Abstract
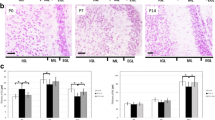
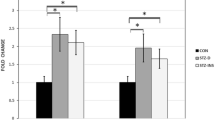
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) has an important role in development of the central nervous system (CNS). Maternal diabetes is associated with a higher risk of developmental abnormalities in their offspring including motor dysfunction and learning deficits. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of maternal diabetes on the distribution pattern of IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in the developing rat cerebellar cortex. Wistar female rats were maintained diabetic from a week before pregnancy through parturition, and male offspring was killed at P0, P7, and P14. In spite of P0, there was a significant increase in the total cerebellar volume in the pups born to diabetic mothers. In diabetic group, the IGF-1R+ granular cell densities in internal granular (IGL) and molecular (ML) layers were increased at P0. Moreover, the number of positive granular and Purkinje cells in the IGL of diabetic neonates’ cerebellum was reduced in comparison with the control group at P7 and P14. There were no differences either in volume or in the number of IGF-1R+ cells in the layers of the cerebellar cortex between the insulin-treated diabetic group and controls. Our data indicate that diabetes in pregnancy strikingly influence the localization of IGF-1R in the developing cerebellar cortex.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abusaad I, MacKay D, Zhao J, Stanford P, Collier DA, Everall IP (1999) Stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the murine hippocampus using the optical disector. J Comp Neurol 408:560–566
Altman J (1972) Postnatal developmentof the cerebellar cortex in the rat. I. The external germinal layer and the transitional molecular layer. J Comp Neurol 145:353–397
Altman J, Bayer SA (1996) Development of the cerebellar system: in relation to its evolution, structure, and functions. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Altman J, Bayer SA (1997) Development of the cerebellar system: in relation to its evolution, structure, and functions. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Altman J, Winfree AT (1977) Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. V. Spatial organization of purkinje cell perikarya. J Comp Neurol 171:1–16
Anderson KM, Seed T, Ou D, Harris JE (1999) Free radicals and reactive oxygen species in programmed cell death. Med Hypotheses 52:451–463
Anderson MF, Aberg MA, Nilsson M, Eriksson PS (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-I and neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 134:115–122
Anlar B, Sullivan KA, Feldman EL (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-I and central nervous system development. Horm Metab Res 31:120–125
Ayer-le Lievre C, Stahlbom PA, Sara VR (1991) Expression of IGF-I and -II mRNA in the brain and craniofacial region of the rat fetus. Development 111:105–115
Babiker OO (2007) Long-term effects of maternal diabetes on their offspring development and behaviours. Sudanese J Ped 8:133–146
Bach MA, Shen-Orr Z, Lowe WL Jr, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D (1991) Insulin-like growth factor I mRNA levels are developmentally regulated in specific regions of the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 10:43–48
Banks WA, Jaspan JB, Kastin AJ (1997) Selective, physiological transport of insulin across the blood–brain barrier: novel demonstration by species-specific radioimmunoassays. Peptides 18:1257–1262
Baron-Van Evercooren A, Olichon-Berthe C, Kowalski A, Visciano G, Van Obberghen E (1991) Expression of IGF-I and insulin receptor genes in the rat central nervous system: a developmental, regional, and cellular analysis. J Neurosci Res 28:244–253
Bartlett WP, Li XS, Williams M, Benkovic S (1991) Localization of insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA in murine central nervous system during postnatal development. Dev Biol 147:239–250
Baskin DG, Wilcox BJ, Figlewicz DP, Dorsa DM (1988) Insulin and insulin-like growth factors in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 11:107–111
Beaton A, Marien P (2010) Language, cognition and the cerebellum: grappling with an enigma. Cotex 46:811–820
