Abstract
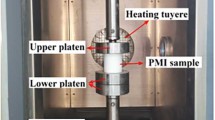
The aim of this article is to examine the influence of the pressing direction on the behavior of the thermal expansion coefficient α(T) of graphite foam in the 300–780 K temperature range. The thermal expansion coefficients of two samples, one pressed along the direction of strong interactions and the other pressed along the direction of weak interactions, were measured along three directions X, Y, and Z. The results show that the dilatometric behavior of the material changes from one direction to another. The values of α(T) vary widely depending on the measurement direction. Anisotropy becomes even more intense when the sample is pressed along the direction of weak interactions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby MF. The properties of foams and lattices. Phil Trans R Soc A. 2006;364:15–30.
Wang X, Zhong J, Wang Y, Yu M, Wang Y. The study on the formation of graphitic foam. Mater Lett. 2007;61:741–6.
Zerrouk I, Ionov SG, Popov VP, Hamamda S. Anisotropy of thermal expansion coefficient of pressed graphite foam measured over the temperature interval 20–500 °C. Mater Sci Forum. 2007;534–536:241–4.
Min G, Zengmin S, Weidong C, Hui L. Anisotropy of mesophase pitch-derived carbon foams. Carbon. 2007;45:141–5.
Tondi G, Fierro V, Pizzi A, Celzard A. Tannin-based carbon foams. Carbon. 2009;47:1480–92.
Novikova CI. Thermal expansion coefficient of solids states. Moscow: Nauka; 1974. (in Russian).
Lima AMF, Musumeci AW, Liu HW, Waclawik ER, Silva GG. Purity evaluation and influence of carbon nanotube on carbon nanotube/graphite thermal stability. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;97:257–63.
Jakubinek MB, Whitman CA, White MA. Negative thermal expansion materials. J Therm Anal Calorim 2009. doi:10.1007/s10973-009-0458-9.
Hamamda S, Popov V. Coefficient de dilatation thermique du graphite pyrolitique mesuré dans l’intervalle de température 4–30 K. Carbon. 1990;28:447–8.
Lifchitz IM. On the thermal properties of chain and layered structures at low temperatures. Zh. Eks. Teor. Fiz. 1952;22(4):475–86 (in Russian); see also Teor. Fiz. Khimii. 1953;27(2):294–5 (in Russian).
Hamamda S, Popov VP, Khotkevitch VI. Effect of pressure on the thermal expansion coefficient of pyrolytic graphite in the strong bonding direction in the temperature interval 5–300 K. Carbon. 1988;26:908–10.
Coronado JS, Chung DDL. Thermomechanical behavior of a graphite foam. Carbon. 2003;41:1175–80.
Gallego NC, Burchell TD, Klett JW. Irradiation effects on graphite foam. Carbon. 2006;44:618–28.
Poco Graphite, Inc. 1601 South State Street, Decatur, TX 76234, USA, Poco foams datasheet.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorbani, T., Zerrouk, I., Aouabdia, Y. et al. Influence of the pressing direction on thermal expansion coefficient of graphite foam. J Therm Anal Calorim 102, 667–670 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-0686-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-0686-z