Abstract
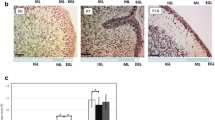
Diabetes during pregnancy is associated with the deficits in balance and motor coordination and altered social behaviors in offspring. In the present study, we have investigated the effect of maternal diabetes and insulin treatment on the cerebellar volume and morphogenesis of the cerebellar cortex of rat neonates during the first two postnatal weeks. Sprague Dawley female rats were maintained diabetic from a week before pregnancy through parturition. At the end of pregnancy, the male offspring euthanized on postnatal days (P) 0, 7, and 14. Cavalieri’s principle and fractionator methods were used to estimate the cerebellar volume, the thickness and the number of cells in the different layers of the cerebellar cortex. In spite of P0, there was a significant reduction in the cerebellar volume and the thickness of the external granule, molecular, and internal granule layers between the diabetic and the control animals. In diabetic group, the granular and purkinje cell densities were increased at P0. Moreover, the number of granular and purkinje cells in the cerebellum of diabetic neonates was reduced in comparison with the control group at P7 and P14. There were no significant differences in either the volume and thickness or the number of cells in the different layers of the cerebellar cortex between the insulin-treated diabetic group and controls. Our data indicate that diabetes in pregnancy disrupts the morphogenesis of cerebellar cortex. This dysmorphogenesis may be part of the cascade of events through which diabetes during pregnancy affects motor coordination and social behaviors in offspring.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abusaad I, MacKay D, Zhao J, Stanford P, Collier DA, Everall IP (1999) Stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the murine hippocampus using the optical disector. J Comp Neurol 408:560–566
Altman J, Bayer SA (1996) Development of the cerebellar system: In relation to its evolution, structure, and functions. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Alves-Wagner AB et al. (2015) Beta-adrenergic blockade increases GLUT4 and improves glycemic control in insulin-treated diabetic wistar rats. Auton neurosci: basic clin 193:108–116. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2015.10.003
Anderson KM, Seed T, Ou D, Harris JE (1999) Free radicals and reactive oxygen species in programmed cell death. Med Hypotheses 52:451–463. doi:10.1054/mehy.1997.0521
Anlar B, Sullivan KA, Feldman EL (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-I and central nervous system development. Hormone and metabolic research = Hormon- und Stoffwechselforschung = Hormones et metabolisme 31:120–125. doi:10.1055/s-2007-978708
Babiker OO (2007) Long-term effects of maternal diabetes on their offspring development and behaviours. Sudanese J Ped 8:133–146
Bahey NG, Soliman GM, El-Deeb TA, El-Drieny EA (2014) Influence of insulin and testosterone on diabetic rat ventral prostate: histological, morphometric and immunohistochemical study. J Microsc Ultrastruct 2:151
Baron-Van Evercooren A, Olichon-Berthe C, Kowalski A, Visciano G, Van Obberghen E (1991) Expression of IGF-I and insulin receptor genes in the rat central nervous system: a developmental, regional, and cellular analysis. J Neurosci Res 28:244–253
Bartlett WP, Li XS, Williams M, Benkovic S (1991) Localization of insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA in murine central nervous system during postnatal development. Dev Biol 147:239–250
Beaton A, Marien P (2010) Language, cognition and the cerebellum: grappling with an enigma. Cortex; a J Devoted Study Nerv Syst Behav 46:811–820. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2010.02.005
Benagiano V et al. (2007) Effects of prenatal exposure to the CB-1 receptor agonist WIN 55212-2 or CO on the GABAergic neuronal systems of rat cerebellar cortex. Neuroscience 149:592–601. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.07.050
Biran V, Verney C, Ferriero DM (2012) Perinatal cerebellar injury in human and animal models. Neurol Res Int 2012:858929. doi:10.1155/2012/858929
Bugalho P, Correa B, Viana-Baptista M (2006) [Role of the cerebellum in cognitive and behavioural control: scientific basis and investigation models] Acta medica portuguesa 19:257–267
Camprubi Robles M, Campoy C, Garcia Fernandez L, Lopez-Pedrosa JM, Rueda R, Martin MJ (2015) Maternal diabetes and cognitive performance in the offspring: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 10:e0142583. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0142583
