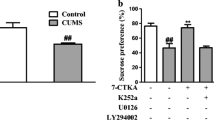
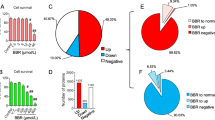
Abstract
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a serious mood disorder and leads to a high suicide rate as well as financial burden. The volume and function (the sensitivity and neurogenesis) of the olfactory bulb (OB) were reported to be altered among the MDD patients and rodent models of depression. In addition, the olfactory epithelium was newly reported to decrease its volume and function under chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) treatment. However, the underlying molecular mechanism still remains unclear. Herein, we conducted the non-targeted metabolomics method based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) coupled with multivariate statistical analysis to characterize the differential metabolites in OB of CUMS rats. Our results showed that 19 metabolites were categorized into two perturbed pathways: purine metabolism and lipid metabolism, which were regarded as the vital pathways concerned with dysfunction of OB. These findings indicated that the turbulence of metabolic pathways may be partly responsible for the dysfunction of OB in MDD.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agren H, Niklasson F, Hallgren R (1983) Brain purinergic activity linked with depressive symptomatology: hypoxanthine and xanthine in CSF of patients with major depressive disorders. Psychiatry Res 9:179–189
Burnstock G, Krugel U, Abbracchio MP, Illes P (2011) Purinergic signalling: from normal behaviour to pathological brain function. Prog Neurobiol 95:229–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.08.006
Cecil KM, DelBello MP, Morey R, Strakowski SM (2002) Frontal lobe differences in bipolar disorder as determined by proton MR spectroscopy. Bipolar Disord 4:357–365
Cetica PD, Pintos LN, Dalvit GC, Beconi MT (2001) Antioxidant enzyme activity and oxidative stress in bovine oocyte in vitro maturation. IUBMB Life 51:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/15216540119253
Chen JJ, Zhou CJ, Liu Z, Fu YY, Zheng P, Yang DY, Li Q, Mu J, Wei YD, Zhou JJ, Huang H, Xie P (2015) Divergent urinary metabolic phenotypes between major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder identified by a combined GC-MS and NMR spectroscopic Metabonomic approach. J Proteome Res 14:3382–3389. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00434
Chen JJ, Bai SJ, Li WW, Zhou CJ, Zheng P, Fang L, Wang HY, Liu YY, Xie P (2018) Urinary biomarker panel for diagnosing patients with depression and anxiety disorders. Transl Psychiatry 8:192. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0245-0
Cheng K, Li J, Yang D, Yang Y, Rao C, Zhang S, Wang W, Guo H, Fang L, Zhu D, Han Y, Xie P (2016) 2D-gel based proteomics unravels neurogenesis and energetic metabolism dysfunction of the olfactory bulb in CUMS rat model. Behav Brain Res 313:302–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.026
Cui Y, Yang Y, Ni Z, Dong Y, Cai G, Foncelle A, Ma S, Sang K, Tang S, Li Y, Shen Y, Berry H, Wu S, Hu H (2018) Astroglial Kir4.1 in the lateral habenula drives neuronal bursts in depression. Nature 554:323–327. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25752
Fekkes D, van der Cammen TJM, van Loon CPM, Verschoor C, van Harskamp F, de Koning I, Schudel WJ, Pepplinkhuizen L (1998) Abnormal amino acid metabolism in patients with early stage Alzheimer dementia. Journal of neural transmission (Vienna, Austria : 1996) 105:287–294
Fu XY, Lu YR, Wu JL, Wu XY, Bao AM (2012) Alterations of plasma aspartic acid, glycine and asparagine levels in patients with major depressive disorder. Zhejiang da xue xue bao Yi xue ban = Journal of Zhejiang University Medical sciences 41:132–138
Han X, Shao W, Liu Z, Fan S, Yu J, Chen J, Qiao R, Zhou J, Xie P (2015) iTRAQ-based quantitative analysis of hippocampal postsynaptic density-associated proteins in a rat chronic mild stress model of depression. Neuroscience 298:220–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.04.006
He Y, Li W, Tian Y, Chen X, Cheng K, Xu K, Li C, Wang H, Qu C, Wang C, Li P, Chen H, Xie P (2018) iTRAQ-based proteomics suggests LRP6, NPY and NPY2R perturbation in the hippocampus involved in CSDS may induce resilience and susceptibility. Life Sci 211:102–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.09.016
Heales SJ, Davies SE, Bates TE, Clark JB (1995) Depletion of brain glutathione is accompanied by impaired mitochondrial function and decreased N-acetyl aspartate concentration. Neurochem Res 20:31–38
Herken H, Gurel A, Selek S, Armutcu F, Ozen ME, Bulut M, Kap O, Yumru M, Savas HA, Akyol O (2007) Adenosine deaminase, nitric oxide, superoxide dismutase, and xanthine oxidase in patients with major depression: impact of antidepressant treatment. Arch Med Res 38:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2006.10.005
Huang C, Yang X, Zeng B, Zeng L, Gong X, Zhou C, Xia J, Lian B, Qin Y, Yang L, Liu L, Xie P (2019) Proteomic analysis of olfactory bulb suggests CACNA1E as a promoter of CREB signaling in microbiota-induced depression. J Proteome 194:132–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2018.11.023
