Abstract
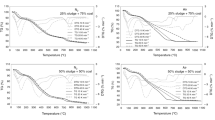
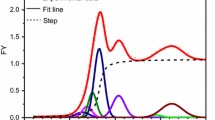
In this work, the pyrolysis characteristics and release of sulphur contaminant were studied under different mass percentages (25%, 50% and 75%) of Zhundong coal in the sample mixtures. The results showed that the yields of volatile products during co-pyrolysis were higher than those calculated from linear combination of corresponding yields of pure sludge and Zhundong coal, which mean that a certain synergistic effect occurs in co-pyrolysis process. The yields of H2S, COS and SO2 decreased with the increase in the content of Zhundong coal in the samples. What’s more, when the content of Zhundong coal were 50%, a great significance on the yields of sulphur contaminant occurs in the process of co-pyrolysis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mills N, Pearce P, Farrow J, et al. Environmental & economic life cycle assessment of current & future sewage sludge to energy technologies. Waste Manag. 2014;34(1):185–95.
Wang Z, Gong Z, Wang Z, et al. A TG–MS study on the coupled pyrolysis and combustion of oil sludge. Thermochim Acta. 2018;663:137–44.
Chen J, Mu L, Jiang B, et al. TG/DSC-FTIR and Py-GC investigation on pyrolysis characteristics of petrochemical wastewater sludge. Bioresour Technol. 2015;192:1–10.
Xu J, Yu D, Fan B, et al. Characterization of ash particles from co-combustion with a Zhundong coal for understanding ash deposition behavior. Energy Fuels. 2013;28(1):678–84.
Yao Y, Jin J, Liu D, et al. Evaluation of vermiculite in reducing ash deposition during the combustion of high-calcium and high-sodium Zhundong coal in a drop-tube furnace. Energy Fuels. 2016;30(4):3488–94.
Wang Y, Jin J, Liu D, et al. Understanding ash deposition for Zhundong coal combustion in 330 MW utility boiler: focusing on surface temperature effects. Fuel. 2018;216:697–706.
Tabakaev RB, Astafev AV, Dubinin YV, et al. Autothermal pyrolysis of biomass due to intrinsic thermal decomposition effects. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;134(2):1045–57.
Ozgur E, Miller BG, Miller SF, Kok MV. Thermal analysis of co-firing of oil shale and biomass fuels. Oil Shale. 2012;29:190–201.
Yang N, Guo H, Liu F, et al. Effects of atmospheres on sulphur release and its transformation behavior during coal thermolysis. Fuel. 2018;215:446–53.
Jayaraman K, Kok MV, Gokalp I. Pyrolysis, combustion and gasification studies of different sized coal particles using TGA–MS. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;125:1446–55.
Zhang Y, Liang P, Jiao T, et al. Effect of foreign minerals on sulphur transformation in the step conversion of coal pyrolysis and combustion. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2017;127:240–5.
Folgueras MB, Díaz RM. Influence of FeCl3 and lime added to sludge on sludge-coal pyrolysis. Energy. 2010;35(12):5250–9.
Chang F, Wang Q, Wang K. Thermogravimetric characteristics and kinetic analysis of co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and coal. Chin J Environ Eng. 2015;9:2412–8.
Xiao P, Xu L, Wang X, et al. Co-pyrolysis characteristics of coal and sludge blends using thermogravimetric analysis. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. 2016;34(6):1780–9.
Kok MV, Ozgur E. Characterization of lignocellulose biomass and model compounds by thermogravimetry. Energy Sources. 2017;39(2):6.
Folgueras MB, Díaz RM, Xiberta J, et al. Thermogravimetric analysis of the co-combustion of coal and sewage sludge. Fuel. 2003;82(15):2051–5.
Weng SF. Fourier transform infrared spectrum analysis. 2nd ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2010.
Domínguez A, Menéndez JA, Inguanzo M, et al. Production of bio-fuels by high temperature pyrolysis of sewage sludge using conventional and microwave heating. Bioresour Technol. 2006;97(10):1185–93.
Jayaraman K, Kok MV, Gokalp I. Combustion properties and kinetics of different biomass samples using TG–MS technique. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127(2):1361–70.
Zhu K, Chen L, Ma A, Huang G. Study on the pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of biomass of the biomass and coal. J Agric Mech Res. 2010;32:202–6.
Domínguez A, Menéndez JA, Pis JJ. Hydrogen rich fuel gas production from the pyrolysis of wet sewage sludge at high temperature. J Anal Appl Pyrolsis. 2006;77(2):127–32.
Li Z, Xu S, Wei Z, et al. Co-pyrolysis of biomass and coal in a free fall reactor. Fuel. 2007;86(3):353–9.
Zhu X, He Q, Hu Y, et al. A comparative study of structure, thermal degradation, and combustion behavior of starch from different plant sources. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;132(2):1–9.
Kok MV, Ozgur E. Thermal analysis and kinetics of biomass samples. Fuel Process Technol. 2013;106(2):739–43.
Cai Z, Ma X, Fang S, et al. Thermogravimetric analysis of the co-combustion of eucalyptus residues and paper mill sludge. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;106:938–43.
Jia X, Wang Q, Cen K, et al. Sulphur transformation during the pyrolysis of coal mixed with coal ash in a fixed bed reactor. Fuel. 2016;177:260–7.
Wang X, Wang X, Xu S, Xu W, Tan H. Release characteristics of N/S/Cl species during pyrolysis of biomass and coal. J China Coal Soc. 2012;37:426–31.
Weng H, Dai Z, Ji Z, et al. Release and control of hydrogen sulfide during sludge thermal drying. J Hazard Mater. 2015;296:61–7.
Liu S, Wei M, Qiao Y, et al. Release of organic sulphur as sulphur-containing gases during low temperature pyrolysis of sewage sludge. Proc Combust Inst. 2015;35(3):2767–75.
Zhang J, Zuo W, Tian Y, et al. Release of hydrogen sulfide during microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge: effect of operating parameters and mechanism. J Hazard Mater. 2017;331:117.
Xu L, Yang J, Li Y, et al. Behavior of organic sulphur model compounds in pyrolysis under coal-like environment. Fuel Process Technol. 2004;85(8–10):1013–24.
Baruah BP, Khare P. Pyrolysis of high sulphur Indian coals. Energy Fuels. 2007;21(6):3346–52.
Liu H, Zhang Q, Hu H, et al. Dual role of conditioner CaO in product distributions and sulphur transformation during sewage sludge pyrolysis. Fuel. 2014;134(9):514–20.
Karaca S. Desulphurization of a Turkish lignite at various gas atmospheres by pyrolysis. Effect of mineral matter. Fuel. 2003;82(12):1509–16.
Wang Baofeng, et al. Effect of some natural minerals on transformation behavior of sulphur during pyrolysis of coal and biomass. J Anal Appl Pyrolsis. 2014;105(6):284–94.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Key Project in Fundamental Research of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 14JC1404800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Jin, J., Li, S. et al. Co-pyrolysis characteristics of sludge mixed with Zhundong coal and sulphur contaminant release regularity. J Therm Anal Calorim 138, 1623–1632 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08300-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08300-x