Abstract
This paper presents the results of testing the flammability of silicone rubber composites containing fillers, such as cenospheres, cenospheres covered with iron, attapulgite, wollastonite, aluminum hydroxide and silica. In order to increase the insulating character of boundary layer, boron trioxide was incorporated into the composites of silicone rubber as a ceramization additive. The flammability of the composites was tested with the use of a cone calorimeter. The composition of the gaseous products of thermal decomposition was determined quantitatively and qualitatively in the system with intensive stirring in the fluidal bed, under isothermal conditions at temperatures T = 550, 650 and 750 °C. All the test results show that the fillers used, especially with ceramization additives considerably reduce the fire hazard of silicone rubber composites containing these fillers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Most organic polymers are characterized by inadequate resistance to the action of heat at elevated temperatures and fire, especially within a long period of time. Moreover, during thermal decomposition and combustion of organic polymers, considerable amounts of fumes and toxic gases are emitted, creating a serious hazard to the health and life of men present in their atmosphere [1, 2].
From the literature review, it follows that 55–80 % of all the fatal accidents during fires are caused by poisoning with the products of thermal decomposition and combustion and fume [3, 4]. These products easily get into human organism due to inhalation and absorption through skin. Great amounts of heat emitted during fires also cause huge material losses.
In recent years, the preparation of flame-retardant polymeric materials characterized by a low emission of toxic gases and fumes has been a key issue of material engineering.
To obtain elastomeric composites with an increased resistance to the action of fire more and more often are used various fillers and nanofillers as well as special rubbers characterized by low values of the heat release rate parameters (HRR) [5].
On account of their unique properties, including high elasticity, electric resistance, biocompatibility, constancy of physical and mechanical properties with a very wide temperature range, especially a high resistance to the action of external heat source, polysiloxanes have found wider and wider use in various branches of industry [6, 7].
A great resistance of silicones to the action of fire is mainly connected with the formation, during their thermal decomposition, of a boundary layer of silica with a high heat capacity that considerably impedes the heat conduction between flame and sample. On the other hand, the forces of cohesive interactions between silica particles are insufficient to form an effective barrier impeding the mass flow from a sample and flame [7].
In order to obtain a considerable reduction in flammability, silicone rubbers are filled with active fillers. Mutual interaction between the particles of active fillers and immobilization of polysiloxane macromolecules on their surface cause the formation of a strongly developed three-dimensional filler network that penetrating the whole polymer volume, considerably improves its thermal and mechanical properties [8, 9].
Most frequently silicone rubbers are filled with amorphous silica [10, 11]. A considerable reduction in the flammability of silicone rubbers can be obtained by combining them with cenospheric filler.
From the literature review it follows that a cenospheric filler, especially that covered with iron, considerably improves the thermal properties of silicone rubbers. It is possible that metals with a variable valence, on account of their low catalytic activity, facilitate the stabilization of boundary layer [12].
The article presents the effect of cenospheres, also those covered with iron, on the flammability of silicone rubber and its capability to ceramize it in relation to conventional mineral fillers, such as silica, attapulgite, wollastonite and aluminum hydroxide.
Methods
Materials
The object of the study was metylvinylsilicone rubber (MVSR), made by Silikony Polskie, with a molecular weight of 60–70 × 104 (kg mol−1) and a content of vinyl groups at a level of 0.05–0.09 % (mol × mol−1). The rubber was cross-linked with the use of dicumyl peroxide (Sigma-Aldrich) in a quantity of 1 part by wt./100 parts by wt. of the rubber.
The following fillers of the rubber blend were used: aluminum hydroxide (POCH Gliwice), wollastonite FW 635, with an average particle size of 3.5 μm, a specific surface of 3.25 m2 g−1 (Nordkalk Corporation), attapulgite Bentonit SWDC (BDC Poland), anhydrous silica Aersil 380 with a specific surface of 380 m2 g−1 (Evonik Degussa) and cenospheres uncoated and coated with iron. The fillers tested were incorporated into the silicone rubber matrix in a quantity of 40 parts by wt./100 parts by wt. of the rubber.
