Abstract
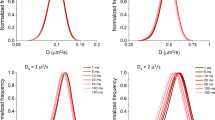
Using a Monte Carlo simulation technique, we have modeled 3D diffusion of low molecular weight metabolites inside a skeletal muscle cell. The following structural elements are considered: (i) a regular lattice of actin and myosin filaments inside a myofibril, (ii) the membranes of sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria surrounding the myofibrils, (iii) a set of myofibrils inside a skeletal muscle cell encircled by the outer cell membrane, and (iv) an additional set of regular intracellular structures (“macrocompartments”) embedded into the cell interior. The macrocompartments are considered to simulate diffusion restrictions because of hypothetical cylindrical structures (16–22 μm in diameter) suggested earlier (de Graaf et al. Biophys J 78: 1657–1664, 2000). This model allowed us to calculate the apparent coefficients of particle diffusion in the radial and axial directions, \( D_{ \bot }^{\text{app}} \) and \( D_{II}^{\text{app}} \), respectively. Particle movements in the axial direction are considered, at first approximation, as unrestricted diffusion (\( D_{II}^{\text{app}} \) = const). The apparent coefficient of radial diffusion, \( D_{ \bot }^{\text{app}} \), decreases with time because of particle collisions with myofilaments and other rigid obstacles. Results of our random walk simulations are in fairly good agreement with experimental data on NMR measurements of restricted radial diffusion of phosphocreatine in white and red skeletal muscles of goldfish (Kinsey et al. NMR Biomed 12:1–7, 1999). Particle reflections from the low-permeable borders of macrocompartments (efficient diameter, \( d_{\text{MC}}^{\text{eff}} \) ≈ 9.2–10.4 μm) are the prerequisite for agreeing theoretical and experimental data. The low-permeable coverage of hypothetical macrocompartments (99.8% of coverage) provides the main contribution to time-dependent decrease in \( D_{ \bot }^{\text{app}} \).










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- PCr:
-
Phosphocreatine
- ICEU:
-
Intracellular energy-transducing unit
- LWM:
-
Low molecular weight metabolites
References
Kao HP, Abney JR, Verkman AS (1993) Determinants of translational mobility of a small solute in cell cytoplasm. J Cell Biol 120:175–184
Verkman AS (2002) Solute and macromolecule diffusion in cellular aqueous compartments. Trends Biochem Sci 27:27–33
Vendelin M, Birkedal R (2008) Anisotropic diffusion of fluorescently labeled ATP in rat cardiomyocytes determined by raster image correlation spectroscopy. Am J Physiol 295:C1302–C1315
Luby-Phelps K (2000) Cytoarchitecture and physical properties of cytoplasm: volume, viscosity, diffusion, intracellular surface area. Int Rev Cytol 192:189–221
Partikian A, Olveczky B, Swaminathan R, Li Y, Verkman AS (1998) Rapid diffusion of green fluorescent protein in the mitochondrial matrix. J Cell Biol 140:821–829
Nicolay K, Braun KPJ, de Graaf RA, Dijkhuizen RM, Kruiskamp MJ (2001) Diffusion NMR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 14:94–111
Papadopoulos S, Jurgens KD, Gros G (2000) Protein diffusion in living skeletal muscle fibers: dependence on protein size, fiber type, and contraction. Biophys J 79:2084–2094
Walter H (2000) Consequences of phase separation in cytoplasm. Int Rev Cytol 192:331–343
Spitzer JJ, Poolman B (2005) Electrochemical structure of the crowded cytoplasm. Trends Biochem Sci 30:536–541
Ovadi J, Srere PA (2000) Macromolecular compartmentation and channeling. Int Rev Cytol 192:255–280
Ovadi J, Saks V (2004) On the origin of intracellular compartmentation and organized metabolic systems. Mol Cell Biochem 256(257):5–12
Vendelin M, Lemba M, Saks VA (2004) Analysis of functional coupling: mitochondrial creatine kinase and adenine nucleotide translocase. Biophys J 87:696–713
van Gelderen P, DesPres D, van Zijl PCM, Moonen CTW (1994) Evaluation of restricted diffusion in cylinders. Phosphocreatine in rabbit leg muscle. J Magn Res B 103:255–260
Kinsey ST, Locke B, Penke B, Moerland TS (1999) Diffusional anisotropy is induced by subcellular barriers in skeletal muscle. NMR Biomed 12:1–7
de Graaf RA, van Kranenburg A, Nicolay K (2000) In vivo 31P-NMR diffusion spectroscopy of ATP and phosphocreatine in rat skeletal muscle. Biophys J 78:1657–1664
