Abstract
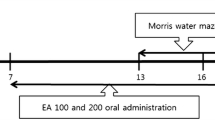
Extracellular deposition of Beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ) is the main finding in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which damages cholinergic neurons through oxidative stress and reduces the cholinergic neurotransmission. Satureja bachtiarica is a medicinal plant from the Lamiaceae family which was widely used in Iranian traditional medicine. The aim of the present study was to investigate possible protective effects of S. bachtiarica methanolic extract on Aβ induced spatial memory impairment in Morris Water Maze (MWM), oxidative stress and cholinergic neuron degeneration. Pre- aggregated Aβ was injected into the hippocampus of each rat bilaterally (10 μg/rat) and MWM task was performed 14 days later to evaluate learning and memory function. Methanolic extract of S.bachtiarica (10, 50 and 100 mg/Kg) was injected intraperitoneally for 19 consecutive days, after Aβ injection. After the probe test the brain tissue were collected and lipid peroxidation, Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity and Cholin Acetyl Transferees (ChAT) immunorectivity were measured in the hippocampus. Intrahipocampal injection of Aβ impaired learning and memory in MWM in training days and probe trail. Methanolic extract of S. bachtiarica (50 and 100 mg/Kg) could attenuate Aβ-induced memory deficit. ChAT immunostaining revealed that cholinergic neurons were loss in Aβ- injected group and S. bachtiarica (100 mg/Kg) could ameliorate Aβ- induced ChAT reduction in the hippocampus. Also S. bachtiarica could ameliorate Aβ-induced lipid peroxidation and AChE activity increase in the hippocampus. In conclusion our study represent that S.bachtiarica methanolic extract can improve Aβ-induced memory impairment and cholinergic loss then we recommended this extract as a candidate for further investigation in treatment of AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahanjan M, Ghaffari J, Mohammadpour G, Nasrolahie M, Haghshenas MR, Mirabi AM (2011) Antibacterial activity of Satureja bakhtiarica bung essential oil against some human pathogenic bacteria. Afr J Microbiol Res 5:4764–4768
Alkam T, Nitta A, Mizoguchi H, Itoh A, Nabeshima T (2007) A natural scavenger of peroxynitrites, rosmarinic acid, protects against impairment of memory induced by abeta(25–35). Behav Brain Res 180:139–145
Azami K, Etminani M, Tabrizian K, Salar F, Belaran M, Hosseini A, Hosseini-Sharifabad A, Sharifzadeh M (2010) The quantitative evaluation of cholinergic markers in spatial memory improvement induced by nicotine–bucladesine combination in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 636:102–107
Bai X, Zhang X, Chen L, Zhang J, Zhang L, Zhao X, Zhao T, Zhao Y (2014) Protective effect of naringenin in experimental ischemic stroke: down-regulated NOD2, RIP2, NF-kappaB, MMP-9 and up-regulated claudin-5 expression. Neurochem Res 39:1405–1415
Balali P, Soodi M, Saeidnia S (2012) Protective effects of some medicinal plants from Lamiaceae family against beta-amyloid induced toxicity in PC12 cell. Tehran Univ Med J (TUMJ) 70:402–409
Birks J (2006) Cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 25
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Butterfield DA (1997) Beta-Amyloid-associated free radical oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Chem Res Toxicol 10:495–506
Camilleri A, Zarb C, Caruana M, Ostermeier U, Ghio S, Hogen T, Schmidt F, Giese A, Vassallo N (2013) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilisation by amyloid aggregates and protection by polyphenols. Biochim Biophys Acta 11:28
Campanari ML, Garcia-Ayllon MS, Blazquez-Llorca L, Luk WK, Tsim K, Saez-Valero J (2014) Acetylcholinesterase protein level is preserved in the Alzheimer’s brain. J Mol Neurosci 53:446–453
Carter J, Lippa CF (2001) Beta-amyloid, neuronal death and Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Mol Med 1:733–737
Cavallucci V, D’amelio M, Cecconi F (2012) Abeta toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 45:366–378
Chen Z, Zhong C (2014) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 30:271–281
Cheng HY, Hsieh MT, Tsai FS, Wu CR, Chiu CS, Lee MM, Xu HX, Zhao ZZ, Peng WH (2010) Neuroprotective effect of luteolin on amyloid beta protein (25–35)-induced toxicity in cultured rat cortical neurons. Phytother Res 24:S102–S108