The obtained vulcanizates were denoted as follows:
-
SRDCP silicone rubber cross-linked with organic peroxide,
-
SR-Al silicone rubber filled with aluminum hydroxide,
-
SR-ATT silicone rubber filled with attapulgite,
-
SR-WL silicone rubber filled with wollastonite,
-
SR-Si silicone rubber filled with silica,
-
SR-CE silicone rubber containing cenospheric filler,
-
SR-CEFE silicone rubber containing cenosphereic filler covered with iron.
In order to increase the insulating character of boundary layer, a ceramization additive in the form of boron trioxide (Sigma-Aldrich) in a quantity of 15 parts by wt. was added to the silicone rubber composites selected. The vulcanizates containing boron trioxide were denoted as follows:
-
SRAl-B silicone rubber containing aluminum hydroxide and boron thrioxide,
-
SRSi-B silicone rubber containing silica and boron trioxide,
-
SRCE-B silicone rubber containing cenospheric filler and boron trioxide,
-
SRCEFE-B silicone rubber containing cenospheric filler, covered with iron, and boron trioxide.
Methods
Preparation of rubber blends and their vulcanization
Silicone rubber blends were prepared at room temperature with the use of a laboratory rolling mill with roll dimensions: D = 150 mm, L = 300 mm. The rotational speed of the front roll was 20 rpm, friction 1:1.
The blends were vulcanized in steel molds placed between the electrically heated press shelves. The optimal vulcanization time (τ 0.9) at a temperature of 160 °C was determined by means of a WG vulcameter, according to standard PN-ISO 3417:1994.
Flammability
The vulcanizates under investigation were examined by the use of a cone calorimeter from Fire Testing Technology Ltd. Elastomer samples with dimensions of (100 × 100 ± 1) mm and thickness of (2 ± 0.5) mm were tested at horizontal position with the heat radiant flux density 35 kW m−2. During tests, the following parameters were recorded: initial sample weight, time to ignition (TTI), sample weight during testing, total heat released (THR), effective combustion heat (EHC), average weight loss rate (MLR), heat release rate (HRR) and sample final weight.
The structure of the rubber combustion residue analyzed by means of a cone calorimeter and the residue after ceramization of composites was assessed on the basis of photographs taken under a microscope equipped with the recording software Motic Images Plus.
Ceramization
The ceramization of silicone rubber composites containing an appropriate filler and boron trioxide was carried out with the use of a muffle furnace Nabertherm equipped with a P320 temperature controller. The sample tested were heated to a temperature of 1000 °C for 2 h and then stored at this temperature for 20 min.
SEM analysis
Microscopic photographs of residues after ceramization were obtained by means of scanning electron microscope (SEM), from Hitachi model TM3000.
Determination of gaseous products of thermal decomposition of silicone composites
The quality and quantity of gaseous products of thermal decomposition of silicone composites without boron trioxide and except for SR-ATT were determined according to an original method in the fluidized bed at the temperature of 550, 650 and 750 °C. For the experiment the laboratory scale installation, which operate under atmospheric pressure was used (Scheme 1). The major part of the setup is fluidized bed reactor, which consists of a quartz tube with an outside diameter of 100 mm, height of 500 mm and a wall thickness of 2 mm. It is placed on a perforated plate (a distributor) made of chrome-nickel steel with a thickness of 1 mm. As a fluidizing medium and for oxidizing process condition, air was applied. Therefore, an oxidative condition of the process was ensured. Approximately, 240 g of purified microspheres with diameter in the range of 0.250–0.500 mm was used as an inert fluidized bed. Pretreatment of the material used as fluidized bed included hydrothermal purification as well as calcination at the temperature of 800 °C. Spherical microspheres provide inert conditions up to 1300 °C (softening point) and its low density enabled maintaining of as low fluidizing gas linear flow as 0.02 m s−1. In order to heat the bed, a heating jacket connected to the autotransformer was applied. Each analyzed type of silicon rubber and its composites were dosed as three samples, each containing several pieces with a mass ca. 0.04 g through the batcher to the reactor. Two NiCr–Ni thermocouples located at a height of 20 and 50 mm above the distributor were used