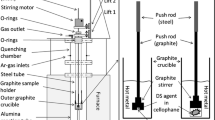
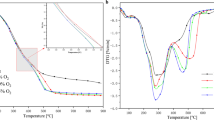
Abstract
As a major air pollutant, SO2 has negative effect on the human health and environment. The desulfurization characteristics of two CaO samples (commercial one and the other one calcined from CaCO3) with high purity were examined by a thermo-gravimetric analyzer under circulating fluidized bed combustion-like condition. The influences of SO2 concentration (1000–4000 ppm), CO2 concentration (0–45%) and temperatures (800–950 °C) on the sulfation conversion degree of CaO samples were addressed, and sulfation kinetic parameters for the two samples were estimated based on the unreacted shrinking core model. The sulfation conversion degree of CaO calcined from CaCO3 at 900 °C and 2000 ppm SO2 was 68% higher than the commercial CaO. The sulfation conversion degree for the commercial CaO at 950 °C with 2000 ppm SO2 was one time higher than at 800 °C, and the sulfation conversion degree for the sample calcined from CaCO3 at 950 °C increased by about 31% compared to that at 800 °C. The calcium conversion degree of the sample calcined from CaCO3 was 0.59 in the absence of CO2, and the conversion degree with the CO2 concentration of 45% reduced by about 31%. The sulfation kinetics of two samples were appropriately described by the shrinking unreacted core model. The sample calcined from CaCO3 had a better sulfation activity than the commercial CaO.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b :
-
Stoichiometric coefficient
- A, B :
- A1, B1 :
- C A0 :
-
SO2 concentration (mol mL−1)
- C S0 :
-
CaO concentration (mol mL−1)
- D 0 :
-
Pre-exponential factor of the product layer diffusion reaction (cm2 min−1)
- D s :
-
Effective diffusivity of reactants in the product layer (cm2 min−1)
- E a :
-
Activation energy for chemical reaction stage (kJ mol−1)
- E p :
-
Activation energy for product layer diffusion (kJ mol−1)
- Gfp(x):
-
Function defined by Eq. (6a)
- k :
-
Rate constant of the surface reaction (cm min−1)
- k 0 :
-
Pre-exponential factor of the surface reaction (cm min−1)
- m :
-
Mass (mg)
- M :
-
Molar mass (g mol−1)
- Pfp(x):
-
Function defined by Eq. (6b)
- R :
-
General gas constant (J mol−1 K−1)
- R p :
-
Original radius of the sorbent particle (cm)
- t :
-
Time (min)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- W :
-
Mass percentage
- x :
-
Conversion degree
- δ :
-
Standard uncertainty
- 0:
-
Initial
References
Xu Y-L, Zuo N, Bu Y-C, Wang L-Y. Experimental study on the characteristics of oxidation kinetics and heat transfer for coal-field fires under axial compression. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(1):597–607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08379-2.
Xian S, Zhang H, Chai Z, Zhu Z. Release characteristics of gaseous products during CO2 gasification of char. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;140(1):177–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08704-9.
Kaljuvee T, Trikkel A, Kuusik R. Decarbonization of natural lime-containing materials and reactivity of calcined products towards SO2 and CO2. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;64(3):1229–40. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011561500091.
Shih SM, Lai JC, Yang CH. Kinetics of the reaction of dense CaO particles with SO2. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2011;50(22):12409–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie2009668.
Li W, Xu M, Li S. Calcium sulfation characteristics at high oxygen concentration in a 1MWth pilot scale oxy-fuel circulating fluidized bed. Fuel Process Technol. 2018;171:192–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.11.005.
Zhang H, Xian S, Zhu Z, Guo X. Release behaviors of sulfur-containing pollutants during combustion and gasification of coals by TG-MS. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-09251-z.
Yang JH, Shih SM, Lin PH. Effect of carbon dioxide on the sulfation of high surface area CaCO3 at high temperatures. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2012;51(6):2553–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie202665a.
Manovic V, Anthony EJ. Sequential SO2/CO2 capture enhanced by steam reactivation of a CaO-based sorbent. Fuel. 2008;87(8):1564–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2007.08.022.
García-Labiano F, Rufas A, de Diego LF, Obras-Loscertales MDL, Gayán P, Abad A, et al. Calcium-based sorbents behaviour during sulphation at oxy-fuel fluidised bed combustion conditions. Fuel. 2011;90(10):3100–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.05.001.
Anthony EJ, Granatstein DL. Sulfation phenomena in fluidized bed combustion systems. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2001;27(2):215–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1285(00)00021-6.
Stewart MC, Symonds RT, Manovic V, Macchi A, Anthony EJ. Effects of steam on the sulfation of limestone and NOx formation in an air- and oxy-fired pilot-scale circulating fluidized bed combustor. Fuel. 2012;92(1):107–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.06.054.
Bolea I, Romeo LM, Pallarés D. The role of external heat exchangers in oxy-fuel circulating fluidized bed. Appl Energy. 2012;94:215–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.01.050.