Beck KD, Powell-Braxton L, Widmer HR, Valverde J, Hefti F (1995) Igf1 gene disruption results in reduced brain size, CNS hypomyelination, and loss of hippocampal granule and striatal parvalbumin-containing neurons. Neuron 14:717–730
Bondy CA, Cheng CM (2004) Signaling by insulin-like growth factor 1 in brain. Eur J Pharmacol 490:25–31
Bondy C, Werner H, Roberts CT Jr, LeRoith D (1992) Cellular pattern of type-I insulin-like growth factor receptor gene expression during maturation of the rat brain: comparison with insulin-like growth factors I and II. Neuroscience 46:909–923
Brooks VB (1981) Comment: on functions of the “cerebellar circuit” in movement control. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 59:776–778
Bugalho P, Correa B, Viana-Baptista M (2006) Role of cerebellum in cognitive and behavioual conntrol: scientific basis and investigation models. Acta Med Port 19:257–268
Cardell BS (1953) Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the pancreatic islets in new-born infants. J Pathol Bacteriol 66:335–346
Castellucci M, Kaufmann P (1995) Basic structure of the villous trees. In: Benirschke K, Kaufmann P (eds) Pathology of the human placenta. Springer, New York, pp 57–115
Cederberg J, Picard JJ, Eriksson UJ (2003) Maternal diabetes in the rat impairs the formation of neural-crest derived cranial nerve ganglia in the offspring. Diabetologia 46:1245–1251
Chang TI, Horal M, Jain SK, Wang F, Patel R, Loeken MR (2003) Oxidant regulation of gene expression and neural tube development: Insights gained from diabetic pregnancy on molecular causes of neural tube defects. Diabetologia 46:538–545
Cheng HL, Steinway ML, Xin X, Feldman EL (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-I and Bcl-X(L) inhibit c-jun N-terminal kinase activation and rescue Schwann cells from apoptosis. J Neurochem 76:935–943
Chrysis D, Calikoglu AS, Ye P, D’Ercole AJ (2001) Insulin-like growth factor-I overexpression attenuates cerebellar apoptosis by altering the expression of Bcl family proteins in a developmentally specific manner. J Neurosci 21:1481–1489
Clutton S (1997) The importance of oxidative stress in apoptosis. Br Med Bull 53:662–668
Comblath M, Schwartz R (1976) Disorders of carbohydrates metabolism in infancy. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
D’Agostino AN, Bahn RC (1963) A histopathologic study of the pancreas of infants of diabetic mothers. Diabetes 12:327–331
D’Ercole AJ, Ye P, Calikoglu AS, Gutierrez-Ospina G (1996) The role of the insulin-like growth factors in the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 13:227–255
D’Ercole AJ, Ye P, O’Kusky JR (2002) Mutant mouse models of insulin-like growth factor actions in the central nervous system. Neuropeptides 36:209–220
De Keyser J, Wilczak N, Goossens A (1994) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor densities in human frontalcortex and white matter during aging, in Alzheimer’s disease, and in Huntington’s disease. Neurosci Lett 172:93–96
de Pablo F, de la Rosa EJ (1995) The developing CNS: a scenario for the action of proinsulin, insulin and insulin-like growth factors. Trends Neurosci 18:143–150
Delascio Lopes C, Sinigaglia-Coimbra R, Mazzola J, Camano L, Mattar R (2011) Neurofunctional evaluation of young male offspring of rat dams with diabetes induced by streptozotocin. ISRN Endocrinol 2011:480656
Dentremont KD, Ye P, D’Ercole AJ, O’Kusky JR (1999) Increased insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) expression during early postnatal development differentially increases neuron number and growth in medullary nuclei of the mouse. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 114:135–141
Drago J, Murphy M, Carroll SM, Harvey RP, Bartlett PF (1991) Fibroblast growth factor-mediated proliferation of central nervous system precursors depends on endogenous production of insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:2199–2203
Eccles JC (1981) Physiology of motor control in man. Appl Neurophys 44:5–15
Eidelman AI, Samueloff A (2002) The pathophysiology of the fetus of the diabetic mother. Semin Perinatol 26:232–336