for temperature measurement. The analyzer of volatile organic compounds VOCs JUM Model 3-200 performs measurements using flame ionization detector (FID). Analyzer ECOM Plus SG measures the concentration of O2, CO, NO, NO2, SO2 using electrochemical sensors (EC). Analyzer Horiba PG250 consists of three kinds of sensors. O2 concentration is measured by electrochemical sensor (EC), for determining the amount of gases such as CO, CO2, SO2 analyzer uses in the IR detectors (non-dispersive infrared NDIR), concentration of nitrogen oxides (II) and (IV)—NO x is measured using a chemiluminescence technique (CLA). Analyzer Gasmet DX-4000 measures the concentration of inorganic and organic compounds based on the method of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. For DX-4000 analysis following list of compound was chosen: H2O, CO2, CO, CH4, C2H6, C3H8, C2H4, HCHO and cyclic siloxanes D3, D4 and D5, which were not presented in the analyzer’s standard library of IR spectra, therefore calibration for these three compounds were performed. Spectra from FTIR analyzer was continuously acquired every 5 s during experiment, and these data served as a basis for further evaluation. Utilization of several analyzers allowed to duplicate measurements of some components and thus eliminated the cross-effects on obtained data [13].
Scheme of the fluidized bed reactor: 1—heated probes for sampling the flue gases; 2—batcher; 3—computer storing data from FTIR analyzer; 4—exhaust fan; 5—cyclone; 6—ash trap for coarser particles; 7—movable radiation shield; 8—heating jacket; 9—bubbling bed; 10—air rotameter; 11—blower for fluidising air; 12—two thermocouples; 13—flat, perforated metal plate distributor; 14—A/D convertor for thermocouple signals; 15—computer storing chemical analyses quantities and temperature; A—total organic compounds analyzer (JUM Model 3-200), B—ECOM SG plus, C—Horiba PG250, P—Peltier’s cooler. D—mobile conditioning system of Gasmet DX-4000, E—analyzer FTIR (Gasmet DX-4000)
Results
Flammability of silicone rubber composites
During combustion of silicone rubber composites with the use of a cone calorimeter one can observe three stages. The first stage constitutes a fumeless thermal decomposition accompanied by the emission of a considerable quantity of opaque fumes. The next stage is connected with ignition and a slow propagation of flame on the whole sample surface. It should be clearly mentioned that the combustion of silicone rubber is not accompanied by the formation of liquid destruction products that are responsible not only for heat transfer but they increase the contact with oxygen. The combustion residue is in the form of white uneven surface that covers a thing brown consolidated layer (Fig. 1).
The shape of HRR curve as a function of time, recorded during the combustion of silicone rubber composites, is different from the HRR curve of typical organic polymers (Fig. 2).
During the combustion of silicone rubbers, contrary to conventional rubbers, after reaching the maximal HRR value, there is established a pseudo-plateau state indicating the formation of boundary insulating, protective layer against external heat source.
The value of HRRmax recorded for silicone rubber amounts to 115 kW m−2, while the value of this parameter for organic polymer, determined for a heat flux equal to 35 kW m−2, amounts to: for polypropylene 1800 kW m−2 [14], for PET 1600 kW m−2 [15], for low density polyethylene 1400 kW m−2 [16], and for NBR rubber 1100 kW m−2 [17].
Contrary to organic polymers, during the thermal decomposition of silicones, especially in the presence of oxygen, there is formed inorganic silica with a high heat capacity. The effectiveness of fuel diffusion to flame and oxygen to the sample surface depends first of all on the structure of boundary layer, whose insulating properties are considerably dependent on the integrity of silica layer formed during the thermal decomposition of polysiloxane.
From literature review, it follows that the forces of cohesive interactions between silica particles resulted from the decomposition of SR are insufficient to form a condensed boundary layer. The available silica is in the form of dust with a low barrier capability that can be easily removed from the surface of boundary layer by the flux of gases within the combustion zone [6].
An increase in the integrity of the boundary layer formed during the combustion of silicone rubbers can be obtained by the incorporation of active fillers into their matrix [18].
