Abstract
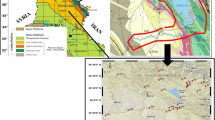
226Ra, 238U, 232Th, and 40K radionuclides have been determined using gamma-ray spectrometry in soil samples collected from urban areas in the southern governorates of Jordan and showed average concentrations of (39 ± 18), (45 ± 20), (23 ± 13), and (233 ± 128) Bq kg−1, respectively. The corresponding radio-elemental concentrations in the existing geological features were obtained and examined for the relative depletion/enrichment processes and state of equilibrium in soils. Radium equivalent activity, hazard indices, and annual gonadal dose equivalent do not exceed the permissible limits. Absorbed dose rates in air outdoor and external effective dose showed average values of 44.0 nGy h−1 and 54.4 μSv y−1, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hamarneh IF, Awadallah MI (2009) Soil radioactivity levels and radiation hazard assessment in the highlands of northern Jordan. Radiat Meas 44:102–110
Al-Shboul KF, Alali AE, Al-Khodire HY, Batayneh IM, Al-Shurafat AW (2017) Assessment of secular equilibrium and determination of natural and artificial radionuclide concentrations in the zone surrounding the site of the first nuclear reactor in Jordan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314(2):1353–1360
Hamideen MS, Sharaf J (2012) Natural radioactivity investigations in soil samples obtained from phosphate hills in the Russaifa region, Jordan. Radiat Phys Chem 81:1559–1562
Al-Khateeb HM, Al-Qudah AA, Alzoubi FY, Alqadi MK, Aljarrah KM (2012) Radon concentration and radon effective dose rate in dwellings of some villages in the district of Ajloun, Jordan. Appl Radiat Isot 70:1579–1582
Abumurad KM, Al-Tamimi MH (2005) Natural radioactivity due to radon in Soum region, Jordan. Radiat Meas 39:77–80
Al-Hamarneh I, Wreikat A, Toukan K (2003) Radioactivity concentrations of 40K, 134Cs, 137Cs, 90Sr, 241Am, 238Pu and 239+240Pu radionuclides in Jordanian soil samples. J Environ Radioact 67:53–67
Al-Jundi J, Al-Bataina BA, Abu-Rukah Y, Shehadeh HM (2003) Natural radioactivity concentrations in soil samples along the Amman Aqaba Highway, Jordan. Radiat Meas 36:555–560
Saleh H, Abu Shayeb M (2014) Natural radioactivity distribution of southern part of Jordan (Ma’an) soil. Annal Nucl Energ 65:184–189
Al-Kharouf SJ, Al-Hamarneh IF, Dababneh M (2008) Natural radioactivity, dose assessment and uranium uptake by agricultural crops at Khan Al-Zabeeb, Jordan. J Environ Radioact 99:1192–1199
Abusini M, Al-ayasreh K, Al-Jundi J (2008) Determination of uranium, thorium and potassium activity concentrations in soil cores in Araba Valley, Jordan. Radiat Protect Dosimet 128:213–216
Harbottle G, Evans CV (1997) Gamma-ray methods for determining natural and anthropogenic radionuclides in environmental and soil science. Radioact Radiochem 8(1):38–46
UNSCEAR (2008) United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effect of Atomic Radiation report to the general assembly. Annex B: exposures of the public and workers from various sources of radiation. United Nations, New York
Srilatha MC, Rangaswamy DR, Sannappa J (2014) Measurement of natural radioactivity and radiation hazard assessment in the soil samples of Ramanagara and Tumkur districts, Karnataka, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303(1):993–1003
Tufail M, Asghar M, Akram M, Javied S, Khan K, Mujahid SA (2013) Measurement of natural radioactivity in soil from Peshawar basin of Pakistan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298:1085–1096
Reddy KU, Ningappa C, Sannappa J (2017) Natural radioactivity level in soils around Kolar Gold Fields, Kolar district, Karnataka, India. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 315:1–9
IAEA-TECDOC-1363 (2003) Guidelines for radioelement mapping using gamma ray spectrometry data. IAEA, Vienna
UNSCEAR (2000) Sources and effects of ionizing radiation. Report to general assembly, with scientific annexes, United Nations, New York
Tzortzis M, Tsertos H, Christofides S, Christodoulides G (2003) Gamma-ray measurements of naturally occurring radioactive samples from Cyprus characteristic geological rocks. Radiat Meas 37:221–229
Chiozzi P, Pasquale V, Verdoya M (2002) Naturally occurring radioactivity at the Alps-Apennines transition. Radiat Meas 35:147–154
NCRP Report No. 77 (1984) Exposures from the uranium series with emphasis on radon and its daughters. Bethesda, Maryland
Orgun Y, Altınsoy N, Sahin SY, Gungor Y, Gültekin AH, Karahan G, Karacık Z (2007) Natural and anthropogenic radionuclides in rocks and beach sands from Ezine region (Çanakkale), Western Anatolia, Turkey. Appl Rad Isot 65:739–747
Clark SP, Peterman ZE, Heier KS (1966) Abundance of uranium, thorium and potassium. Handbook of physical constants. Geol Soc Am Mem 97:521–524
Tzortzis M, Tsertos H (2004) Determination of thorium, uranium and potassium elemental concentrations in surface soils in Cyprus. J Environ Radioact 77:325–338
OECD (1979) Exposure to radiation from the natural radioactivity in building materials. Reported by a group of experts of the OECD. Nuclear Energy Agency, Paris
Beretka J, Mathew PJ (1985) Natural radioactivity of Australian building materials, industrial wastes and by-products. Health Phys 48:87–95
Kurnaz A, Küçükömeroğlu B, Keser R, Okumusoglu NT, Korkmaz F, Karahan G, Çevik U (2007) Determination of radioactivity levels and hazards of soil and sediment samples in Fırtına Valley (Rize, Turkey). Appl Radiat Isot 65:1281–1289
Arafa W (2004) Specific activity and hazards of granite samples collected from the Eastern Desert of Egypt. J Environ Radioact 75:315–327
Orgun Y, Altınsoy N, Gultekin AH, Karahan G, Celebi N (2005) Natural radioactivity levels in granitic plutons and groundwaters in Southeast part of Eskisehir, Turkey. Appl Radiat Isot 63:267–275
ICRP 60 (1990) Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. Annals of the ICRP. Pergamon Press, Oxford
UNSCEAR (1988) Sources, effects and risks of ionizing radiation. Report on the general assembly. UNSCEAR, New York
Mamont-Ciesla K, Gwiazdowski B, Biernacka M, Zak A (1982) Radioactivity of building materials in Poland. In: Vohra G, Pillai KC, Sadavisan S (eds) Natural radiation environment. Halsted Press, New York
Xinwei L, Lingqing W, Xiaodan J, Leipeng Y, Gelian D (2006) Specific activity and hazards of Archeozoic-Cambrian rock samples collected from the Weibei area of Shaanxi, China. Radiat Prot Dosim 118(3):352–359
Acknowledgements
The author would like to acknowledge the technical and financial support received by Al-Balqa Applied University, Salt, Jordan. Many thanks are due to Dr. M. Awadallah and Prof. M. Imran for their valuable assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Hamarneh, I.F. Hazard indices and annual effective dose due to terrestrial radioactivity in the urban areas in the south of Jordan. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 316, 139–151 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-5723-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-5723-6