Abstract
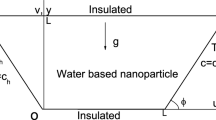
A numerical investigation of entropy generation due to MHD-free convective of Cu–water nanofluid in a porous I-shaped cavity is reported. The cavity is under Darcy law with inclined uniform magnetic field. The cavity is cooled from the top and a part of bottom wall subjected to uniform heat flux, while the other parts of walls of the cavity are adiabatic. Mathematical pattern formulated employing the single-phase nanofluid approach in governing equations the problem has been solved by finite difference technique. Prime efforts have been concentrated on the impacts of the pertinent parameters on the fluid flow and heat transfer inside the cavity. Numerical data have been plotted in the form of streamlines, isotherms, and average Nusselt numbers. The results show that the Nu number decreases via increasing the Ha number. It increases when the Ra number is increased. The maximum and minimum values of Nusselt occur at B = 0.2 and B = 0.8, respectively. Exerting an angle for magnetic flux leads to the improvement in thermal performance for all amount of B. The effects of Ha, nanofluid volume fraction, heat source size, location and angle of magnetic field on heat transfer, entropy generation, and thermal performance are completely studied and discussed.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
Dimensionless of heat source/sink length
- B 0 :
-
Magnetic field strength, T
- b :
-
Length of heat source, m
- C p :
-
Specific heat, J kg−1 K−1
- C T :
-
Difference temperature
- D :
-
Dimensionless heat source position
- d :
-
Location of heat sink and source, m
- Da:
-
Darcy number
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity, m s−2
- H :
-
Length of cavity, m
- Ha:
-
Hartmann number, \( B_{0} L\sqrt {\sigma_{\text{f}} /\rho_{\text{f}} \nu_{\text{f}} } \)
- K :
-
Permeability of porous medium, m2
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity, Wm−1 K−1
- Nus :
-
Local Nusselt number
- Num :
-
Average Nusselt number of heat source
- p :
-
Fluid pressure, Pa
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure, \( {\text{pH}}/\rho_{\text{nf}} \,\alpha_{\text{f}}^{2} \)
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number, vf/αf
- Q 0 :
-
Heat generation coefficient, W m−2
- \(q''\) :
-
Heat flux
- Ra:
-
Rayleigh number, gβf (Th − Tc)H3/αfνf
- S :
-
Entropy generation, WK−1 m−3
- T :
-
Temperature, K
- T c :
-
Cold wall temperature, K
- T h :
-
Heated wall temperature, K
- u, v :
-
Velocity components in x, y directions, m2 s−1
- U, V :
-
Dimensionless velocity components, u/v0, v/v0
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates, m
- X, Y :
-
Dimensionless coordinates, x/L, y/L
- \( \alpha \) :
-
Thermal diffusivity, m2 s−1, k/ρcp
- \( \beta \) :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient, K−1
- ϕ :
-
Solid volume fraction
- σ :
-
Effective electrical conductivity, μS cm−1
- \( \theta \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature, (T − Tc)/(Th − Tc)
- \( \mu \) :
-
Dynamic viscosity, N s m−2
- \( \nu \) :
-
Kinematic viscosity, m2 s−1
- \( \rho \) :
-
Density, kg m−3
- Ф:
-
Angle of enclosure
- c:
-
Cold
- 0:
-
Reference
- f:
-
Pure fluid
- h:
-
Hot
- m:
-
Average
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- p:
-
Nanoparticle
References
Sajid MU, Ali HM. Recent advances in application of nanofluids in heat transfer devices: a critical review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2019;103:556–92.
Izadi S, Armaghani T, Ghasemi-Asl R, Chamkha AJ, Molana M. A comprehensive review on mixed convection of nanofluids in various shapes of enclosures. Powder Technol. 2019;343:880–907.
Kasaeian A, Daneshazarian R, Mahian O, Kolsi L, Chamkha AJ, Wongwises S, Pop I. Nanofluid flow and heat transfer in porous media: a review of the latest developments. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;107:778–91.
Rahimi A, Dehghan Saee A, Kasaeipoor A, Hasani Malekshah E. A comprehensive review on natural convection flow and heat transfer: the most practical geometries for engineering applications. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow. 2019;29:834–77.
Bejan A. A study of entropy generation in fundamental convective heat transfer. J Heat Transf. 1979;101:718.
Bejan A. Second-law analysis in heat and thermal design. Adv Heat Transf. 1982;15:1–58.
Bejan A. Entropy generation minimization. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1996.
Ismael MA, Armaghani T, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate heat transfer and entropy generation in a cavity filled with a nanofluid-saturated porous media and heated by a triangular solid. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2016;59:138.
Kefayati GHR. Heat transfer and entropy generation of natural convection on non-Newtonian nanofluids in a porous cavity. Powder Technol. 2016;299:127–49.
Chamkha AJ, Rashad AM, Armaghani T, Mansour MA. Entropy generation and MHD natural convection of a nanofluid in an inclined square porous cavity: effects of a heat sink and source size and location. Chin J Phys. 2018;56:193–211.
Armaghani T, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ. Analysis of entropy generation and natural convection in an inclined partially porous layered cavity filled with a nanofluid. Can J Phys. 2017;95:238–52.
Mansour MA, Ahmed SE, Chamkha AJ. Entropy generation optimization for MHD natural convection of a nanofluid in porous media-filled enclosure with active parts and viscous dissipation. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow. 2017;27:379–99.