Choi SH, Hur JM, Yang EJ, Jun M, Park HJ, Lee KB, Moon E, Song KS (2008) Beta-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors from Perilla frutescens var. acuta. Arch Pharm Res 31:183–187
Chtourou Y, Fetoui H, Gdoura R (2014) Protective effects of naringenin on iron-overload-induced cerebral cortex neurotoxicity correlated with oxidative stress. Biol Trace Elem Res 158:376–383
Contestabile A (2002) Cerebellar granule cells as a model to study mechanisms of neuronal apoptosis or survival in vivo and in vitro. Cerebellum 1:41–55
Dashti A, Soodi M, Amani N (2014) Cr (VI) induced oxidative stress and toxicity in cultured cerebellar granule neurons at different stages of development and protective effect of Rosmarinic acid. Environ Toxicol 12:22041
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres Jr V, Feather-Stone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Garcia-Ayllon MS, Small DH, Avila J, Saez-Valero J (2011) Revisiting the role of acetylcholinesterase in Alzheimer’s disease: cross-talk with P-tau and beta-amyloid. Front Mol Neurosci 4:1–9
Ghahremanitamadon F, Shahidi S, Zargooshnia S, Nikkhah A, Ranjbar A, Soleimani Asl S (2014) Protective effects of Borago officinalis extract on amyloid beta-peptide(25–35)-induced memory impairment in male rats: a behavioral study. Biomed Res Int 798535:11
Hajimehdipoor H, Ajani AGY, Saeidnia S (2014a) Comparative study of the total phenol content and antioxidant activity of some medicinal herbal extracts. Res J Pharmacognosy 1:21–25
Hajimehdipoor H, Mosaddegh M, Naghibi F, Haeri A, Hamzeloo-Moghadam M (2014b) Natural sesquiterpen lactones as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. An Acad Bras Cienc 86(2):801–805
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297:353–356
Heo JH, Hyon L, Lee KM (2013) The possible role of antioxidant vitamin C in Alzheimer’s disease treatment and prevention. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 28:120–125
Hosseini-Sharifabad A, Mohammadi-Eraghi S, Tabrizian K, Soodi M, Khorshidahmad T, Naghdi N, Abdollahi M, Beyer C, Roghani A, Sharifzadeh M (2011) Effects of training in the Morris water maze on the spatial learning acquisition and VAChT expression in male rats. DARU, J Pharm Sci 19:166–172
Howes MJ, Houghton PJ (2012) Ethnobotanical treatment strategies against Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:67–85
Iuvone T, De Filippis D, Esposito G, D’amico A, Izzo AA (2006) The spice sage and its active ingredient rosmarinic acid protect PC12 cells from amyloid-beta peptide-induced neurotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:1143–1149
Kar S, Slowikowski SP, Westaway D, Mount HT (2004) Interactions between beta-amyloid and central cholinergic neurons: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Psychiatry Neurosci 29:427–441
Khodabakhsh A, Gohari A, Davood A, Saeidnia S, Thesis, 1388–1389 (2010). Phytochemical Investigation of Satureja bachtiarica. Pharm.D, Islamic Azad university of Tehran
Kramer D, Minichiello L (2010) Cell culture of primary cerebellar granule cells. Methods Mol Biol 633:233–239
Liu R, Meng F, Zhang L, Liu A, Qin H, Lan X, Li L, Du G (2011) Luteolin isolated from the medicinal plant Elsholtzia rugulosa (Labiatae) prevents copper-mediated toxicity in beta-amyloid precursor protein Swedish mutation overexpressing SH-SY5Y cells. Molecules 16:2084–2096
Lleo A, Greenberg SM, Growdon JH (2006) Current pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Med 57:513–533
Luquin MR, Martinez-Vila E, Saldise L (1997) Mechanisms of cell death in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Med Univ Navarra 41:34–45
Manayi A, Mirnezami T, Saeidnia S, Ajani Y (2012) Pharmacognostical evaluation, phytochemical analysis and antioxidant activity of the roots of Achillea tenuifolia LAM. Pharmacogn J 4:14–19
Mohammadpour G, Marzony ET, Farahmand M (2012) Evaluation of the anti-Leishmania major activity of Satureja bakhtiarica essential oil in vitro. Nat Prod Commun 7:133–136
Naghibi F, Mosaddegh M, Motamed SM, Ghorbani A (2005) Labiatae family in folk medicine in Iran: from ethnobotany to pharmacology. IJPR 2:63–79
