Abstract
In this study, large-sized monolithic methyltrimethoxysilane-based silica aerogels were prepared via a facile sol–gel route using ambient pressure drying. The structural, morphological, and hydrophobic properties of the aerogels were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method, and contact angle. Thermal conductivity, thermal stability, and mechanical properties of the samples were also evaluated. The ambient pressure dried aerogels showed macro-pore structure and low density (as low as 75 kg m−3). The Young’s modulus of the aerogels was observed to increase from 0.043 to 1.102 MPa with an increase in the density of the aerogels from 75 to 141 kg m−3. Simultaneously, the aerogels exhibited superhydrophobicity (>150°), low thermal conductivity (0.036 W m−1 K−1), and good thermal stability in air atmosphere. Both the simple fabricating process and the superior performance of the monolithic silica aerogel make it as a promising candidate for energy-saving sector.
Graphical Abstract
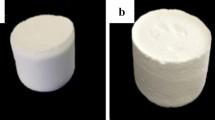
Large-sized monolithic methyltrimethoxysilane-based silica aerogel with superhydrophobicity was successfully prepared by a one-step sol–gel method via ambient pressure drying using methyltrimethoxysilane as precursor, distilled water as solvent, and ammonia as alkali catalyst.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt M, Schwertfeger F (1998) Applications for silica aerogel products. J Non-Cryst Solids 225:364–368
Hüsing N, Schubert U (1998) Aerogels-airy materials: chemistry, structure, and properties. Angew Chem Int Ed 37:22–45
Kistler S (1932) Coherent expanded-aerogels. J Phys Chem 36:52–64
Scherer GW (1990) Theory of drying. J Am Ceram Soc 73:3–14
Leventis N, Lu H (2011) Polymer-crosslinked aerogels. In: Aegerter MA, Leventis N, Koebel MM (eds) Aerogels handbook, Springer, New York, p 251–285
Wei TY, Lu SY, Chang YC (2008) Transparent, hydrophobic composite aerogels with high mechanical strength and low high-temperature thermal conductivities. J Phys Chem B 112:11881–11886
Prakash SS, Brinker CJ, Hurd AJ (1995) Silica aerogel films at ambient pressure. J Non-Cryst Solids 190:264–275
Prakash SS, Hurd AJ, Rao SM, Brinker CJ (1995) Silica aerogel films prepared at ambient pressure by using surface derivatization to induce reversible drying shrinkage. Nature 374:439
Wang J, Zhang Y, Wei Y, Zhang X (2015) Fast and one-pot synthesis of silica aerogels via a quasi-solvent-exchange-free ambient pressure drying process. Micropor Mesopor Mater 218:192–198
Yun S, Luo H, Gao Y (2014) Ambient-pressure drying synthesis of large resorcinol-formaldehyde-reinforced silica aerogels with enhanced mechanical strength and superhydrophobicity. J Mater Chem A 2:14542–14549
Yun S, Luo H, Gao Y (2015) Low-density, hydrophobic, highly flexible ambient-pressure-dried monolithic bridged silsesquioxane aerogels. J Mater Chem A 3:3390–3398
Einarsrud MA, Nilsen E (1998) Strengthening of water glass and colloidal sol based silica gels by aging in TEOS. J Non-Cryst Solids 226:122–128
Rolison DR, Dunn B (2001) Electrically conductive oxide aerogels: new materials in electrochemistry. J Mater Chem 11:963–980
Haereid S, Dahle M, Lima S, Einarsrud MA (1995) Preparation and properties of monolithic silica xerogels from TEOS-based alcogels aged in silane solutions. J Non-Cryst Solids 186:96–103
Hæreid S, Nilsen E, Einarsrud MA (1996) Properties of silica gels aged in TEOS. J Non-Cryst Solids 204:228–234
Wei TY, Chang TF, Lu SY, Chang YC (2007) Preparation of monolithic silica aerogel of low thermal conductivity by ambient pressure drying. J Am Ceram Soc 90:2003–2007
Rao AP, Rao AV, Pajonk G (2007) Hydrophobic and physical properties of the ambient pressure dried silica aerogels with sodium silicate precursor using various surface modification agents. Appl Surf Sci 253:6032–6040
Sarawade PB, Shao GN, Quang DV, Kim HT (2013) Effect of various structure directing agents on the physicochemical properties of the silica aerogels prepared at an ambient pressure. Appl Surf Sci 287:84–90
He P, Gao XD, Li XM, Jiang ZW, Yang ZH, Wang CL, Gu ZY (2014) Highly transparent silica aerogel thick films with hierarchical porosity from water glass via ambient pressure drying. Mater Chem Phys 147:65–74
Shao Z, Luo F, Cheng X, Zhang Y (2013) Superhydrophobic sodium silicate based silica aerogel prepared by ambient pressure drying. Mater Chem Phys 141:570–575
Bangi UK, Jung IK, Park CS, Baek S, Park HH (2013) Optically transparent silica aerogels based on sodium silicate by a two step sol-gel process and ambient pressure drying. Solid State Sci 18:50–57
Schwertfeger F, Frank D, Schmidt M (1998) Hydrophobic waterglass based aerogels without solvent exchange or supercritical drying. J Non-Cryst Solids 225:24–29
Lee C, Kim G, Hyun S (2002) Synthesis of silica aerogels from waterglass via new modified ambient drying. J Mater Sci 37:2237–2241
Hwang SW, Kim TY, Hyun SH (2010) Effect of surface modification conditions on the synthesis of mesoporous crack-free silica aerogel monoliths from waterglass via ambient-drying. Micropor Mesopor Mater 130:295–302