Kaddurah-Daouk R, Yuan P, Boyle SH, Matson W, Wang Z, Zeng ZB, Zhu H, Dougherty GG, Yao JK, Chen G, Guitart X, Carlson PJ, Neumeister A, Zarate C, Krishnan RR, Manji HK, Drevets W (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid metabolome in mood disorders-remission state has a unique metabolic profile. Sci Rep 2:667. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00667
Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE (2005) Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:593–602. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.593
Levant B, Ozias MK, Davis PF, Winter M, Russell KL, Carlson SE, Reed GA, McCarson K (2008) Decreased brain docosahexaenoic acid content produces neurobiological effects associated with depression: interactions with reproductive status in female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 33:1279–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2008.06.012
Li J, Tang G, Cheng K, Yang D, Chen G, Liu Z, Zhang R, Zhou J, Fang L, Fang Z, du X, Xie P (2014) Peripheral blood mononuclear cell-based metabolomic profiling of a chronic unpredictable mild stress rat model of depression. Mol BioSyst 10:2994–3001. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4mb00388h
Li Q, Yang D, Wang J, Liu L, Feng G, Li J, Liao J, Wei Y, Li Z (2015) Reduced amount of olfactory receptor neurons in the rat model of depression. Neurosci Lett 603:48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.07.007
Li J, Zhang SX, Wang W, Cheng K, Guo H, Rao CL, Yang DY, He Y, Zou DZ, Han Y, Zhao LB, Li PF, Xie P (2017) Potential antidepressant and resilience mechanism revealed by metabolomic study on peripheral blood mononuclear cells of stress resilient rats. Behav Brain Res 320:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.11.035
Liu L, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Yang L, Pu J, Zhu D, Zhou C, Xie P (2016) The identification of metabolic disturbances in the prefrontal cortex of the chronic restraint stress rat model of depression. Behav Brain Res 305:148–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.03.005
Liu L, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Pu J, Yang L, Yuan S, Zhao L, Zhou C, Zhang H, Xie P (2018) Hippocampal metabolic differences implicate distinctions between physical and psychological stress in four rat models of depression. Transl Psychiatry 8:4. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-017-0018-1
Mu J, Xie P, Yang ZS, Yang DL, Lv FJ, Luo TY, Li Y (2007) Neurogenesis and major depression: implications from proteomic analyses of hippocampal proteins in a rat depression model. Neurosci Lett 416:252–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2007.01.067
Mueller A, Abolmaali ND, Hakimi AR, Gloeckler T, Herting B, Reichmann H, Hummel T (2005) Olfactory bulb volumes in patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease a pilot study. J Neural Transm 112:1363–1370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-005-0280-x
Negoias S, Croy I, Gerber J, Puschmann S, Petrowski K, Joraschky P, Hummel T (2010) Reduced olfactory bulb volume and olfactory sensitivity in patients with acute major depression. Neuroscience 169:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.05.012
Niklasson F, Agren H, Hallgren R (1983) Purine and monoamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid: parallel purinergic and monoaminergic activation in depressive illness? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:255–260
Page T, Coleman M (2000) Purine metabolism abnormalities in a hyperuricosuric subclass of autism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1500:291–296
Patkar AA, Rozen S, Mannelli P, Matson W, Pae CU, Krishnan KR, Kaddurah-Daouk R (2009) Alterations in tryptophan and purine metabolism in cocaine addiction: a metabolomic study. Psychopharmacology 206:479–489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1625-1
Pears MR, Cooper JD, Mitchison HM, Mortishire-Smith RJ, Pearce DA, Griffin JL (2005) High resolution 1H NMR-based metabolomics indicates a neurotransmitter cycling deficit in cerebral tissue from a mouse model of batten disease. J Biol Chem 280:42508–42514. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507380200
Perez MA, Terreros G, Dagnino-Subiabre A (2013) Long-term omega-3 fatty acid supplementation induces anti-stress effects and improves learning in rats. Behav Brain Funct 9:25–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-9081-9-25
Rezin GT, Amboni G, Zugno AI, Quevedo J, Streck EL (2009) Mitochondrial dysfunction and psychiatric disorders. Neurochem Res 34:1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-008-9865-8
Rottstadt F et al (2018) Reduced olfactory bulb volume in depression-a structural moderator analysis. Hum Brain Mapp 39:2573–2582. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.24024
Rottstaedt F, Weidner K, Strauß T, Schellong J, Kitzler H, Wolff-Stephan S, Hummel T, Croy I (2018) Size matters - the olfactory bulb as a marker for depression. J Affect Disord 229:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.12.047
Shao W-H, Fan SH, Lei Y, Yao GE, Chen JJ, Zhou J, Xu HB, Liu HP, Wu B, Zheng P, Fang L, Xie P (2013) Metabolomic identification of molecular changes associated with stress resilience in the chronic mild stress rat model of depression. Metabolomics 9:433–443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0460-2