Park K, Lee JM, Kim DW, Lee GH, Kang Y. Characteristics of co-combustion of strongly caking and non-caking coals in a pilot circulating fluidized bed combustor (CFBC). Fuel. 2019;236:1110–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.09.052.
de Diego LF, Rufas A, García-Labiano F, Obras-Loscertales MDL, Abad A, Gayán P, et al. Optimum temperature for sulphur retention in fluidised beds working under oxy-fuel combustion conditions. Fuel. 2013;114:106–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.02.064.
Zhao J, Li D, Liao S, Wang D, Wang H, Yan P. Influence of mechanical grinding on pozzolanic characteristics of circulating fluidized bed fly ash (CFA) and resulting consequences on hydration and hardening properties of blended cement. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132(3):1459–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7103-4.
Zhao J, Yang G, Wang D, Liao S, Zhai M. The hydration properties of blended cement containing ultrafine fly ash with particle size less than 17 μm from the circulating fluidized bed combustion of coal gangue. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139(5):2971–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08685-9.
Stewart MC, Manovic V, Anthony EJ, Macchi A. Enhancement of indirect sulphation of limestone by steam addition. Environ Sci Technol. 2010;44(22):8781–6. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1021153.
Chen L, Wang C, Wang Z, Anthony EJ. The kinetics and pore structure of sorbents during the simultaneous calcination/sulfation of limestone in CFB. Fuel. 2017;208:203–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.07.018.
Abanades JC, de Diego LF, García-Labiano F, Adánez J. Residual activity of sorbent particles with a long residence time in a CFBC. AIChE J. 2000;46(9):1888–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690460916.
Li W, Li S, Xu M, Wang X. Study on the limestone sulfation behavior under oxy-fuel circulating fluidized bed combustion condition. J Energy Inst. 2018;91(3):358–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2017.02.005.
Wang C, Jia L, Tan Y, Anthony EJ. The effect of water on the sulphation of limestone. Fuel. 2010;89(9):2628–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2010.04.022.
Manovic V, Anthony EJ, Loncarevic D. SO2 retention by CaO-based sorbent spent in CO2 looping cycles. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2009;48(14):6627–32. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie9002365.
Han R, Sun F, Gao J, Wei S, Su Y, Qin Y. Trace Na2CO3 addition to limestone inducing high-capacity SO2 capture. Environ Sci Technol. 2017;51(21):12692–8. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b04141.
Scala F, Chirone R, Meloni P, Carcangiu G, Manca M, Mulas G, et al. Fluidized bed desulfurization using lime obtained after slow calcination of limestone particles. Fuel. 2013;114:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.11.072.
Anthony EJ, Bulewicz EM, Jia L. Reactivation of limestone sorbents in FBC for SO2 capture. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2007;33(2):171–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2006.10.001.
Hu G, Dam-Johansen K, Wedel S, Hansen JP. Review of the direct sulfation reaction of limestone. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2006;32(4):386–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2006.03.001.
Bragança SR, Castellan JL. FBC desulfurization process using coal with low sulfur content, high oxidizing conditions and metamorphic limestones. Braz J Chem Eng. 2009;26(2):375–83. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0104-66322009000200015.
Lages VP, da Cunha ALC, Dweck J. Evaluation of SO2 capture efficiency of combustion gases using commercial limestone. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;138(5):3833–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08056-4.
Tarelho LAC, Matos MAA, Pereira FJMA. The influence of operational parameters on SO2 removal by limestone during fluidised bed coal combustion. Fuel Process Technol. 2005;86(12):1385–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2005.03.002.
Obras-Loscertales MDL, Rufas A, de Diego LF, García-Labiano F, Gayán P, Abad A, et al. Morphological analysis of sulfated Ca-based sorbents under conditions corresponding to oxy-fuel fluidized bed combustion. Fuel. 2015;162:264–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.09.016.
Wang C, Chen L, Jia L, Tan Y. Simultaneous calcination and sulfation of limestone in CFBB. Appl Energy. 2015;155:478–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.05.070.
Gullett BK, Bruce KR. Pore distribution changes of calcium-based sorbents reacting with sulfur dioxide. AIChE J. 1987;33(10):1719–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690331015.
Ghosh-Dastidar A, Mahuli S, Agnihotri R, Fan LS. Ultrafast calcination and sintering of Ca(OH)2 powder: experimental and modeling. Chem Eng Sci. 1995;50(13):2029–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2509(95)00043-5.
Mahuli SK, Agnihotri R, Chauk S, Ghosh-Dastidar A, Wei SH, Fan LS. Pore-structure optimization of calcium carbonate for enhanced sulfation. AIChE J. 1997;43(9):2323–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690430917.
de Diego LF, Obras-Loscertales MDL, García-Labiano F, Rufas A, Abad A, Gayán P, et al. Characterization of a limestone in a batch fluidized bed reactor for sulfur retention under oxy-fuel operating conditions. Int J Greenhouse Gas Control. 2011;5(5):1190–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2011.05.032.
Fonseca AM, Órfão JJ, Salcedo RL. A new approach to the kinetic modeling of the reaction of gaseous HCl with solid lime at low temperatures. Chem Eng Sci. 2003;58(15):3499–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(03)00219-7.