The mutual interaction between filler particles and the immobilization of polysiloxane macromolecules on their surface that results from physical and chemical interactions between polymer macromolecules and the active sites in chemical, energetic, or steric terms on the filler surface, causes the formation of a strongly developed three-dimensional network that penetrating the whole polymer volume, improves its thermal properties, and reduces the fire hazard created by the composite.
The mineral fillers commonly used in polymer technology can be divided into passive fillers such as calcium carbonate or kaolin, whose role is to decrease the product price, and active fillers (reinforcing) that should improve the functional parameters of polymers. The properties of active filler considerably depend on factors such as shape, size, its distribution in the polymer matrix and the number and quality of functional groups on its surface. For example, laminar or fibrous fillers, contrary to nanofillers, can undergo orientation in processing, while the functional groups on their surface can interact with a polymeric chain, which results in an increase in the composite mechanical properties [8, 19].
The fillers fulfilling the function of flame-retardant agents after heating undergo endothermic decomposition releasing water, while their decomposition residue inhibits the energy transport inside the sample by thermal feedback.
The most often used fillers of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) include: aluminum hydroxide, silica, laminar fillers, and recently also cenospheric fillers.
Undoubtedly, a reduction in the flammability of silicone rubber in the presence of aluminum hydroxide results from the thermal decomposition of Al(OH)3 to water and Al2O3. Both the endothermic decomposition of Al(OH)3 and water evaporation decrease the energetic balance of the elastomer under combustion. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the values of HRRmax and MLR are slightly lower than those of unfilled silicone rubber (Figs. 2, 3; Table 1).
The high value of MLR parameter results from releasing considerable amounts of water vapor at relatively low temperatures, ΔT = 200–250 °C, that not only impedes the diffusion of oxygen to boundary layer but first of all lowers its temperature and consequently the efficiency of thermal degradation as confirmed by the relatively low value of THR parameter THR (Table 1; Fig. 4).
Water vapor can, however, initiate the cracking of the thermally stable Al2O3 layer, which negatively influences the value of HRRmax (Fig. 2).
The flame-retardant action of attapulgite consists in both releasing considerable amounts of water with a wide temperature range, ΔT = 160–320 °C, as confirmed by the value of MLR and forming an insulating boundary layer. However, from the literature review it follows that the boundary layer of burning elastomer formed in the presence of attapulgite is characterized by a high heterogeneity, which increases the values of HRRmax parameter [20].
Silica is the most often used filler of SR. However, it should be noted that precipitated silacas, especially non-hydrophobized silicas, contain from 5 to 8 % by wt. of physically combined water. With increasing temperature, the released water molecules can initiate the thermal degradation of PDMS by the hydrolysis of siloxane chain [21]. Flame silicas, commonly used as fillers of silicones, do not contain physically combined water, while the water chemically combined with their surface results from the presence of three types of hydroxyl groups, i.e., isolated, free single silanol groups, ≡SiOH, free germinal silanol or silanodiol groups, =Si(OH)2 and vicynal hydroxyl groups (combined with hydrogen bond single silanol or geminal groups or both silanol and geminal groups) [22, 23].
Single silanol groups are more reactive than vicinal silanol groups combined with hydrogen bond, which results from the presence of reactive acidic hydrogen in their structure.
On the surface of silica are also siloxane bridges, ≡Si–O–Si≡, that are converted to silanol groups as a result of dehydroxylation.
The flame silica used considerably decreases the value of HRR and especially that of MLR of the polysiloxane tested. The flame-retardant action of silica results from the formation of hydrogen bonds between oxygen present in the main chain of silicone rubber (Si–O–Si) and hydrogen of silanol groups located on the silica surface, which reduces the segmental mobility of silicone rubber chains and leads to the formation of strong internal polymer–filler interactions [24].
In the presence of flame silica, one can also observe an increase in the viscosity of liquid destruction products, whose rheological properties are similar to those of gel, which radically decreases the rate of their diffusion to the flame zone, compared to the destruction products of unfilled silicone rubbers. Extremely important is also the balance between the filler density and specific surface and the viscosity of fused polymer. It depends on this balance whether silica will accumulate near the surface of the polymer under combustion or will it be immersed in the fused mass of polymer [25].