Cardell BS (1953) Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the pancreatic islets in new-born infants. J Pathol Bacteriol 66:335–346
Castellucci M, Kaufmann P (1995) Basic structure of the villous trees. In: Benirschke K, Kaufmann P (eds) Pathology of the human placenta, 3 edn. Springer, New York, pp. 57–115
Cederberg J, Picard JJ, Eriksson UJ (2003) Maternal diabetes in the rat impairs the formation of neural-crest derived cranial nerve ganglia in the offspring. Diabetologia 46:1245–1251. doi:10.1007/s00125-003-1100-1
Chandna AR, Kuhlmann N, Bryce CA, Greba Q, Campanucci VA, Howland JG (2015) Chronic maternal hyperglycemia induced during mid-pregnancy in rats increases RAGE expression, augments hippocampal excitability, and alters behavior of the offspring. Neuroscience 303:241–260. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.063
Chang TI, Horal M, Jain SK, Wang F, Patel R, Loeken MR (2003) Oxidant regulation of gene expression and neural tube development: insights gained from diabetic pregnancy on molecular causes of neural tube defects. Diabetologia 46:538–545. doi:10.1007/s00125-003-1063-2
Clancy B, Finlay BL, Darlington RB, Anand KJ (2007) Extrapolating brain development from experimental species to humans. Neurotoxicology 28:931–937. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2007.01.014
Clutton S (1997) The importance of oxidative stress in apoptosis. Br Med Bull 53:662–668
Comblath M, Schwartz R (1976) Disorders of carbohydrates metabolism in infancy, 2nd edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
D’Angelo E, Casali S (2012) Seeking a unified framework for cerebellar function and dysfunction: from circuit operations to cognition. Front neural circ 6:116. doi:10.3389/fncir.2012.00116
D Agostino AN, Bahn RC (1963) A histopathologic study of the pancreas of infants of diabetic mothers. Diabetes 12:327–331
de Pablo F, de la Rosa EJ (1995) The developing CNS: a scenario for the action of proinsulin, insulin and insulin-like growth factors. Trends Neurosci 18:143–150
Dobbing J, Sands J (1979) Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum Dev 3:79–83
Dowling D, Corrigan N, Horgan S, Watson CJ, Baugh J, Downey P, McAuliffe FM (2014) Cardiomyopathy in offspring of pregestational diabetic mouse pregnancy. J Diabetes Res 2014:624939. doi:10.1155/2014/624939
Eidelman AI, Samueloff A (2002) The pathophysiology of the fetus of the diabetic mother. Semin Perinatol 26:232–236
Engelkamp D, Rashbass P, Seawright A, van Heyningen V (1999) Role of Pax6 in development of the cerebellar system. Development 126:3585–3596
Eriksson RS, Thunberg L, Eriksson UJ (1989a) Effects of interrupted insulin treatment on fetal outcome of pregnant diabetic rats. Diabetes 38:764–772
Eriksson U, Dahlstrom E, Larsson KS, Hellerstrom C (1982) Increased incidence of congenital malformations in the offspring of diabetic rats and their prevention by maternal insulin therapy. Diabetes 31:1–6
Eriksson UJ, Bone AJ, Turnbull DM, Baird JD (1989b) Timed interruption of insulin therapy in diabetic BB/E rat pregnancy: effect on maternal metabolism and fetal outcome. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 120:800–810
Eriksson UJ, Borg LA (1991) Protection by free oxygen radical scavenging enzymes against glucose-induced embryonic malformations in vitro. Diabetologia 34:325–331
Eriksson UJ, Borg LA (1993) Diabetes and embryonic malformations. Role of substrate-induced free-oxygen radical production for dysmorphogenesis in cultured rat embryos Diabetes 42:411–419
Eriksson UJ, Siman CM (1996) Pregnant diabetic rats fed the antioxidant butylated hydroxytoluene show decreased occurrence of malformations in offspring. Diabetes 45:1497–1502
Fonnum F, Lock EA (2000) Cerebellum as a target for toxic substances. Toxicol Lett 112-113:9–16
Freitas HS, Schaan BD, Seraphim PM, Nunes MT, Machado UF (2005) Acute and short-term insulin-induced molecular adaptations of GLUT2 gene expression in the renal cortex of diabetic rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol 237:49–57. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.03.005
Gardella D, Hatton WJ, Rind HB, Rosen GD, von Bartheld CS (2003) Differential tissue shrinkage and compression in the z-axis: implications for optical disector counting in vibratome-, plastic- and cryosections. J Neurosci Methods 124:45–59
Geuna S, Herrera-Rincon C (2015) Update on stereology for light microscopy. Cell Tissue Res 360:5–12. doi:10.1007/s00441-015-2143-6
Golalipour MJ, Kafshgiri SK, Ghafari S (2012) Gestational diabetes induced neuronal loss in CA1 and CA3 subfields of rat hippocampus in early postnatal life. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 71:71–77