Entingh-Pearsall A, Kahn CR (2004) Differential roles of the insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptors in response to insulin and IGF-I. J Biol Chem 279:38016–38024
Eriksson UJ, Borg LA (1991) Protection by free oxygen radical scavenging enzymes against glucose-induced embryonic malformations in vitro. Diabetologia 34:325–331
Eriksson UJ, Borg LA (1993) Diabetes and embryonic malformations. Role of substrate-induced free-oxygen radical production for dysmorphogenesis in cultured rat embryos. Diabetes 42:411–419
Eriksson UJ, Siman CM (1996) Pregnant diabetic rats fed the antioxidant butylated hydroxytoluene show decreased occurrence of malformations in offspring. Diabetes 45:1497–1502
Eriksson U, Dahlstrom E, Larsson KS, Hellerstrom C (1982) Increased incidence of congenital malformations in the offspring of diabetic rats and their prevention by maternal insulin therapy. Diabetes 31:1–6
Eriksson RS, Thunberg L, Eriksson UJ (1989a) Effects of interrupted insulin treatment on fetal outcome of pregnant diabetic rats. Diabetes 38:764–772
Eriksson UJ, Bone AJ, Turnbull DM, Baird JD (1989b) Timed interruption of insulin therapy in diabetic BB/E rat pregnancy: effect on maternal metabolism and fetal outcome. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 120:800–810
Fu J, Tay SS, Ling EA, Dheen ST (2006) High glucose alters the expression of genes involved in proliferation and cell-fate specification of embryonic neural stem cells. Diabetologia 49:1027–1038
Gao Q, Gao YM (2007) Hyperglycemic condition disturbs the proliferation and cell death of neural progenitors in mouse embryonic spinal cord. Int J Dev Neurosci 25:349–357
Georgieff MK (2006) The effect of maternal diabetes during pregnancy on the neurodevelopment of offspring. Minn Med 89:44–47
Goddard DR, Berry M, Butt AM (1999) In vivo actions of fibroblast growth factor-2 and insulin-like growth factor-I on oligodendrocyte development and myelination in the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 57:74–85
Golalipour MJ, Kafshgiri SK, Ghafari S (2012) Gestational diabetes induced neuronal loss in CA1 and CA3 subfields of rat hippocampus in early postnatal life. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 71:71–77
Gundersen HJ, Bagger P, Bendtsen TF, Evans SM, Korbo L, Marcussen N, Moller A, Nielsen K, Nyengaard JR, Pakkenberg B et al (1988) The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS 96:857–881
Gutierrez-Ospina G, Calikoglu AS, Ye P, D’Ercole AJ (1996) In vivo effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on the development of sensory pathways: analysis of the primary somatic sensory cortex (S1) of transgenic mice. Endocrinology 137:5484–5492
Hagay ZJ, Weiss Y, Zusman I, Peled-Kamar M, Reece EA, Eriksson UJ, Groner Y (1995) Prevention of diabetes-associated embryopathy by overexpression of the free radical scavenger copper zinc superoxide dismutase in transgenic mouse embryos. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173:1036–1041
Haghir H, Rezaee AA, Nomani H, Sankian M, Kheradmand H, Hami J (2013a) Sexual dimorphism in expression of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptors in developing rat cerebellum. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:369–377
Haghir H, Rezaee AA, Sankian M, Kheradmand H, Hami J (2013b) The effects of induced type-I diabetes on developmental regulation of insulin & insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) receptors in the cerebellum of rat neonates. Metab Brain Dis 28:397–410
Hami J, Sadr-Nabavi A, Sankian A, Balali-Mood M, Haghir H (2012) The effects of maternal diabetes on expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin receptors in male developing rat hippocampus. Brain Struct Funct 218(1):73–84
Hami J, Shojae F, Vafaee-Nezhad S, Lotfi N, Kheradmand H, Haghir H (2015) Some of the experimental and clinical aspects of the effects of the maternal diabetes on developing hippocampus. World J Diabetes 6:412–422
Hawkins CL, Davies MJ (2001) Generation and propagation of radical reactions on proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504:196–219
Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Rincon J, Pedreanez A, Viera N, Arcaya JL, Carrizo E, Mosquera J (2009) Structural and ultrastructural analysis of cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and hypothalamus from diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res 2009:329632