It should be mentioned that the composites of silicone rubber filled with silica are characterized by the highest value of released heat and flame temperature from among all the composites tested (Table 1, Fig. 3). This indicates that the flame silica used releases small amounts of water that are insufficient to cool the sample surface.
From the test results presented in Table 1 it follows that cenospheric filler is characterized by a comparable flame-retardant effectiveness to that of silica in relation to silicone rubber (Table 1).
Cenospheres are light, chemically neutral, hollow spheres consisting of silica and aluminum, mostly filled with air, obtainable in the process of fine coal combustion [26, 27]. They are characterized by unique properties, including low mass, good insulating properties, low water absorption and great chemical and thermal resistance [28].
The test results obtained show that cenospheres, especially those covered with iron, incorporated into the matrix of silicone rubber are characterized by a high effectiveness of stamping out fire.
At present, the effect of a metal with variable valence on the thermal stability and flammability of polymeric materials is not fully explained. From the literature review it clearly follows that metal ions, e.g., of cobalt or titanium act as catalysts of the decomposition of hydroperoxides, so increasing the rate of polymer depolymerization and degradation [29].
Cobalt, through the electron transfer in 3D subshell, generates a great amount of macroradical [30], initiating the thermal decomposition of SR as well as PE or PP. It should be, however, clearly mentioned that other transient metals such as Ni or Fe that could potentially initiate radical reactions, contrary to cobalt, are characterized by a low catalytic activity.
The test results obtained clearly shows that an increase in the thermal stability of polymeric composites containing iron oxide is connected with the adsorption of polymeric chains on the surface of iron oxide particles, which results in a considerable decrease in the segmental mobility of polymeric chains and consequently in a decrease in the effectiveness of decomposition and chain transfer. It is also possible that iron facilitates the stabilization of boundary layer [8].
From among all the fillers used, wollastonite is characterized by the highest effectiveness of stamping out the fire of SR composite (Table 1).
It is highly probable that the high effectiveness of wollastonite in stamping fire out is connected with the formation, at elevated temperature, of microbridges between the particles of silica and wollastonite that considerably reduce the processes of pyrolysis and facilitate the formation of thermally stable insulating boundary layer.
A significant improvement in the insulating character of boundary layer, exerting a key impact on the reduction in mass and energy transport between sample and flame, one can obtain by incorporating ceramization additives into the elastomer matrix.
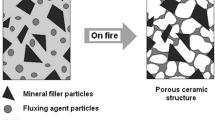
An activator of the ceramic layer in silicone rubber composites can be mica. The reaction between inorganic fillers, e.g., mica, wollastonite and the silica formed as a result of thermal decomposition of silicone rubber, in the boundary layer of the composite under combustion, a eutectic fluid phase is formed, showing great capabilities to penetrate the polymeric matrix. The eutectic liquid penetrates the structure of composite, acting as a bridge between silica and filler to form a coherent structure at the fire temperature. As shown, the properties of eutectic phase depend on both particle size and chemical composition of fillers incorporated into the SR [31]. The formation of the eutectic phase-bonding mineral fillers with silica proceeds at a temperature above 800 °C. The additional incorporation of specified inorganic fluxing agents, mainly in the form of borates, on account of their low melting point, results in lowering the temperature of the formation of filler–silica eutectic phase, which advantageously influence the process of ceramization and consequently a reduction in the flammability of elastomeric composites (Table 2; Figs. 5–7) [32, 33].
Boric acid and borates form a protective glassy layer at a temperature of 325 °C that then begins to melt already at a temperature of 500 °C initiating the formation of eutectic phase [34, 35]. From the results presented in Figs. 5 and 6, it clearly follows that the incorporation of zinc borate decisively reduces the flammability of silicone rubber containing both silica and cenospheric filler. Undoubtedly, this is connected with the formation of ceramic uniform boundary layer (Fig. 7).
