role of retinoids in animal models. Neurochem Int 59:535–541
Kim EA, Cho CH, Hahn HG (2014) 2-Cyclopropylimino-3-methyl-1,3-thiazoline hydrochloride protects against beta-amyloid-induced activation of the apoptotic cascade in cultured cortical neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34:963–972
Acknowledgments
Authors sincerely thank Professor Dr. Yukio Nagasaki, Department of Materials Science, Graduate School of Pure and Applied Sciences, University of Tsukuba, Tennodai 1-1-1, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan for this generous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obulesu, M., Lakshmi, M.J. Apoptosis in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Understanding of the Physiology, Pathology and Therapeutic Avenues. Neurochem Res 39, 2301–2312 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1454-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1454-4