Rao AV, Kulkarni MM, Pajonk GM, Amalnerkar DP, Seth T (2003) Synthesis and characterization of hydrophobic silica aerogels using trimethylethoxysilane as a co-precursor. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 27:103–109
Rao AV, Kulkarni MM, Amalnerkar DP, Seth T (2003) Superhydrophobic silica aerogels based on methyltrimethoxysilane precursor. J Non-Cryst Solids 330:187–195
Ochoa M, Durães L, Beja A (2012) Portugal, study of the suitability of silica based xerogels synthesized using ethyltrimethoxysilane and/or methyltrimethoxysilane precursors for aerospace applications. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 61:151–160
Rao AV, Bhagat SD, Hirashima H, Pajonk G (2006) Synthesis of flexible silica aerogels using methyltrimethoxysilane (MTMS) precursor. J Colloid Interf Sci 300:279–285
Nadargi DY, Rao AV (2009) Methyltriethoxysilane: new precursor for synthesizing silica aerogels. J Alloys Comp 467:397–404
Nadargi D, Latthe S, Rao AV (2009) Effect of post-treatment (gel aging) on the properties of methyltrimethoxysilane based silica aerogels prepared by two-step sol-gel process. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 49:53–59
Aravind PR, Soraru GD (2011) High surface area methyltriethoxysilane-derived aerogels by ambient pressure drying. J Porous Mater 18:159–165
Bhagat SD, Oh CS, Kim YH, Ahn YS, Yeo JG (2007) Methyltrimethoxysilane based monolithic silica aerogels via ambient pressure drying. Micropor Mesopor Mater 100:350–355
Xu B, Cai JY, Xie Z, Wang L, Burgar I, Finn N, Cai Z, Wong L (2012) An improved method for preparing monolithic aerogels based on methyltrimethoxysilane at ambient pressure part II: microstructure and performance of the aerogels. Micropor Mesopor Mater 148:152–158
Xu B, Cai JY, Finn N, Cai Z (2012) An improved method for preparing monolithic aerogels based on methyltrimethoxysilane at ambient pressure part I: process development and macrostructures of the aerogels. Micropor Mesopor Mater 148:145–151
Yun S, Luo H, Gao Y (2014) Superhydrophobic silica aerogel microspheres from methyltrimethoxysilane: rapid synthesis via ambient pressure drying and excellent absorption properties. RSC Adv 4:4535–4542
Wong JC, Kaymak H, Tingaut P, Brunner S, Koebel MM (2015) Mechanical and thermal properties of nanofibrillated cellulose reinforced silica aerogel composites. Micropor Mesopor Mater 217:150–158
Kanamori K, Aizawa M, Nakanishi K, Hanada T (2007) New transparent methylsilsesquioxane aerogels and xerogels with improved mechanical properties. Adv Mater 19:1589–1593
Liu M, Gan L, Pang Y, Xu Z, Hao Z, Chen L (2008) Synthesis of titania-silica aerogel-like microspheres by a water-in-oil emulsion method via ambient pressure drying and their photocatalytic properties. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 317:490–495
Deshpande R, Hua DW, Smith DM, Brinker CJ (1992) Pore structure evolution in silica gel during aging/drying. III. Effects of surface tension. J Non-Cryst Solids 144:32–44
Brinker CJ, Deshpande R, Smith DM (1996) Preparation of high porosity xerogels by chemical surface modification. U.S. Patent No. 5,565,142.
Hrubesh L (1990) Aerogels: the world’s lightest solids. Chem Ind 24:824–827.
Swimm K, Reichenauer G, Vidi S, Ebert HP (2009) Gas pressure dependence of the heat transport in porous solids with pores smaller than 10 μm. Int J Thermophys 30:1329–1342
Lu X, Schuster MA (1992) Thermal conductivity of monolithic organic aerogels. Science 255:971
Hayase G, Kanamori K, Abe K, Yano H, Maeno A, Kaji H, Nakanishi K (2014) Polymethylsilsesquioxane-cellulose nanofiber biocomposite aerogels with high thermal insulation, bendability, and superhydrophobicity. ACS Appl Mater Interf 6:9466–9471
Wang Z, Wang D, Qian Z, Guo J, Dong H, Zhao N, Xu J (2015) Robust superhydrophobic bridged silsesquioxane aerogels with tunable performances and their applications. ACS Appl Mater Interf 7:2016–2024
Groβ J, Fricke J (1995) Scaling of elastic properties in highly porous nanostructured aerogels. Nanostruct Mater 6:905–908
Parmenter KE, Milstein F (1998) Mechanical properties of silica aerogels. J Non-Cryst Solids 223:179–189
Girona MM, Roig A, Molins E, Martınez E, Esteve J (1999) Micromechanical properties of silica aerogels. Appl Phys Lett 75:653–655
Kucheyev S, Stadermann M, Shin S, Satcher J, Gammon S, Letts S, Van Buuren T, Hamza A (2012) Super-compressibility of ultralow-density nanoporous silica. Adv Mater 24:776–780
Yokogawa H, Yokoyama M (1995) Hydrophobic silica aerogels. J Non-Cryst Solids 18:23–29
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by State Outstanding Young Scholars (contract No: 51325203), Opening Funding of Jiangsu Provincial Engineering Laboratory for Advanced Materials of Salt Chemical Industry (contract No: SF201506 and SF201507), and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grants No: BK20130420).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yun, S., Guo, T., Zhang, J. et al. Facile synthesis of large-sized monolithic methyltrimethoxysilane-based silica aerogel via ambient pressure drying. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 83, 53–63 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4377-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4377-0