Gabr RE, El-Sharkawy A-MM, Schar M, Weiss RG, Bottomley PA (2011) High-energy phosphate transfer in human muscle: the diffusion of phosphocreatine. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00500.2010
Kinsey ST, Locke BR, Dillaman RM (2011) Molecules in motion: influences of diffusion on metabolic structure and function in skeletal muscle. J Exp Biol 214:263–274
Kushmerick MJ, Podolsky RJ (1969) Ionic mobility in muscle cells. Science 166:1297–1298
Aliev MK, Tikhonov AN (2004) Random walk analysis of restricted metabolite diffusion in skeletal myofibril systems. Mol Cell Biochem 256(257):257–266
Saks VA, Kaambre T, Sikk P, Eimre M, Orlova E, Paju K, Piirsoo A, Appaix F, Kay L, Regitz-Zagrosek V, Fleck E, Seppet E (2001) Intracellular energetic units in red muscle cells. Biochem J 356:643–657
Seppet EK, Kaambre T, Sikk P, Tiivel T, Vija H, Tonkonogi M, Sahlin K, Kay L, Appaix F, Braun U, Eimre M, Saks VA (2001) Functional complexes of mitochondria with Ca, MgATPases of myofibrils and sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504:379–395
Vendelin M, Eimre M, Seppet E, Peet N, Andrienko T, Lemba M, Engelbrecht J, Seppet EK, Saks VA (2004) Intracellular diffusion of adenosine phosphates is locally restricted in cardiac muscle. Mol Cell Biochem 256(257):229–241
Saks V, Beraud N, Wallimann T (2008) Metabolic compartmentation—a system level property of muscle cells: real problems of diffusion in living cells. Int J Mol Sci 9:751–767
Shorten PR, Sneyd J (2009) A mathematical analysis of obstructed diffusion within skeletal muscle. Biophys J 96:4764–4778
Sommer RJ, Johnson EA (1979) Ultrastructure of cardiac muscle. In: Burns RM (ed) Handbook of physiology. The cardiovascular system. Bethesda, MD, Am Physiol Soc, pp 113–186 Section 2, Vol. 1, Chapter 5
Eisenberg BR, Kuda AM, Peter JB (1974) Stereological analysis of mammalian skeletal muscle I. Soleus muscle of the adult guinea pig. J Cell Biol 60:732–754
Eisenberg BR, Kuda AM (1975) Stereological analysis of mammalian skeletal muscle II. White Vastus muscle of the adult guinea pig. J Ultrastruct Res 51:176–187
Crowe LM, Baskin RJ (1979) Stereologic analysis of dystrophic chicken muscle. Am J Pathol 95:295–316
Mobley BA, Eisenberg BR (1975) Sizes of components in frog skeletal muscle measured by methods of stereology. J Gen Physiol 66:31–45
Uhrik B, Novotova M, Zachar J (1980) A quantitative estimation of components in Crayfish muscle fibers by stereological methods. Pflug Arch 387:281–286
Crowe LM, Baskin RJ (1981) Activation of the contractile system in crustacean muscle: ultrastructural evidence for the role of the T system. Tissue Cell 13:153–164
Anversa P, Olivetti G, Melissari M, Loud AV (1979) Morphometric study of myocardial hypertrophy induced by abdominal aortic stenosis. Lab Invest 40:341–349
Kinsey ST, Moerland TS (2002) Metabolite diffusion in giant muscle fibers of the spiny lobster Panulirus argus. J Exp Biol 205:3377–3386
Tyler S, Sidell BD (1984) Changes in mitochondrial distribution and diffusion distances in muscle of Goldfish upon acclimation to warm and cold temperatures. J Exp Zool 232:1–9
Korostyshevskaya IM, Maksimov VF, Shoshenko KA (2001) Features of capillarization and mitochondria from gastrocnemius and pectoral muscle fibers in chickens of various age. Morfologiia 120:30–36 Article in Russian
Jahromi SS, Atwood HL (1971) Structural and contractile properties of lobster leg-muscle fibers. J Exp Zool 176:475–486
Meyer RA, Sweeney HL, Kushmerick MJ (1984) A simple analysis of the “phosphocreatine shuttle”. Am J Physiol 246:C365–C377
Aliev MK, Saks VA (1997) Compartmentalized energy transfer in cardiomyocytes: use of mathematical modeling for analysis of in vivo regulation of respiration. Biophys J 73:428–445
Matsumoto M, Nishimura T (1998) Mersenne twister: a 623-dimensionally equidistributed uniform pseudorandom number generator. ACM T Model Comput S 8:3–30
Eisenberg BR, Mathias RT, Gilai A (1979) Intracellular localization of markers within injected or cut frog muscle fibers. Am J Physiol 237:C50–C505
Kaasik A, Veksler V, Boehm E, Novotova M, Minaeva A, Ventura-Clapier R (2001) Energetic crosstalk between organelles. Architectural integration of energy production and utilization. Circ Res 89:153–159