Gonzalez-Burgos I, Alejandre-Gomez M (2005) Cerebellar granule cell and Bergmann glial cell maturation in the rat is disrupted by pre- and post-natal exposure to moderate levels of ethanol. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience: the Official Journal of the International Society For Developmental Neuroscience 23:383–388. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.11.002
Gressens P (2006) Pathogenesis of migration disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 19:135–140. doi:10.1097/01.wco.0000218228.73678.e1
Guillery RW (2002) On counting and counting errors. J Comp Neurol 447:1–7. doi:10.1002/cne.10221
Gundersen HJ (1986) Stereology of arbitrary particles. A review of unbiased number and size estimators and the presentation of some new ones, in memory of William R. Thompson. J Microsc 143:3–45
Gundersen HJ et al. (1988a) The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS 96:857–881
Gundersen HJ et al. (1988b) Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS 96:379–394
Hagay ZJ, Weiss Y, Zusman I, Peled-Kamar M, Reece EA, Eriksson UJ, Groner Y (1995) Prevention of diabetes-associated embryopathy by overexpression of the free radical scavenger copper zinc superoxide dismutase in transgenic mouse embryos. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173:1036–1041
Haghir H, Rezaee AA, Sankian M, Kheradmand H, Hami J (2013) The effects of induced type-I diabetes on developmental regulation of insulin & insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptors in the cerebellum of rat neonates. Metab Brain Dis 28:397–410. doi:10.1007/s11011-013-9386-2
Hami J, Karimi R, Haghir H, Gholamin M, Sadr-Nabavi A (2015a) Diabetes in pregnancy adversely affects the expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in the hippocampus of rat neonates. J Mol Neurosci 57:273–281. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0617-3
Hami J, Kerachian MA, Karimi R, Haghir H, Sadr-Nabavi A (2015b) Effects of streptozotocin-induced type 1 maternal diabetes on PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the hippocampus of rat neonates. J Recept Signal Transduct Res: 1–7. doi:10.3109/10799893.2015.1086884
Hami J, Sadr-Nabavi A, Sankian M, Balali-Mood M, Haghir H (2013) The effects of maternal diabetes on expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptors in male developing rat hippocampus. Brain Struct Funct 218:73–84. doi:10.1007/s00429-011-0377-y
Hami J, Shojae F, Vafaee-Nezhad S, Lotfi N, Kheradmand H, Haghir H (2015c) Some of the experimental and clinical aspects of the effects of the maternal diabetes on developing hippocampus. World journal of diabetes 6:412–422. doi:10.4239/wjd.v6.i3.412
Hami J, Vafaei-Nezhad S, Haghir D, Haghir H (2015d) Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor Is differentially distributed in developing cerebellar cortex of rats born to diabetic mothers. J Mol Neurosci. doi:10.1007/s12031-015-0661-z
Hawkins CL, Davies MJ (2001) Generation and propagation of radical reactions on proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504:196–219
Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Rincon J, Pedreanez A, Viera N, Arcaya JL, Carrizo E, Mosquera J (2009) Structural and ultrastructural analysis of cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and hypothalamus from diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res 2009:329632. doi:10.1155/2009/329632
Howard CV, Reed MG (1998) Unbiased stereology: three-dimensional measurement in microscopy. Bios Scientific Publisher, Oxford
Jackson-Guilford J, Leander JD, Nisenbaum LK (2000) The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on cell proliferation in the rat dentate gyrus. Neurosci Lett 293:91–94
Jawerbaum A, White V (2010) Animal models in diabetes and pregnancy. Endocr Rev 31:680–701. doi:10.1210/er.2009-0038
Junod A, Lambert AE, Stauffacher W, Renold AE (1969) Diabetogenic action of streptozotocin: relationship of dose to metabolic response. J Clin Invest 48:2129–2139. doi:10.1172/JCI106180
Kafshgiri SK, Ghafari S, Golalipour MJ (2014) Gestational diabetes induces neuronal loss in dentate gyrus in rat offspring. J Neurol Sci [Turkish] 31:316–324
Kamal A, Biessels GJ, Urban IJ, Gispen WH (1999) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: impairment of long-term potentiation and facilitation of long-term depression. Neuroscience 90:737–745
Khaksar Z, Jelodar GA, Hematian H (2011) Morphometric study of cerebrum in fetuses of diabetic mothers. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Research 12:199–204