Al-Zamily A, Ruhul Amin M. Natural convection and entropy generation in a cavity filled with two horizontal layers of nanofluid and porous medium in presence of a magnetic field, Volume 8B: Heat Transfer and Thermal Engineering, Houston, Texas, USA, November 13–19, 2015.
Chamkha AJ, Selimefendigil F. MHD free convection and entropy generation in a corrugated cavity filled with a porous medium saturated with nanofluids. Entropy. 2018;20:2–17.
Izadi M, Shahmardan MM, Norouzi M, Rashidi AM, Behzadmehr A. Cooling performance of a nanofluid flow in a heat sink microchannel with axial conduction effect. Appl Phys A. 2014;117(4):1821–33.
Izadi M, Behzadmehr A, Shahmardan MM. Effects of inclination angle on mixed convection heat transfer of a nanofluid in a square cavity. Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech. 2015;16(1):11–21.
Izadi M, Mehryan SAM, Sheremet MA. Natural convection of CuO–water micropolar nanofluids inside a porous enclosure using local thermal non-equilibrium condition. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2018;88:89–103.
Mohebbi R, Izadi M, Amiri Delouei A, Sajjadi H. Effect of MWCNT-Fe3O4/water hybrid nanofluid on the thermal performance of ribbed channel with apart sections of heating and cooling. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135:3029–42.
Izadi M, Hashemi Pour SMR, Karimdoost Yasuri A, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection of a nanofluid in a three-dimensional channel, effect of opposed buoyancy force on hydrodynamic parameters, thermal parameters and entropy generation. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;136:2461–75.
Izadi M, Maleki N, Pop I, Mehryan S. Natural convection of a hybrid nanofluid subjected to non-uniform magnetic field within porous medium including circular heater. Int J Numer Meth Heat Fluid Flow. 2019;29(4):1211–31.
Izadi M, Oztop HF, Sheremet MA, Mehryan SAM, Abu-Hamdeh N. Coupled FHD-MHD free convection of a hybrid nanoliquid in an inversed T-shaped enclosure occupied by partitioned porous media. Numer Heat Transf A. 2019;76(6):479–98.
Izadi M, Mohammadi SA, Mehryan SAM, Yang T, Sheremet MA. Thermogravitational convection of magnetic micropolar nanofluid with coupling between energy and angular momentum equations. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;145:118748.
Izadi M, Mohebbi R, Sajjadi H, Amiri Delouei A. LTNE modeling of Magneto-Ferro natural convection inside a porous enclosure exposed to nonuniform magnetic field. Phys A: Stat Mech Appl. 2019;535:122394.
Izadi M, Sheremet MA, Mehryan SAM, Pop I, Öztop HF, Abu-Hamdeh N. MHD thermogravitational convection and thermal radiation of a micropolar nanoliquid in a porous chamber. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2020;110:104409.
Aminossadati SM, Ghasemi B. Natural convection cooling of a localized heat source at the bottom of a nanofluid-filled enclosure. Eur J Mech B/Fluids. 2009;28:630–40.
Khanafer K, Vafai K, Lightstone M. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2003;46:3639–53.
Abu-Nada E, Chamkha AJ. Effect of nanofluid variable properties on natural convection in enclosures filled with a CuO–EG–water nanofluid. Int J Therm Sci. 2010;49:2339–52.
Maxwell JA. Treatise on electricity and magnetism. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Oxford University Press; 1904.
Brinkman HC. The viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solution. J Chem Phys. 1952;20:571–81.
Chamkha AJ, Rashad AM, Mansour MA, Armaghani T, Ghalambaz M. Effects of heat sink and source and entropy generation on MHD mixed convection of a Cu–water nanofluid in a lid-driven square porous enclosure with partial slip. Phys Fluids. 2017;29:052001.
Rashad AM, Mansour MA, Armaghani T, Chamkha AJ. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid in a lid-driven U-shaped cavity with internal heat and partial slip. Phys Fluids. 2019;31:042006.
Walker KL, Homsy GM. Convection in a porous cavity. J FluidMech. 1978;87:449–74.
Gross RJ, Bear MR, Hickox CE. The application of flux-corrected transport (FCT) to high Rayleigh number natural convection in a porous medium, paper presented at the 8th International Heat Transfer Conference, San Francisco, 1986.
Manole DM, Lage JL. Numerical benchmark results for natural convection in a porous medium cavity. Heat and mass transfer in porous media, vol. 216., ASME conferenceAnaheim, CA: ASME; 1992. p. 55–60.
Bekermann C, Viskanta R, Ramadhyani S. A numerical study of non-Darcian natural convection in a vertical enclosure filled with a porous medium. Numer Heat Transf A. 1986;10:557–70.
Moya SM, Ramos E, Sen M. Numerical study of natural convection in a tilted rectangular porous material. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 1987;30:741–56.
Baytas AC, Pop I. Natural convection in a trapezoidal enclosure filled with a porous medium. Int J Eng Sci. 2001;39:125–34.
Misirlioglu A, Baytas AC, Pop I. Free convection in a wavy cavity filled with a porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2005;48:1840–50.
Badruddin IA, Zainal A, Narayana PAA, Seetharamu KN. Numerical analysis of convection conduction and radiation using a non-equilibrium model in a square porous cavity. Int J Therm Sci. 2007;46:20–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armaghani, T., Chamkha, A., Rashad, A.M. et al. Inclined magneto: convection, internal heat, and entropy generation of nanofluid in an I-shaped cavity saturated with porous media. J Therm Anal Calorim 142, 2273–2285 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09449-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09449-6