Song C, Killeen AA, Leonard BE (1994) Catalase, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activity in neutrophils of sham-operated and olfactory-bulbectomised rats following chronic treatment with desipramine and lithium chloride. Neuropsychobiology 30:24–28
Sun JD, Liu Y, Yuan YH, Li J, Chen NH (2012) Gap junction dysfunction in the prefrontal cortex induces depressive-like behaviors in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1305–1320. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2011.319
Venna VR, Deplanque D, Allet C, Belarbi K, Hamdane M, Bordet R (2009) PUFA induce antidepressant-like effects in parallel to structural and molecular changes in the hippocampus. Psychoneuroendocrinology 34:199–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2008.08.025
Wang W, Guo H, Zhang SX, Li J, Cheng K, Bai SJ, Yang DY, Wang HY, Liang ZH, Liao L, Sun L, Xie P (2016) Targeted Metabolomic pathway analysis and validation revealed Glutamatergic disorder in the prefrontal cortex among the chronic social defeat stress mice model of depression. J Proteome Res 15:3784–3792. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00577
Wu Y, Tang J, Zhou C, Zhao L, Chen J, Zeng L, Rao C, Shi H, Liao L, Liang Z, Yang Y, Zhou J, Xie P (2016) Quantitative proteomics analysis of the liver reveals immune regulation and lipid metabolism dysregulation in a mouse model of depression. Behav Brain Res 311:330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.057
Xu HB, Zhang RF, Luo D, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Fang L, Li WJ, Mu J, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Xie P (2012) Comparative proteomic analysis of plasma from major depressive patients: identification of proteins associated with lipid metabolism and immunoregulation. The international journal of neuropsychopharmacology / official scientific journal of the Collegium Internationale Neuropsychopharmacologicum (CINP) 15:1413–1425. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1461145712000302
Yang D, Li Q, Fang L, Cheng K, Zhang R, Zheng P, Zhan Q, Qi Z, Zhong S, Xie P (2011a) Reduced neurogenesis and pre-synaptic dysfunction in the olfactory bulb of a rat model of depression. Neuroscience 192:609–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.06.043
Yang D, Liu X, Zhang R, Cheng K, Mu J, Fang L, Xie P (2011b) Increased apoptosis and different regulation of pro-apoptosis protein bax and anti-apoptosis protein bcl-2 in the olfactory bulb of a rat model of depression. Neurosci Lett 504:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.08.046
Yang Y, Yang D, Tang G, Zhou C, Cheng K, Zhou J, Wu B, Peng Y, Liu C, Zhan Y, Chen J, Chen G, Xie P (2013) Proteomics reveals energy and glutathione metabolic dysregulation in the prefrontal cortex of a rat model of depression. Neuroscience 247:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.031
Zheng P, Gao HC, Qi ZG, Jia JM, Li FF, Chen JJ, Wang Y, Guo J, Melgiri ND, Xie P (2012a) Peripheral metabolic abnormalities of lipids and amino acids implicated in increased risk of suicidal behavior in major depressive disorder. Metabolomics 9:688–696. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0474-9
Zheng P, Gao HC, Li Q, Shao WH, Zhang ML, Cheng K, Yang DY, Fan SH, Chen L, Fang L, Xie P (2012b) Plasma metabonomics as a novel diagnostic approach for major depressive disorder. J Proteome Res 11:1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr2010082
Zheng P, Wang Y, Chen L, Yang D, Meng H, Zhou D, Zhong J, Lei Y, Melgiri ND, Xie P (2013) Identification and validation of urinary metabolite biomarkers for major depressive disorder. Mol Cell Proteomics 12:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M112.021816
Zheng P, Chen JJ, Zhou CJ, Zeng L, Li KW, Sun L, Liu ML, Zhu D, Liang ZH, Xie P (2016) Identification of sex-specific urinary biomarkers for major depressive disorder by combined application of NMR- and GC-MS-based metabonomics. Transl Psychiatry 6:e955. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.188
Zhou X, Liu L, Lan X, Cohen D, Zhang Y, Ravindran AV, Yuan S, Zheng P, Coghill D, Yang L, Hetrick SE, Jiang X, Benoliel JJ, Cipriani A, Xie P (2018) Polyunsaturated fatty acids metabolism, purine metabolism and inosine as potential independent diagnostic biomarkers for major depressive disorder in children and adolescents. Mol Psychiatry 24:1478–1488. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0047-z
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFA0505700), the Non-profit Central Research Institute Fund of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (2019PT320002) and the National Key Program International Cooperation Project (No. 81820108015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have declared no conflict of interest in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Y., Wang, Y., Wu, Z. et al. Metabolomic abnormalities of purine and lipids implicated olfactory bulb dysfunction of CUMS depressive rats. Metab Brain Dis 35, 649–659 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00557-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00557-8