The tests carried out by the method of cone calorimetry show that a decisive decrease in fire hazard occurs in the case of silicone rubber containing the mixture of zinc borate and cenospheric filler covered with iron. Undoubtedly, the adsorption of polymeric chains on the particles of iron oxide reduces the segmental mobility of silicone rubber and consequently inhibits the radical reactions of chain transfer, characteristic of SR.
Analysis of the gaseous, thermal decomposition products, composites of silicone rubber
Based on the analysis of the FTIR spectra of gaseous products of the thermal decomposition of cross-linked silicone rubber, one can state that at the temperature of decomposition T = 550 °C, first of all carbon oxide and dioxide are recorded in the FTIR spectrum, as confirmed by an intensive peak at a wavelength of 2400 cm−1 and water, whose presence is confirmed by the signals at wavelength of 1800 and 3700 cm−1, respectively. It should be mentioned that within the spectral range 750–1300 cm−1, there appear distinct signals characteristic of cyclic siloxane compounds containing trimers D3, tetramers D4 and pentamers D5 [36] (Fig. 8).
Low molecular weight products of the thermal decomposition of silicone rubber in the form of volatile organic compounds (aliphatic hydrocarbons and aldehydes) are recorded at wavelength of 1300–1500 and 2600–3200 cm−1.
The character of FTIR spectra of gaseous products of the thermal decomposition of silicone rubber is practically unchanged after incorporation inorganic filler into its matrix (Fig. 9).
From the analysis of results presented in Figs. 10, 11 and 12, it follows that the cyclic siloxanes are recorded in FTIR spectra only at temperature T = 550 °C, while at T = 650 and 750 °C siloxanes undergo thermal decomposition and combustion (Fig. 10), as confirmed by an increase in the concentration of volatile organic hydrocarbons at T = 650 °C (Fig. 11) and carbon oxide, dioxide and water at T = 650 and 750 °C (Fig. 12). This indicates a low thermal decomposition rate of cyclic oligomers at a temperature of 550 °C. Under the conditions prevailing in the reactor, i.e., with a relatively short dwell time of the gaseous products of thermal decomposition of SR composites in the zone of high temperature (550 °C), the destruction processes of cyclic siloxanes proceed with a low effectiveness. It should be noted that at this temperature also methanal reaches a high concentration over 600 ppm. As a product of incomplete polysiloxane oxidation, as cyclic siloxanes, it undergoes thermal degradation and destruction at a higher range of temperature.
From among the gaseous organic hydrocarbons, it is methane that reaches the highest concentration over 200 ppm at T = 650 °C, with low concentrations of ethane, propane and ethylene (Fig. 11).
It deserves attention that at T = 550 °C, thus within the range of the maximal decomposition rate of silicone rubber composites, the lowest emission of cyclic siloxanes and volatile organic hydrocarbons is shown by the silicone rubber composites characterized by the highest thermal stability expressed with parameter T 5 , i.e., those filled with wollastonite or cenospheric filler covered with an iron layer. The increased thermal stability of composites SR-WO and SR-CEFE in relation to that of cross-linked silicone rubber is connected first of all with the adsorption of polymeric chains on the surface of filler particles. It should be also underlined that the analyses performed have shown a low catalytic activity of iron in relation to the radical reactions of thermal degradation.
Conclusions
The mineral fillers used decisively decrease the fire hazard created by silicone rubber composites. A decrease in the flammability of silicone rubber in the presence of aluminum hydroxide results from the thermal decomposition of Al(OH)3 to water and Al2O3. Both the endothermic decomposition of Al(OH)3 and the evaporation of water decrease the energetic balance of the elastomer under combustion, as confirmed by the values of THR parameter.
Flame silica considerably influences the decrease in the value of HRR parameter, especially MLR of the polysiloxane tested. The flame-retardant action of silica results from the formation of hydrogen bonds between oxygen in the main chain of silicone rubber (Si–O–Si) and hydrogen of silently groups present on the surface of silica, which reduces the segmental mobility of the silicone rubber chains and leads to the formation of strong internal polymer–filler interactions.