Lapolla A, Dalfra MG, Fedele D (2005) Insulin therapy in pregnancy complicated by diabetes: are insulin analogs a new tool? Diabetes Metab Res Rev 21:241–252. doi:10.1002/dmrr.551
Lin X, Bulleit RF (1997) Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is a critical trophic factor for developing cerebellar granule cells. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 99:234–242
Lopes CD, Sinigaglia-Coimbra R, Mazzola J, Camano L, Mattar R (2011) Neurofunctional evaluation of young Male offspring of rat dams with diabetes induced by streptozotocin. ISRN Endocrinology. doi:10.5402/2011/480656
Malomo AO, Imosemi IO, Osuagwu FC, Oladejo OW, Akang EE, Shokunbi MT (2004) Histomorphometric studies on the effect of cyanide consumption of the developing cerebellum of wistar rat (rattus novergicus). West Afr J Med 23:323–328
Manto M et al. (2012) Consensus paper: roles of the cerebellum in motor control–the diversity of ideas on cerebellar involvement in movement. Cerebellum 11:457–487. doi:10.1007/s12311-011-0331-9
Moazzen H, Lu X, Liu M, Feng Q (2015) Pregestational diabetes induces fetal coronary artery malformation via reactive oxygen species signaling. Diabetes 64:1431–1443. doi:10.2337/db14-0190
Mouton PR (2002) Principles and practices of unbiased stereology: an introduction for bioscientists. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Mwangi DK (2001) Cerebellar parameters in developing 15 day old rat pups treated with propylthiouracil in comparison with 5 and 24 day old. East Afr Med J 78:322–326
Nelson CA, Wewerka S, Thomas KM, Tribby-Walbridge S, deRegnier R, Georgieff M (2000) Neurocognitive sequelae of infants of diabetic mothers. Behav Neurosci 114:950–956
Odaci E et al. (2004) Effects of low-dose oxcarbazepine administration on developing cerebellum in newborn rat: A stereological study. Neurosci Res Commun 34:28–36
Ornoy A (2005) Growth and neurodevelopmental outcome of children born to mothers with pregestational and gestational diabetes. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 3:104–113
Ornoy A, Ratzon N, Greenbaum C, Peretz E, Soriano D, Dulitzky M (1998) Neurobehaviour of school age children born to diabetic mothers. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 79:F94–F99
Ornoy A, Ratzon N, Greenbaum C, Wolf A, Dulitzky M (2001) School-age children born to diabetic mothers and to mothers with gestational diabetes exhibit a high rate of inattention and fine and gross motor impairment. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 14(Suppl 1):681–689
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Persaud OD (2007) Maternal diabetes and the consequences for her offspring. J Develop Disab 1:101–134
Petersen MB, Pedersen SA, Greisen G, Pedersen JF, Mølsted-Pedersen L (1988) Early growth delay in diabetic pregnancy: relation to psychomotor development at age 4. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296:598–600
Pettitt DJ, Bennett PH (1995) Long-term outcome of infant of diabetic mothers. In: Reece AE, Coustan DR (eds) Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy, 2 edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp. 379–388
Popken GJ, Hodge RD, Ye P, Zhang J, Ng W, O’Kusky JR, D’Ercole AJ (2004) In vivo effects of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on prenatal and early postnatal development of the central nervous system. The European J Neuroscience 19:2056–2068. doi:10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03320.x
Ratzon N, Greenbaum C, Dulitzky M, Ornoy A (2000) Comparison of the motor development of school-age children born to mothers with and without diabetes mellitus. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr 20:43–57
Rizzo T, Metzger BE, Burns WJ (1991) Burns K. Correlations between antepartum maternal metabolism and child intelligence N Engl J Med 325:911–916. doi:10.1056/NEJM199109263251303
Rizzo TA, Dooley SL, Metzger BE, Cho NH, Ogata ES, Silverman BL (1995) Prenatal and perinatal influences on long-term psychomotor development in offspring of diabetic mothers. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173:1753–1758
Rudow G et al. (2008) Morphometry of the human substantia nigra in ageing and Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 115:461–470. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0352-8
Ryder EF, Cepko CL (1994) Migration patterns of clonally related granule cells and their progenitors in the developing chick cerebellum. Neuron 12:1011–1028
Schwartz R, Teramo KA (2000) Effects of diabetic pregnancy on the fetus and newborn. Semin Perinatol 24:120–135
