Abstract
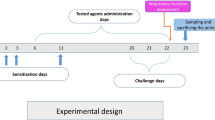
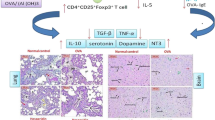
During chronic inflammatory disease, such asthma, leukocytes can invade the central nervous system (CNS) and together with CNS-resident cells, generate excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) production as well as disbalance in the antioxidant system, causing oxidative stress, which contributes a large part to neuroinflammation. In this sense, the aim of this study is to investigate the effects of treatment with neostigmine, known for the ability to control lung inflammation, on oxidative stress in the cerebral cortex of asthmatic mice. Female BALB/cJ mice were submitted to asthma model induced by ovalbumin (OVA). Control group received only Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline (DPBS). To evaluate neostigmine effects, mice received 80 μg/kg of neostigmine intraperitoneally 30 min after each OVA challenge. Our results revealed for the first time that treatment with neostigmine (an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that no crosses the BBB) was able to revert ROS production and change anti-oxidant enzyme catalase in the cerebral cortex in asthmatic mice. These results support the communication between the peripheral immune system and the CNS and suggest that acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, such as neostigmine, should be further studied as possible therapeutic strategies for neuroprotection in asthma.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi, H. (1984). [13] catalase in vitro Methods in enzymology (Vol. 105, pp. 121-126): Elsevier
Antunes GL, Silveira JS, Kaiber DB, Luft C, da Costa MS, Marques EP et al (2019) Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway confers airway protection against oxidative damage and attenuates inflammation in an allergic asthma model. J Cell Physiol
Biasibetti-Brendler H, Schmitz F, Pierozan P, Zanotto BS, Prezzi CA, de Andrade RB, Wyse AT (2018) Hypoxanthine induces neuroenergetic impairment and cell death in striatum of young adult Wistar rats. Mol Neurobiol 55(5):4098–4106
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR et al (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405(6785):458
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Chan KM, Delfert D, Junger KD (1986) A direct colorimetric assay for Ca2+−stimulated ATPase activity. Anal Biochem 157(2):375–380
Chou WH, Choi DS, Zhang H, Mu D, McMahon T, Kharazia VN et al (2004) Neutrophil protein kinase Cδ as a mediator of stroke-reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 114(1):49–56
Danielski LG, Della Giustina A, Badawy M, Barichello T, Quevedo J, Dal-Pizzol F, Petronilho F (2017) Brain barrier breakdown as a cause and consequence of neuroinflammation in sepsis. Mol Neurobiol:1–9
de Souza Wyse AT, Streck EL, Worm P, Wajner A, Ritter F, Netto CA (2000) Preconditioning prevents the inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity after brain ischemia. Neurochem Res 25(7):971–975
Deckers J, De Bosscher K, Lambrecht BN, Hammad H (2017) Interplay between barrier epithelial cells and dendritic cells in allergic sensitization through the lung and the skin. Immunol Rev 278(1):131–144
Duan J, Kang J, Qin W, Deng T, Liu H, Li B et al (2018) Exposure to formaldehyde and diisononyl phthalate exacerbate neuroinflammation through NF-κB activation in a mouse asthma model. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 163:356–364
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–95
Greenwald, R. A. (2018). Handbook Methods For Oxygen Radical Research: CRC press
Gwilt CR, Donnelly LE, Rogers DF (2007) The non-neuronal cholinergic system in the airways: an unappreciated regulatory role in pulmonary inflammation? Pharmacol Ther 115(2):208–222
Haider L, Fischer MT, Frischer JM, Bauer J, Höftberger R, Botond G et al (2011) Oxidative damage in multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain 134(7):1914–1924
Hofer S, Eisenbach C, Lukic IK, Schneider L, Bode K, Brueckmann M et al (2008) Pharmacologic cholinesterase inhibition improves survival in experimental sepsis. Crit Care Med 36(2):404–408
Hritcu L, Ciobica A (2013) Intranigral lipopolysaccharide administration induced behavioral deficits and oxidative stress damage in laboratory rats: relevance for Parkinson's disease. Behav Brain Res 253:25–31