Hodge RD, D’Ercole AJ, O’Kusky JR (2004) Insulin-like growth factor-I accelerates the cell cycle by decreasing G1 phase length and increases cell cycle reentry in the embryonic cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 24:10201–10210
Hodge RD, D’Ercole AJ, O’Kusky JR (2005) Increased expression of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) during embryonic development produces neocortical overgrowth with differentially greater effects onspecific cytoarchitectonic areas and cortical layers. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 154:227–237
Hodge RD, D’Ercole AJ, O’Kusky JR (2007) Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) inhibits neuronal apoptosis in the developing cerebral cortex in vivo. Int J Dev Neurosci 25:233–241
Howard CV, Reed MG (1998) Unbiased stereology: three-dimensional measurement in microscopy. Bios Scientific Publisher, Oxford
Humphrey T (1967) The development of the human hippocampal fissure. J Anat 101:655–676
Jackson-Guilford J, Leander JD, Nisenbaum LK (2000) The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on cell proliferation in the rat dentate gyrus. Neurosci Lett 293:91–94
Jawerbaum A, White V (2010) Animal models in diabetes and pregnancy. Endocr Rev 31:680–701
Joseph D’Ercole A, Ye P (2008) Expanding the mind: insulin-like growth factor I and brain development. Endocrinology 149:5958–5962
Kafshgiri SK, Ghafari S, Golalipour MJ (2014) Gestational diabetes induces neuronal loss in dentate gyrus in rat offspring. J Neurol Sci [Turk] 31:316–324
Kamal A, Biessels GJ, Urban IJ, Gispen WH (1999) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity in streptozotocin-diabetic rats: impairment of long-term potentiation and facilitationof long-term depression. Neuroscience 90:737–745
Kar S, Chabot JG, Quirion R (1993) Quantitative autoradiographic localization of [125I]insulin-like growth factor I, [125I]insulin-like growth factor II, and [125I]insulin receptor binding sites indeveloping and adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol 333:375–397
Khaksar Z, Jelodar GA, Hematian H (2011) Morphometric study of cerebrum in fetuses of diabetic mothers. Iran J Vet Res 12:199–204
Lapolla A, Dalfra MG, Fedele D (2005) Insulin therapy in pregnancy complicated by diabetes: are insulin analogs a new tool? Diabetes Metab Res Rev 21:241–252
Lin X, Bulleit RF (1997) Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is a critical trophic factor for developing cerebellar granule cells. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 99:234–242
Lindsay RS, Westgate JA, Beattie J, Pattison NS, Gamble G, Mildenhall LF, Breier BH, Johnstone FD (2007) Inverse changes in fetal insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 and IGF binding protein-1 in association with higher birth weight in maternal diabetes. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 66:322–328
Liu W, Ye P, O’Kusky JR, D’Ercole AJ (2009) Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling is essential for the development of the hippocampal formation and dentate gyrus. J Neurosci Res 87:2821–2832
Loeken MR (2005) Current perspectives on the causes of neural tube defects resulting from diabetic pregnancy. Am J Med Genet C: Semin Med Genet 135C:77–87
McMorris FA, Dubois-Dalcq M (1988) Insulin-like growth factor I promotes cell proliferation and oligodendroglial commitment in rat glial progenitor cells developing in vitro. J Neurosci Res 21:199–209
Mouton PR (2002) Principles and practices of unbiased stereology: an introduction for bioscientists. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Mozell RL, McMorris FA (1991) Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates oligodendrocyte development and myelination in rat brain aggregate cultures. J Neurosci Res 30:382–390
Nelson CA, Wewerka S, Thomas KM, Tribby-Walbridge S, deRegnier R, Georgieff M (2000) Neurocognitive sequelae of infants of diabetic mothers. Behav Neurosci 114:950–956
O’Kusky JR, Ye P, D’Ercole AJ (2000) Insulin-like growth factor-I promotes neurogenesis and synaptogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus during postnatal development. J Neurosci 20:8435–8442