Maina P, Mbarawa M. Enhancement of lime reactivity by addition of diatomite. Fuel Process Technol. 2011;92(10):1910–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.05.011.
Cordero JM, Alonso M. Modelling of the kinetics of sulphation of CaO particles under CaL reactor conditions. Fuel. 2015;150:501–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.02.075.
Liu H, Katagiri S, Kaneko U, Okazaki K. Sulfation behavior of limestone under high CO2 concentration in O2/CO2 coal combustion. Fuel. 2000;79(8):945–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-2361(99)00212-4.
Qiu K, Lindqvist O. Direct sulfation of limestone at elevated pressures. Chem Eng Sci. 2000;55(16):3091–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2509(99)00589-8.
Liu H, Katagiri S, Okazaki K. Drastic SOx removal and influences of various factors in O2/CO2 pulverized coal combustion system. Energy Fuels. 2001;15(2):403–12. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef000171p.
Wang S, Zhao Y, Zhang P, Liu Y. Study of the sulfation kinetics between SO2 and CaO catalyzed by TiO2 nano-particles. Chem Eng Res Des. 2011;89(7):1061–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2010.12.006.
Kim YB, Gwak YR, Keel SI, Yun JH, Lee SH. Direct desulfurization of limestones under oxy-circulating fluidized bed combustion conditions. Chem Eng J. 2019;377:119650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.036.
Wu ZH, Kou P, Yu ZW. The modulation of desulphurization properties of calcium oxide by alkali carbonates. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2002;67(3):745–50. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1014381510955.
Ar İ, Balci S. Sulfation reaction between SO2 and limestone: application of deactivation model. Chem Eng Process. 2002;41(2):179–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0255-2701(01)00133-7.
Li Y, Sun R, Zhao J, Han K, Lu C. Sulfation behavior of white mud from paper manufacture as SO2 sorbent at fluidized bed combustion temperatures. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107(1):241–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-1537-2.
Yang JH, Shih SM. Preparation of high surface area CaCO3 by bubbling CO2 in aqueous suspensions of Ca(OH)2: effects of (NaPO3)6, Na5P3O10, and Na3PO4 additives. Powder Technol. 2010;197(3):230–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2009.09.020.
Wang C, Zhang Y, Jia L, Tan Y. Effect of water vapor on the pore structure and sulfation of CaO. Fuel. 2014;130(130):60–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.04.007.
Galloway BD, MacDonald RA, Padak B. Characterization of sulfur products on CaO at high temperatures for air and oxy-combustion. Int J Coal Geol. 2016;167:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2016.09.007.
Jeong S, Lee KS, Keel SI, Yun JH, Kim YJ, Kim SS. Mechanisms of direct and in-direct sulfation of limestone. Fuel. 2015;161:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2015.08.034.
Han K, Lu C, Cheng S, Zhao G, Wang Y, Zhao J. Effect of characteristics of calcium-based sorbents on the sulfation kinetics. Fuel. 2005;84(14):1933–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2005.04.001.
Li YR, Qi HY, You CF, Xu XC. Kinetic model of CaO/fly ash sorbent for flue gas desulphurization at moderate temperatures. Fuel. 2007;86(5):785–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.09.011.
Wei F, Guo L, Liu Z, Shen X, Liu H. Thermogravimetric analysis of desulfurization characteristics and kinetic parameters of limestone modified by red mud. Adv Mater Res. 2012;512–515:2339–42. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.512-515.2339.
Chen H, Zhao Z, Huang X, Patchigolla K, Cotton A, Oakey J. Novel optimized process for utilization of CaO-based sorbent for capturing CO2 and SO2 sequentially. Energy Fuels. 2012;26(9):5596–603. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef300487q.
Hu G, Dam-Johansen K, Wedel S, Hansen JP. Direct sulfation of limestone. AIChE J. 2007;53(4):948–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.11129.
Chen L, Wang C, Yan G, Zhao F, Anthony EJ. The simultaneous calcination/sulfation reaction of limestone under oxy-fuel CFB conditions. Fuel. 2019;237:812–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.060.
Chen L, Wang Z, Wang C, Wang H, Anthony EJ. Sulfation of limestone under O2/H2O combustion conditions in circulating fluidized bed. Int J Greenh Gas Control. 2020;95:102979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2020.102979.
Hu G, Dam-Johansen K, Wedel S, Hansen JP. Enhancement of the direct sulfation of limestone by alkali metal salts, calcium chloride, and hydrogen chloride. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2007;46(16):5295–303. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie070208u.
Cheng J, Zhou J, Liu J, Zhou Z, Huang Z, Cao X, et al. Sulfur removal at high temperature during coal combustion in furnaces: a review. Prog Energy Combust Sci. 2003;29(5):381–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-1285(03)00030-3.
Chen C, Zhao C. Mechanism of highly efficient in-furnace desulfurization by limestone under O2/CO2 coal combustion atmosphere. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2006;45(14):5078–85. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060196x.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2017YFB0603901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Y.J., Chen, M.Q., Li, Q.H. et al. Sulfation performance of CaO under circulating fluidized bed combustion-like condition. J Therm Anal Calorim 142, 1031–1042 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09857-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09857-8