Shin BC, Fujikura K, Suzuki T, Tanaka S, Takata K (1997) Glucose transporter GLUT3 in the rat placental barrier: a possible machinery for the transplacental transfer of glucose. Endocrinology 138:3997–4004
Siman CM, Eriksson UJ (1997a) Vitamin C supplementation of the maternal diet reduces the rate of malformation in the offspring of diabetic rats. Diabetologia 40:1416–1424. doi:10.1007/s001250050844
Siman CM, Eriksson UJ (1997b) Vitamin E decreases the occurrence of malformations in the offspring of diabetic rats. Diabetes 46:1054–1061
Singh BS, Westfall TC, Devaskar SU (1997) Maternal diabetes-induced hyperglycemia and acute intracerebral hyperinsulinism suppress fetal brain neuropeptide Y concentrations. Endocrinology 138:963–969
Sivan E, Reece EA, Wu YK, Homko CJ, Polansky M, Borenstein M (1996) Dietary vitamin E prophylaxis and diabetic embryopathy: morphologic and biochemical analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:793–799
Som S et al. (1981) Ascorbic acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 30:572–577
Sterio DC (1984) The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the disector. J Microsc 134:127–136
Styrud J, Thunberg L, Nybacka O, Eriksson UJ (1995) Correlations between maternal metabolism and deranged development in the offspring of normal and diabetic rats. Pediatr Res 37:343–353
Takata K, Fujikura K, Shin BC (1997) Ultrastructure of the rodent placental labyrinth: a site of barrier and transport. J Reprod Develop 43:13–24
Tapias V, Greenamyre JT, Watkins SC (2013) Automated imaging system for fast quantitation of neurons, cell morphology and neurite morphometry in vivo and in vitro. Neurobiol Dis 54:158–168. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2012.11.018
Tehranipour M, Khakzad MR (2008) Effect of maternal diabetes on hippocampus neuronal density in neonatal rats. J Biol Sci 8:1027–1032
Torres-Aleman I, Pons S, Arevalo MA (1994) The insulin-like growth factor I system in the rat cerebellum: developmental regulation and role in neuronal survival and differentiation. J Neurosci Res 39:117–126. doi:10.1002/jnr.490390202
Van Lieshout RJ, Voruganti LP (2008) Diabetes mellitus during pregnancy and increased risk of schizophrenia in offspring: a review of the evidence and putative mechanisms. J psychiatry neuroscience: JPN 33:395–404
Viana M, Herrera E, Bonet B (1996) Teratogenic effects of diabetes mellitus in the rat. Prevention with Vitamin E Diabetologia 39:1041–1046
von Bartheld C (2002) Counting particles in tissue sections: choices of methods and importance of calibration to minimize biases. Histol Histopathol 17:639–648
von Bartheld CS (2012) Distribution of particles in the Z-axis of tissue sections: relevance for counting methods. NeuroQuantology: An Interdisciplinary J Neurosci Quantum Physics 10:66–75
Wentzel P, Thunberg L, Eriksson UJ (1997) Teratogenic effect of diabetic serum is prevented by supplementation of superoxide dismutase and N-acetylcysteine in rat embryo culture. Diabetologia 40:7–14. doi:10.1007/s001250050636
Xiang AH et al. (2015) Association of maternal diabetes with autism in offspring. JAMA 313:1425–1434. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.2707
Yamano T, Shimada M, Yoshiki F, Kawasaki H, Onaga A (1986) Quantitative synaptic changes on purkinjie cell dendritic spines of rats born from streptozotocin-induced diabetic mothers. Brain Dev 8:269–273
Yong Y et al. (2015) PACT/RAX regulates the migration of cerebellar granule neurons in the developing cerebellum. Sci Report 5:7961. doi:10.1038/srep07961
Zhou J, Wang L, Ling S, Zhang X (2007) Expression changes of growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and in hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic cognitive impairment rats. Exp Neurol 206:201–208. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2007.04.013
Zhu Y, Yu T, Rao Y (2004) Temporal regulation of cerebellar EGL migration through a switch in cellular responsiveness to the meninges. Dev Biol 267:153–164. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.10.037
Acknowledgments
We thank the vice chancellor of Research of Birjand University of Medical Sciences for financial support of this research (Grant number:1288).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no financial or nonfinancial conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hami, J., Vafaei-nezhad, S., Ghaemi, K. et al. Stereological study of the effects of maternal diabetes on cerebellar cortex development in rat. Metab Brain Dis 31, 643–652 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9802-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9802-5