Saks V, Vendelin M, Aliev MK, Kekelidze T, Engelbrect J (2007) Mechanisms and modeling of energy transfer between and among intracellular compartments. In: Gibson Gary, Dienel Gerry (eds) Handbook of neurochemistry, molecular neurobiology “Brain energetics: integration of molecular, cellular processes,” Vol. 5, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 815–860
Saks V, Guzun R, Timohhina N, Tepp K, Varikmaa M, Monge C, Beraud N, Kaambre T, Kuznetsov A, Kadaja L, Eimre M, Seppet E (2010) Structure-function relationships in feedback regulation of energy fluxes in vivo in health and disease: mitochondrial interactosome. Biochim Biophys Acta 1797:678–697
Guzun R, Karu-Varikmaa M, Granillo MG, Kuznetsov AV, Michel L, Cottet-Rousselle C, Saaremae M, Kaambre T, Metsis M, Grimm M, Auffray C, Saks V (2011) Mitochondria-cytoskeleton interaction: distribution of β-tubulins in cardiomyocytes and HL-1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:458–469
Ramay HR, Vendelin M (2009) Diffusion restrictions surrounding mitochondria: a mathematical model of heart muscle fibers. Biophys J 97:443–452
Tiegs OW (1935) Observations on the structure of striated muscle fibre. Proc Roy Soc Lond B 116:38–54
Peachey LD, Eisenberg BR (1978) Helicoids in the T system and striations of frog skeletal muscle fibers seen by high voltage electron microscopy. Biophys J 22:145–154
Rudel R, Thaer A (1981) Helical arrangements of myofibrils in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol (Lond) 318:28P–29P
Sundell CL, Goldman YE, Peachey LD (1986) Fine structure in near-field and far-field laser diffraction patterns from skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J 49:521–530
Brenner B (1985) Sarcomeric domain organization within single skinned rabbit psoas fibers and its effects on laser diffraction patterns. Biophys J 48:967–982
Zite-Ferenczy F, Haberle K-D, Rudel R, Wilke W (1986) Correlation between the light diffraction pattern and the structure of a muscle fibre realized with Ewald’s construction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 7:197–214
Tiegs OW (1955) The flight muscles of insects—their anatomy and histology; with some observations on the structure of striated muscle in general. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 238:221–348
Rudel R, Zite-Ferenczy F (1979) Do laser diffraction studies on striated muscle indicate stepwise sarcomere shortening? Nature 278:573–575
Brenner B (1983) Technique for stabilizing the striation pattern in maximally calcium-activated skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J 41:99–102
Palmer RE, Roos KP (1997) Extent of radial sarcomere coupling revealed in passively stretched cardiac myocytes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 37:378–388
Hawke TJ, Garry DJ (2001) Myogenic satellite cells: physiology to molecular biology. J Appl Physiol 91:534–551
Allen DL, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (1999) Myonuclear domains in muscle adaptation and disease. Muscle Nerve 22:1350–1360
Wakelam MJO (1985) The fusion of myoblasts. Biochem J 228:1–12
Doberstein SK, Fetter RD, Mehta AY, Goodman CS (1997) Genetic analysis of myoblast fusion: blown fuse is required for progression beyond the prefusion complex. J Cell Biol 136:1249–1261
Towler MC, Kaufman SJ, Brodsky FM (2004) Membrane traffic in skeletal muscle. Traffic 5:129–139
Fulton AB, Prives J, Farmer SR, Penman S (1981) Developmental reorganization of the skeletal framework and its surface lamina in fusing muscle cells. J Cell Biol 91:103–112
Kadi F, Eriksson A, Holmner S, Butler-Browne GS, Thornell L-E (1999) Cellular adaptation of the trapezius muscle in strength-trained athletes. Histochem Cell Biol 111:189–195
Bruusgaard JC, Liestol K, Ekmark M, Kollstad K, Gundersen K (2003) Number and spatial distribution of nuclei in the muscle fibres of normal mice studied in vivo. J Physiol 551:467–478
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant 09-04-00978a from the Russian Foundation for Basic Researches. We thank Prof. Valery I. Kapelko for continuous support of our work, Dr. Valdur A. Saks for valuable consultations and encouragement of our work, and anonymous reviewer for useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aliev, M.K., Tikhonov, A.N. Obstructed metabolite diffusion within skeletal muscle cells in silico . Mol Cell Biochem 358, 105–119 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0926-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-011-0926-y