Abstract
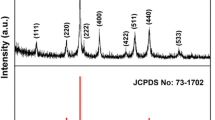
Hydrothermal method was adapted to synthesis NiCo2O4 nanoparticles by varying nickel and cobalt precursor concentration as 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3 ratios. X-ray diffraction (XRD) results revealed the spinel NiCo2O4 structure belongs to \({\rm{Fd}}\overline {\rm{3}} {\rm{m}}\) space group system with face-centered cubic crystal structure. Raman characteristic peaks observed at 495 and 654 cm−1 explored Eg and A2g modes of spinel NiCo2O4 product. Photoluminescence (PL) results revealed the hole recombination of Ni2+/Co2+ ions from 3d-Eg and 3d-Tg electronic state of spinel NiCo2O4 material. The characteristic Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) metal–oxygen bands appeared at 658 and 558 cm−1 revealed the spinel-type crystal structure. SEM image revealed the NiCo2O4 spherical nanoparticles formation with an average particle size of around 500 nm. The cyclic voltammetry studies revealed the estimated average specific capacitance value of NC3 (NiCo2O4 spherical nanoparticles) as 542 F g−1 relatively higher than NC1 and NC2. The electro impendence spectroscopy results explored the small arc formation in high frequency range and very low charge transfer resistance (R ct), which resulted high conductive active materials. The estimated specific capacitance for NC3 exhibited superior galvanstatic charging and discharging (GCD) characteristics with high specific capacitance of 294 F g−1 at high current density of 1 A g−1 and revealed that the obtained electrode is suitable for supercapacitor applications.
Graphical abstract
Hydrothermal synthesis using an excess of Co source leads to smaller and more uniform particle size. This particle size and the slightly larger crystallite size formed in the materials leads to the improved electrochemical performance of the particles.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Umeshbabu E, Rajeshkhanna G, Ranga Rao G (2016) J Solid State Electrochem 20:837–1844
Jokar E, Izad A, Shahrokhian S (2015) J Solid State Electrochem 19:269–274
Zhang Y, Wang J, Yu L, Wang L, Wan P, Wei H, Lin L, Hussain S (2017) Ceramics International 43:2057–2062
Qi X, Zheng W, He G, Tian T, Du N, Wang L (2017) Chem Eng J 309:426–434
Ezeigwe ER, Khiew PS, Siong CW, Tan TT (2017) J Alloys Compd 693:133–1142
Huanga W, Cao Y, Huang W, Chen Y, Peng J, Lee X, Tu J (2017) Appl Surf Sci 396:804–811
Chen S, Chen H, Fan M, Li C, Shu K (2016) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 80:119–125
Xue J, Ma W, Wang L, Cui H (2016) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 78:120–125
Bera S, Das N, Pal M, Mahanty S, Jana S (2015) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 76:402–413
Xu L, Chen H, Shu K (2016) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 77:463–469
Wang L, Ma W, Li Y, Cui H (2016) Synthesis of δ-MnO2 with nanoflower-like architecture by a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4275-x
Zou L, Shen X, Wang Q, Wang Z, Yang X, Jing M (2015) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 75:54–62
Sathishkumar K, Shanmugam N, Kannadasan N, Cholan S, Viruthagiri G (2015) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 74:621–630
Ge C, Hou Z, He B, Zeng F, Cao J, Liu Y, Kuang Y (2012) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 63:146–152
Cui H, Zhang F, Ma W, Wang L, Xue J (2016) J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 79:83–88
Umeshbabu E, Rajeshkhanna G, Justin P, Ranga Rao G (2015) RSC Adv 5:66657–66666
Liu Q, Xiao K, Xu Z, Li N, Su Z, Wanga J, Chen S (2013) RSC Adv 3:34372–34380
Zhong H, Wang L, Li R, Wang W, Ou N, Tong X (2012) Mater Chem 22:5656–5665
Delong Li, Youning Gong, Miaosheng Wang, Chunxu Pan (2017) Nano-Micro Lett. https://doi.org/doi 10.1007/s40820-016-0117-1
Cui B, Lin H, Liu Z, Li B, Sun P, Zhao X, Liu C (2009) J Phys Chem C 113:14083–14087
Rada H, Haghighia M, Eslamia A, Rahmania F, Rahemia N (2016) Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:5335–5350
Patzke GR, Zhou Y, Kontic R, Conrad F (2010) Angew Chem Int Edn 50:826–859
Meher SK, Justin P, RangaRao G (2011) Nanoscale 3:683–692
Wang X, Han X, Lim M, Singh N, Gan CL, Jan M, Lee PS (2012) J. Phys. Chem. C 116:12448–12454
Nicholson RS, Shain I (1964) Anal. Chem. 36(706):1351–1355
Ma G, Zhang Z, Peng H, Sun K, Ran F, Lei Z (2016) J Solid State Electrochem 20:1613–1624
Yang L, Cheng S, Ding Y, Zhu X, Wang ZL, Liu M (2012) Nano Lett 12:321–325
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by UGC Start-Up Research Grant No.F.30-326/2016 (BSR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saravanakumar, B., Priyadharshini, T., Ravi, G. et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of spherical NiCO2O4 nanoparticles as a positive electrode for pseudocapacitor applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 84, 297–305 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4504-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4504-y