The flame-retardant action of cenospheric filler covered with iron is connected with both the advantageous effect of cenospheres on the structure of boundary layer and the adsorption of polymeric chains on the surface of iron oxide particles, which results in a considerable decrease in the segmental mobility of polymeric chains and consequently a reduction in the effectiveness of decomposition and chain transfer.
The high effectiveness of wollastonite in the processes of stamping out flame is connected with the formation, at elevated temperatures, of microbridges between silica particles and wollastonite that considerably reduce he processes of pyrolysis and facilitate the formation of a thermally stable insulating boundary layer.
An additional incorporation to the elastomer matrix specified inorganic fluxing agents, mainly in the form of borates, on account of their low melting point results in a decrease in the temperature of forming the eutectic filler–silica phase, which advantageously influences the ceramization process and consequently a reduction in the flammability of elastomeric composites.
Within the temperature range of the maximal rate of silicone rubber decomposition, the lowest emission of cyclic siloxanes and volatile organic hydrocarbons is shown by the composites of silicone rubber filled with wollastonite or cenospheric filler covered with iron layer.
The thermal decomposition of silicone rubber composites in the oxidizing atmosphere in fluidized bed strongly depends on the process temperature. At a temperature lower than 650 °C, the main thermal decomposition products include cyclic trimmers D3–D5, water, CO and CO2 as well as HCOH. An increase in temperature causes the decomposition of oligomeric cyclic siloxanes, hydrocarbons and aldehydes to CO, CO2 and H2O.
References
Rybiński P, Janowska G, Kucharska-Jastrząbek A, Pająk A, Wójcik I, Wesołek D, Bujnowicz K. Flammability of vulcanizates of diene rubbers. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;107:1219–24.
Rybiński P, Janowska G, Dobrzyńska R, Kucharska A. Effect of halogenless flame retardants on the thermal properties and fire hazard of cross-linked EVM/NBR rubber blends. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:771–82.
Purser DA, Woolley WD. Biological studies of combustion atmosphere. J Fire Sci. 1983;1:118–44.
Purser DA. Behavioral impairment in smoke environments. Toxicology. 1996;115:7–23.
Rybiński P, Janowska G. Thermal properties and flammability of nanocomposites based on nitrile rubbers and activated halloysite nanotubes and carbon nanofibers. Thermochim Acta. 2012;549:6–12.
Bouch RR. Rate of heat release and related fire parameters for silicones. Fire Safety. 1991;17:1–12.
Hshieh F-Y. Shielding effects of silica ash layer on the combustion of silicones and their possible applications on the fire retardancy of organic polymers. Fire Mater. 1998;22:69–76.
Hamdani S, Longuet C, Perrin D, Lopez-Cuesta J-M, Ganachaud F. Flame retardancy of silicone-based materials. Polym Degrad Stab. 2009;94:465–95.
Hanu LG, Simon GP, Cheng Y-B. Thermal stability and flammability of silicone polymer composites. Polym Degrad Stab. 2006;91:1373–9.
Demir MM, Menceloglu YZ, Erman B. Effect of filler amount on thermoplastic properties of poly(dimethylsiloxane) networks. Polymer. 2005;46:4127–34.
Arrighi V, Higgins JS, Burgess AN, Floudas G. Local dynamics of poly(dimethylsiloxane) in the presence of reinforcing filler particles. Polymer. 1998;39:6369–76.
Rybiński P, Żukowski W, Bradło D. Influence of cenosphere particles on thermal properties composites of silicone rubber. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1097. doi:10.1007/s3-015-4829-0.
Kowarska B, Żukowski W, Baron J. Conversion of diethylamine into nitrogen oxides during combustion in chemically active fluidized bed. Proc Ecopole. 2015. doi:10.2429/proc.2015.9(1)013.
Gilman JW, Ritchie SJ, Kashiwagi T, Lomakin S. Fire retardant additives for polymeric materials- Char formation from silica gel- potassium carbonate. Fire Mater. 1997;21:23–32.
Pape PG, Romanesko DJ, The role of silicone powders in reducing the heat release rate and evolution of smoke in flame retardant thermoplastic, in Presented at ANTEC 97, Toronto 1997.
