Abstract
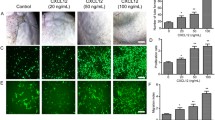
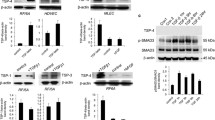
Thymosin beta4 (Tβ4) has multi-functional roles in angiogenesis and arteriogenesis, but little is known about its mechanism. The Notch signaling pathway is important in regulation of angiogenic behavior of endothelial cells, in addition to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Whether, Tβ4 regulates angiogenesis through Notch signaling pathway is not clear. In this article, we evaluated the effect of Notch signaling in Tβ4-induced angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC). Our results revealed that Tβ4 increased Notch1 and Notch4 expression in a dose and time-dependent manner. The inhibition of Notch1 or Notch4 with siRNA or the Notch receptor inhibitor DAPT significantly prevented Tβ4-induced HUVEC tube formation and lymphocyte transendothelial migration. The inhibition of Notch1 or Notch4 also blocked Tβ4-induced VEGF and HIF-1α expression. VE-cadherin is the major endothelial adhesion molecule in the control of angiogenesis. Tβ4 significantly reduced VE-cadherin expression levels in HUVEC, while the inhibition of Notch signaling prevented Tβ4-induced VE-cadherin down-regulation. The results of this study suggest that Tβ4 induces HUVEC angiogenesis through Notch signaling pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sosne G, Qiu P, Goldstein AL, Wheater M (2010) Biological activities of thymosin beta4 defined by active sites in short peptide sequences. FASEB J 24:2144–2151
Grant DS, Kinsella JL, Kibbey MC, LaFlamme S, Burbelo PD, Goldstein AL, Kleinman HK (1995) Matrigel induces thymosin beta 4 gene in differentiating endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 12):3685–3694
Malinda KM, Goldstein AL, Kleinman HK (1997) Thymosin beta 4 stimulates directional migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. FASEB J 11:474–481
Smart N, Risebro CA, Melville AA, Moses K, Schwartz RJ, Chien KR, Riley PR (2007) Thymosin beta4 induces adult epicardial progenitor mobilization and neovascularization. Nature 445:177–182
Lv S, Cheng G, Xu Y, Wang Y, Xu G (2011) Relationship between serum thymosin beta4 levels and coronary collateral development. Coron Artery Dis 22:401–404
Ehebauer M, Hayward P, Arias AM (2006) Notch, a universal arbiter of cell fate decisions. Science 314:1414–1415
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, Shutter JR, Maguire M, Sundberg JP, Gallahan D, Closson V, Kitajewski J, Callahan R, Smith GH, Stark KL, Gridley T (2000) Notch signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes Dev 14:1343–1352
Sainson RC, Harris AL (2008) Regulation of angiogenesis by homotypic and heterotypic notch signalling in endothelial cells and pericytes: from basic research to potential therapies. Angiogenesis 11:41–51
Noria S, Cowan DB, Gotlieb AI, Langille BL (1999) Transient and steady-state effects of shear stress on endothelial cell adherens junctions. Circ Res 85:504–514
Hinkel R, El-Aouni C, Olson T, Horstkotte J, Mayer S, Muller S, Willhauck M, Spitzweg C, Gildehaus FJ, Munzing W, Hannappel E, Bock-Marquette I, DiMaio JM, Hatzopoulos AK, Boekstegers P, Kupatt C (2008) Thymosin beta4 is an essential paracrine factor of embryonic endothelial progenitor cell-mediated cardioprotection. Circulation 117:2232–2240
Srivastava D, Saxena A, Michael Dimaio J, Bock-Marquette I (2007) Thymosin beta4 is cardioprotective after myocardial infarction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1112:161–170
Gale NW, Dominguez MG, Noguera I, Pan L, Hughes V, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Adams NC, Lin HC, Holash J, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD (2004) Haploinsufficiency of delta-like 4 ligand results in embryonic lethality due to major defects in arterial and vascular development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15949–15954
Bock-Marquette I, Shrivastava S, Pipes GC, Thatcher JE, Blystone A, Shelton JM, Galindo CL, Melegh B, Srivastava D, Olson EN, DiMaio JM (2009) Thymosin beta4 mediated PKC activation is essential to initiate the embryonic coronary developmental program and epicardial progenitor cell activation in adult mice in vivo. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46:728–738
Philp D, Scheremeta B, Sibliss K, Zhou M, Fine EL, Nguyen M, Wahl L, Hoffman MP, Kleinman HK (2006) Thymosin beta4 promotes matrix metalloproteinase expression during wound repair. J Cell Physiol 208:195–200
Takeshita K, Satoh M, Ii M, Silver M, Limbourg FP, Mukai Y, Rikitake Y, Radtke F, Gridley T, Losordo DW, Liao JK (2007) Critical role of endothelial Notch1 signaling in postnatal angiogenesis. Circ Res 100:70–78
Kikuchi R, Takeshita K, Uchida Y, Kondo M, Cheng XW, Nakayama T, Yamamoto K, Matsushita T, Liao JK, Murohara T (2011) Pitavastatin-induced angiogenesis and arteriogenesis is mediated by Notch1 in a murine hindlimb ischemia model without induction of VEGF. Lab Invest 91:691–703
Shawber CJ, Funahashi Y, Francisco E, Vorontchikhina M, Kitamura Y, Stowell SA, Borisenko V, Feirt N, Podgrabinska S, Shiraishi K, Chawengsaksophak K, Rossant J, Accili D, Skobe M, Kitajewski J (2007) Notch alters VEGF responsiveness in human and murine endothelial cells by direct regulation of VEGFR-3 expression. J Clin Invest 117:3369–3382
Lee SH, Kim MH, Han HJ (2009) Arachidonic acid potentiates hypoxia-induced VEGF expression in mouse embryonic stem cells: involvement of Notch, Wnt, and HIF-1 alpha. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297:C207–C216
Lin CL, Wang FS, Hsu YC, Chen CN, Tseng MJ, Saleem MA, Chang PJ, Wang JY (2010) Modulation of notch-1 signaling alleviates vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 59:1915–1925
Coleman ML, McDonough MA, Hewitson KS, Coles C, Mecinovic J, Edelmann M, Cook KM, Cockman ME, Lancaster DE, Kessler BM, Oldham NJ, Ratcliffe PJ, Schofield CJ (2007) Asparaginyl hydroxylation of the Notch ankyrin repeat domain by factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor. J Biol Chem 282:24027–24038
Venkatesh D, Fredette N, Rostama B, Tang Y, Vary CP, Liaw L, Urs S (2011) RhoA-mediated signaling in Notch-induced senescence-like growth arrest and endothelial barrier dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:876–882
Esser S, Lampugnani MG, Corada M, Dejana E, Risau W (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces VE-cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 13):1853–1865
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (Project 2012C33028).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, S., Cheng, G., Zhou, Y. et al. Thymosin beta4 induces angiogenesis through Notch signaling in endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 381, 283–290 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1713-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1713-8