Orhan IE, Senol FS, Sener B (2012) Recent approaches towards selected lamiaceae plants for their prospective use in neuroprotection. Stud Nat Prod Chem 38:397–415
Pandey KB, Rizvi SI (2009) Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2:270–278
Parks JK, Smith TS, Trimmer PA, Bennett Jr JP, Parker Jr WD (2001) Neurotoxic Abeta peptides increase oxidative stress in vivo through NMDA-receptor and nitric-oxide-synthase mechanisms, and inhibit complex IV activity and induce a mitochondrial permeability transition in vitro. J Neurochem 76:1050–1056
Paxinos G, Watson C (eds) (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Perry E, Howes MJ (2011) Medicinal plants and dementia therapy: herbal hopes for brain aging? CNS Neurosci Ther 17:683–698
Schliebs R, Arendt T (2006) The significance of the cholinergic system in the brain during aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 113:1625–1644
Sepand MR, Soodi M, Hajimehdipoor H, Sahraei E (2013) Comparison of neuroprotective effects of melissa officinalis total extract and its acidic and non-acidic fractions against A β-induced toxicity. Iran J Pharm Res 12:415–423
Singhal AK, Naithani V, Bangar OP (2012) Medicinal plants with a potential to treat Alzheimer and associated symptoms. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis 2:84–91
Soodi M, Sharifzadeh M, Naghdi N, Ostad N, Abdollahi M, Roghani A (2007) Systemic and developmental exposure to lead causes spatial memory deficits and a reduction in COX-2 immunoreactivity in the hippocampus of male rats. J Neurosci Res 85:3183–3192
Soodi M, Naghdi N, Hajimehdipoor H, Choopani S, Sahraei E (2014) Memory-improving activity of Melissa officinalis extract in naïve and scopolamine-treated rats. Res Pharm Sci 9:107–114
Stepanichev MY, Zdobnova IM, Zarubenko II, Moiseeva YV, Lazareva NA, Onufriev MV, Gulyaeva NV (2004) Amyloid-beta(25–35)-induced memory impairments correlate with cell loss in rat hippocampus. Physiol Behav 80:647–655
Sun MK, Alkon DL (2002) Impairment of hippocampal CA1 heterosynaptic transformation and spatial memory by beta-amyloid(25–35). J Neurophysiol 87:2441–2449
Tayeb HO, Yang HD, Price BH, Tarazi FI (2012) Pharmacotherapies for Alzheimer’s disease: beyond cholinesterase inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther 134:8–25
Tepe B (2015) Inhibitory effect of Satureja on certain types of organisms. Rec Nat Prod 9:1–18
Topcu G, Kusman T (2014) Lamiaceae family plants as a potential anticholinesterase source in the treatment ofAlzheimer’s disease. Bezmialem Science 1:1–25
Tsai FS, Cheng HY, Hsieh MT, Wu CR, Lin YC, Peng WH (2010) The ameliorating effects of luteolin on beta-amyloid-induced impairment of water maze performance and passive avoidance in rats. Am J Chin Med 38:279–291
Vauzour D (2012) Dietary polyphenols as modulators of brain functions: biological actions and molecular mechanisms underpinning their beneficial effects. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 914273:3
Wei H, Leeds PR, Qian Y, Wei W, Chen R, Chuang D (2000) Beta-amyloid peptide-induced death of PC 12 cells and cerebellar granule cell neurons is inhibited by long-term lithium treatment. Eur J Pharmacol 392:117–123
Yamaguchi Y, Kawashima S (2001) Effects of amyloid-beta-(25–35) on passive avoidance, radial-arm maze learning and choline acetyltransferase activity in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 412:265–272
Yamaguchi Y, Matsuno T, Kawashima S (2002) Antiamnesic effects of azaindolizinone derivative ZSET845 on impaired learning and decreased ChAT activity induced by amyloid-beta 25–35 in the rat. Brain Res 945:259–265
Yang W, Ma J, Liu Z, Lu Y, Hu B, Yu H (2014) Effect of naringenin on brain insulin signaling and cognitive functions in ICV-STZ induced dementia model of rats. Neurol Sci 35:741–751
Acknowledgments
The Author wish to thank Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services Grant No. 9108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soodi, M., Saeidnia, S., Sharifzadeh, M. et al. Satureja bachtiarica ameliorate beta-amyloid induced memory impairment, oxidative stress and cholinergic deficit in animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Metab Brain Dis 31, 395–404 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9773-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-015-9773-y