Hunter M, Nlemadim B, Davidson D (1985) Lipid peroxidation products and antioxidant proteins in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid from multiple sclerosis patients. Neurochem Res 10(12):1645–1652
Jeremias IC, Scaini G, Constantino L, Vuolo F, Ferreira AK, Scherer EBS et al (2012) The decrease on Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the cortex, but not in hippocampus, is reverted by antioxidants in an animal model of sepsis. Mol Neurobiol 46(2):467–474
Kalb A, von Haefen C, Sifringer M, Tegethoff A, Paeschke N, Kostova M et al (2013) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors reduce neuroinflammation and-degeneration in the cortex and hippocampus of a surgery stress rat model. PLoS One 8(5):e62679
Kanashiro A, Talbot J, Peres RS, Pinto LG, Bassi GS, Cunha TM, Cunha FQ (2016) Neutrophil recruitment and articular hyperalgesia in antigen-induced arthritis are modulated by the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Basic & clinical pharmacology & toxicology 119(5):453–457
Kumar H, Lim HW, More SV, Kim BW, Koppula S, Kim IS, Choi DK (2012) The role of free radicals in the aging brain and Parkinson’s disease: convergence and parallelism. Int J Mol Sci 13(8):10478–10504
LeBel CP, Ischiropoulos H, Bondy SC (1992) Evaluation of the probe 2′, 7′-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress. Chem Res Toxicol 5(2):227–231
Lu F, Selak M, O’Connor J, Croul S, Lorenzana C, Butunoi C, Kalman B (2000) Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA and activity of mitochondrial enzymes in chronic active lesions of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 177(2):95–103
Machado FR, Ferreira AG, da Cunha AA, Tagliari B, Mussulini BHM, Wofchuk S, Wyse AT (2011) Homocysteine alters glutamate uptake and Na+, K+-ATPase activity and oxidative status in rats hippocampus: protection by vitamin C. Metab Brain Dis 26(1):61–67
Naeem A, Silveyra P (2019) Sex differences in Paediatric and adult asthma. EMJ 4(2):27–35
Netto MB, de Oliveira Junior AN, Goldim M, Mathias K, Fileti ME, da Rosa N et al (2018) Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly rats. Brain Behav Immun 73:661–669
Obermeier B, Daneman R, Ransohoff RM (2013) Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med 19(12):1584
Odorcyk F, Nicola F, Duran-Carabali L, Figueiró F, Kolling J, Vizuete A et al (2017) Galantamine administration reduces reactive astrogliosis and upregulates the anti-oxidant enzyme catalase in rats submitted to neonatal hypoxia ischemia. Int J Dev Neurosci 62:15–24
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S et al (2003) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 421(6921):384
Wendel, A. (1981). [44] glutathione peroxidase Methods in enzymology (Vol. 77, pp. 325-333): Elsevier
Wyse AT, Streck EL, Barros SV, Brusque AM, Zugno AI, Wajner M (2000) Methylmalonate administration decreases Na+, K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex of rats. Neuroreport 11(10):2331–2334
Xia MX, Ding X, Qi J, Gu J, Hu G, Sun XL (2014) Inhaled budesonide protects against chronic asthma-induced neuroinflammation in mouse brain. J Neuroimmunol 273(1–2):53–57
Yu SP (2003) Na+, K+-ATPase: the new face of an old player in pathogenesis and apoptotic/hybrid cell death. Biochem Pharmacol 66(8):1601–1609
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnologico (CNPq), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The experiments were conducted in accordance with the Brazilian Society of Laboratory Animal Science (SBCAL), using fewer animals and adequate management of pain and suffering, during the study procedures and euthanasia. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee for the Use of Animals of the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio Grande do Sul (CEUA, 7934).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antunes, G.L., Silveira, J.S., Kaiber, D.B. et al. Neostigmine treatment induces neuroprotection against oxidative stress in cerebral cortex of asthmatic mice. Metab Brain Dis 35, 765–774 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00558-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00558-7