Hermansson A, Hjertberg T, Sultan BA. The flame retardant mechanism of polyolefins modified with chalk and silicon elastomer. Fire Mater. 2003;27:51–70.
Rybiński P, Janowska G, Helwig M, Dąbrowski W, Majewski K. Flammability of butadiene-acrylonitrile rubbers. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2004;4:249–56.
Hamandi S, Longuet C, Lopez-Cuesta J-M, Ganachaud F. Calcium and aluminum- based fillers as flame retardant additives in silicone matrices. I. Blend preparation and thermal properties. Polym Degrad Stab. 2010;95:1911–9.
Harper CA. Modern plastic Handbook. Maryland: McGraw Hill; 1999. p. 4.26–36.
Rybiński P, Janowska G, Jóźwiak MA, Jóźwiak M. Thermal stability and flammability of styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) composites. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;113:43–52.
Kozakiewicz J, Huang SJ. The effect of filler surface modifications on the properties of poly(dimethyl siloxane) elastomers. Org Coat Plast Chem. 1981;44:343–6.
Zhuralvlev LT, Potapov VV. Density of silanol groups on the surface of silica precipitated from hydrothermal solution. Rus J Phys Chem. 2006;80(7):1119–28.
Rybiński P, Janowska G. Flammability and other properties of elastomeric materials and nanomaterials. Part II. Polimery. 2013;58(7–8):533–42.
Yuan QW, Mark JE. Reinforcement of PDMS networks by blended and in situ generated silica fillers having various sizes, size distributions, and modified surfaces. Macromol Chem Phys. 1999;200:206–20.
Kashiwagi T, Gilman JW, Butler KM, Harris RH, Shields JR, Asano A. Flame retardant mechanism of silica gel/silicas. Fire Mater. 2000;94:465–95.
Kolay PK, Bhusal S. Recovery of hollow spherical particles with two different (densities from coal fly ash and their characterization. Fuel. 2014;117:118–24.
Kolay PK, Singh DN. Physical, chemical, mineralogical and thermal properties of cenospheres from as ash lagoon. Cem Concr Res. 2001;31:539–42.
Yih SM, Tu CH, Kuo ST, Quo LW. Recovery of cenospheres and application to the manufacture of insulation materials. J Chin Inst Chem Eng. 1998;18(1):23–9.
Li Z, Lin W, Moon K-S, Wilkins SJ, Yao Y, Watkins K, Morato L, Wong Ch. Metal catalyst residues in carbon nanotubes decrease the thermal stability of carbon nanotube/silicone composites. Carbon. 2011;49:4138–48.
Roy PK, Surekha P, Rajagopal C, Chatterjee SN, Choudhary V. Effect of benzil and cobalt stearate on the aging of low-density polyethylene films. Polym Degrad Stab. 2005;90(3):577–85.
Mansouri J, Burford RP, Cheng YB, Hanu L. Formation of strong ceramified ash from silicone-based compositions. J Mater Sci. 2005;40:5741–9.
Mansuri J, Burford RP, Cheng YB. Pyrolysis behaviour of silicone based ceramifying composites. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2006;425:7–14.
Hanu LG, Simon GP, Mancouri J, Burford RP, Cheng YB. Development of polymer-ceramic composites for improved fire resistance. J Mater Process Technol. 2004;153–154:401–7.
Marosi G, Marton A, Anna P, Bertlan G, Marosfoi B, Szep A. Ceramic precusor in flame retardant system. Polym Degrad Stab. 2002;77:259–65.
Volf MB. Chemical approach to glass. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 1984. p. 194, 419.
Hamandi-Devarennes S, Longuet C, Sonnier R, Ganachaud F, Lopez-Cuesta J-M. Calcium and aluminum -based fillers as flame- retardant additives in silicone matrices. III. Investigations on fire reaction. Polym Degrad Stab. 2013;98:2021–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Rybiński, P., Żukowski, W. & Bradło, D. Effect of cenospheric fillers on the flammability and fire hazard of silicone rubber composites. J Therm Anal Calorim 125, 1373–1386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5741-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5741-y