Ornoy A (2005) Growth and neurodevelopmental outcome of children born to mothers with pregestational and gestational diabetes. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 3:104–113
Ornoy A, Ratzon N, Greenbaum C, Peretz E, Soriano D, Dulitzky M (1998) Neurobehaviour of school age children born to diabetic mothers. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 79:F94–F99
Ornoy A, Ratzon N, Greenbaum C, Wolf A, Dulitzky M (2001) School-age children born to diabetic mothers and to mothers with gestational diabetes exhibit a high rate of inattention and fine and gross motor impairment. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 14(Suppl 1):681–689
Persaud OD (2007) Maternal diabetes and the consequences for her offspring. J Dev Disab 1:101–134
Petersen MB, Pedersen SA, Greisen G, Pedersen JF, Mølsted-Pedersen L (1988) Early growth delay in diabetic pregnancy: relation to psychomotor development at age 4. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296:598–600
Pettitt DJ, Bennett PH (1995) Long-term outcome of infant of diabetic mothers. In: Reece AE, Coustan DR (eds) Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 379–388
Popken GJ, Hodge RD, Ye P, Zhang J, Ng W, O’Kusky JR, D’Ercole AJ (2004) In vivo effects of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on prenatal and early postnatal development of the central nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 19:2056–2068
Pulford BE, Ishii DN (2001) Uptake of circulating insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) into cerebrospinal fluid appears to be independent of the IGF receptors as well as IGF-binding proteins. Endocrinology 142:213–220
Ratzon N, Greenbaum C, Dulitzky M, Ornoy A (2000) Comparison of the motor development of school-age children born to mothers with and without diabetes mellitus. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr 20:43–57
Reinhardt RR, Bondy CA (1994) Insulin-like growth factors cross the blood–brain barrier. Endocrinology 135:1753–1761
Riikonen R (2006) Insulin-like growth factor delivery across the blood–brain barrier. Potential use of IGF-1 as a drug in child neurology. Chemotherapy 52:279–281
Rizzo T, Freinkel N, Metzger BE, Hatcher R, Burns WJ, Barglow P (1990) Correlations between antepartum maternal metabolism and newborn behavior. Am J Obstet Gynecol 163(5 Pt 1):1458–1464
Rizzo T, Metzger BE, Burns WJ, Burns K (1991) Correlations between antepartum maternal metabolism and child intelligence. N Engl J Med 325:911–916
Rizzo TA, Dooley SL, Metzger BE, Cho NH, Ogata ES, Silverman BL (1995) Prenatal and perinatal influences on long-term psychomotor development in offspring of diabetic mothers. Am J Obstet Gynecol 173:1753–1758
Rotwein P, Burgess SK, Milbrandt JD, Krause JE (1988) Differential expression of insulin-like growth factor genes in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:265–269
Russo VC, Gluckman PD, Feldman EL, Werther GA (2005) The insulin-like growth factor system and its pleiotropic functions in brain. Endocr Rev 26:916–943
Salehi Z, Mashayekhi F, Naji M (2008) Insulin like growth factor-1 and insulin like growth factor binding proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Biofactors 33:99–106
Schmahmann JD, Caplan D (2006) Cognition, emotionand the cerebellum. Brain Res 129:290–292
Schwartz R, Teramo KA (2000) Effects of diabetic pregnancy on the fetus and newborn. Semin Perinatol 24:120–135
Shin BC, Fujikura K, Suzuki T, Tanaka S, Takata K (1997) Glucose transporter GLUT3 inthe rat placental barrier: a possible machinery for the transplacental transfer of glucose. Endocrinology 138:3997–4004
Siman CM, Eriksson UJ (1997a) Vitamin C supplementation of the maternal diet reduces the rate of malformation in the offspringof diabetic rats. Diabetologia 40:1416–1424
Siman CM, Eriksson UJ (1997b) Vitamin E decreases the occurrence of malformations in the offspring of diabetic rats. Diabetes 46:1054–1061
Singh BS, Westfall TC, Devaskar SU (1997) Maternal diabetes-induced hyperglycemia and acute intracerebral hyperinsulinism suppress fetal brain neuropeptide Y concentrations. Endocrinology 138:963–969
Sivan E, Reece EA, Wu YK, Homko CJ, Polansky M, Borenstein M (1996) Dietary vitamin E prophylaxis anddiabetic embryopathy: morphologic and biochemical analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 175:793–799
Som S, Basu S, Mukherjee D, Deb S, Choudhury PR, Mukherjee S, Chatterjee SN, Chatterjee IB (1981) Ascorbic acid metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 30:572–577
Sotelo C (2004) Cellular and genetic regulation of the development of the cerebellar system. Prog Neurobiol 72:295–339
Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares RXJX, Wands JR, de la Monte SM (2005) Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease - is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimers Dis 7:63–80
Styrud J, Thunberg L, Nybacka O, Eriksson UJ (1995) Correlations between maternal metabolism and deranged development in the offspring of normal and diabetic rats. Pediatr Res 37:343–353
Takata K, Fujikura K, Shin BC (1997) Ultrastructure of the rodent placental labyrinth: a site of barrier and transport. J Reprod Dev 43:13–24
Tavano A, Grasso R, Gagliardi C, Triulzi F, Bresolin N, Fabbro F (2007) Disorders of cognitive and affective development in cerebellar malformations. Brain 130:2646–2660
Tehranipour M, Khakzad MR (2008) Effect of maternal diabetes on hippocampus neuronal density in neonatal rats. J Biol Sci 8:1027–1032
Torres-Aleman I, Pons S, Arevalo MA (1994) The insulin-like growth factor I system in the rat cerebellum: developmental regulation and role in neuronal survival and differentiation. J Neurosci Res 39:117–126
Venkatasubramanian G, Chittiprol S, Neelakantachar N, Naveen MN, Thirthall J, Gangadhar BN, Shetty KT (2007) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 abnormalities in antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 164:1557–1560
Viana M, Herrera E, Bonet B (1996) Teratogenic effects of diabetes mellitus in the rat. Prevention with vitamin E. Diabetologia 39:1041–1046
Wentzel P, Thunberg L, Eriksson UJ (1997) Teratogenic effect of diabetic serum is prevented by supplementation of superoxide dismutase and N-acetylcysteine in rat embryo culture. Diabetologia 40:7–14
Yamada M, Tanabe K, Wada K, Shimoke K, Ishikawa Y, Ikeuchi T, Koizumi S, Hatanaka H (2001) Differences in survival-promoting effects and intracellular signaling properties of BDNF and IGF-1 in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. J Neurochem 78:940–951
Yamano T, Shimada M, Yoshiki F, Kawasaki H, Onaga A (1986) Quantitative synaptic changes on Purkinje cell dendritic spines of rats born from streptozotocin-induced diabetic mothers. Brain Dev 8:269–273
Ye P, Xing Y, Dai Z, D’Ercole AJ (1996) In vivo actions of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on cerebellum development in transgenic mice: evidence that IGF-I increases proliferation of granule cell progenitors. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 95:44–54
Ye P, Li L, Richards RG, DiAugustine RP, D’Ercole AJ (2002) Myelination is altered in insulin-like growth factor-I null mutant mice. J Neurosci 22:6041–6051
Zemva J, Schubert M (2011) Central insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling - implications for diabetes associated dementia. Curr Diabetes Rev 7:356–366
Zhao WQ, Chen H, Quon MJ, Alkon DL (2004) Insulin and the insulin receptor in experimental models of learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 490:71–81
Zhou J, Wang L, Ling S, Zhang X (2007) Expression changes of growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) and in hippocampus of streptozotocin-induced diabetic cognitive impairment rats. Exp Neurol 206:201–208
Acknowledgments
We thank the vice chancellor of Research of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences for financial support of this research (Grant No. 88631).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hami, J., Vafaei-Nezhad, S., Haghir, D. et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Is Differentially Distributed in Developing Cerebellar Cortex of Rats Born to Diabetic Mothers. J Mol Neurosci 58, 221–232 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0661-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0661-z