Abstract
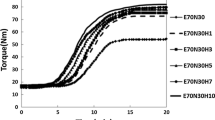
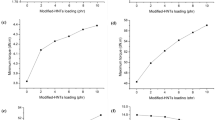
Halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) are not only promising as reinforcing fillers for rubber materials but also have potential for storing stearic acid (SA), an important sulfurization agent. In this study, SA/HNT intercalation compounds were prepared by a secondary intercalation method to improve the mechanical properties of styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) composites. The intercalation compounds were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and thermogravimetry. SA molecules successfully intercalated into the interlayer of the HNTs, with d001 increasing from 0.72 to 3.89 nm, and the intercalation rate of SA/HNTs reached 89.6%. The intercalation compound modified the processing properties and significantly improved the mechanical parameters of the filled SBR composites. The tensile and tear strengths of the obtained composites were improved by 454.1% and 193.5%, respectively, compared to those of the raw rubber material. The crosslinking density of the filled composites gradually increased with increasing filler content. SEM and TEM images indicated that the SA/HNT intercalation compound was physically dispersed in the SBR matrix. Further, many nanotubes exhibited a bending phenomenon caused by processing. The reinforcement effect of the intercalation compound is ascribed to its physical dispersion in the rubber matrix, which restricts rubber chain motion via trapping of the rubber chains and strong interactions between the rubber chains and SA functional groups.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin J, Luo C, Zhang Z, Yang W, Xing Z, He S, Bian X (2018) Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites Filled with KH560 Modified Halloysite Nanotubes. 2018 IEEE 2nd International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC) 617–620. https://doi.org/10.1109/cieec.2018.8745935
Akbari V, Jouyandeh M, Paran SMR, Ganjali MR, Abdollahi H, Vahabi H, Saeb MR (2020) Effect of surface treatment of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) on the kinetics of epoxy resin cure with amines. Polymers 12(4):930. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040930
Cavallaro G, Milioto S, Lazzara G (2020) Halloysite nanotubes: interfacial properties and applications in cultural heritage. Langmuir 36(14):3677–3689. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00573
Karami Z, Jazani OM, Navarchian AH, Karrabi M, Vahabi H, Saeb MR (2019) Well-cured silicone/halloysite nanotubes nanocomposite coatings. Prog Org Coat 129:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.01.029
Lvov Y, Wang W, Zhang L, Fakhrullin R (2016) Halloysite clay nanotubes for loading and sustained release of functional compounds. Adv Mater 28(6):1227–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201502341
Dulebová Ľ, Glogowska K, Hájek J, Fic J (2018) The effect of adding halloysite nanotubes as filler on the mechanical properties of low-density polyethylene. Mater Sci Forum 919:144–151. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.919.144
Jelić A, Marinković A, Sekulić M, Dikić S, Ugrinović V, Pavlović V, Putić S (2021) Design of halloysite modification for improvement of mechanical properties of the epoxy based nanocomposites. Polym Compos 42(5):2180–2192. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25967
Ahamad A, Kumar P (2020) Effect of reinforcing ability of halloysite nanotubes in styrene-butadiene rubber nanocomposites. Compos Commun 22:100440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100440
Du M, Guo B, Wan J, Zou Q, Jia D (2010) Effects of halloysite nanotubes on kinetics and activation energy of non-isothermal crystallization of polypropylene. J Polym Res 17(1):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-009-9296-5
Bai S, Sun X, Wu M, Shi X, Chen X, Yu X, Zhang Q (2020) Effects of pure and intercalated halloysites on thermal properties of phthalonitrile resin nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 177:109192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109192
Zheng Y, Wang X, Wu G (2020) Chemical modification of carbon fiber with diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid/halloysite nanotube as a multifunctional interfacial reinforcement for silicone resin composites. Polym Adv Technol 31(3):527–535. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4793
Du M, Guo B, Jia D (2006) Thermal stability and flame retardant effects of halloysite nanotubes on poly (propylene). Eur Polym J 42(6):1362–1369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2005.12.006
Zhang M, Zhao W, Zhang X, Li Z, Yu L, Li X, Zhang Z (2021) Nonfluoride-modified halloysite nanotube-based hybrid: potential for acquiring super-hydrophobicity and improving flame retardancy of epoxy resin. J Nanostruct Chem 11(3):353–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-020-00371-9
Deng Y, White GN, Dixon JB (2002) Effect of structural stress on the intercalation rate of kaolinite. J Colloid Interface Sci 250(2):379–393. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.2001.8208
Frost RL, Kristof J, Paroz GN, Kloprogge JT (1998) Molecular structure of dimethyl sulfoxide intercalated kaolinites. J Phys Chem B 102(43):8519–8532. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp982035f
Fu Y, Zhao D, Yao P, Wang W, Zhang L, Lvov Y (2015) Highly aging-resistant elastomers doped with antioxidant-loaded clay nanotubes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(15):8156–8165. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b00993
De Falco A, Goyanes S, Rubiolo GH, Mondragon I, Marzocca A (2007) Carbon nanotubes as reinforcement of styrene–butadiene rubber. Appl Surf Sci 254(1):262–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.07.049
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Zhang Q, Lu Y (2010) Gas barrier properties of natural rubber/kaolin composites prepared by melt blending. Appl Clay Sci 50(2):255–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2010.08.006
Flory PJ, Rehner J Jr (1943) Statistical mechanics of cross-linked polymer networks I. Rubberlike elasticity. J Chem Phys 11(11):512–520. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1723791
Tkach E, Bichaev M (2022) Properties of epoxy composites with halloysite nanotubes subjected to tensile testing. Proc FORM 2021:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79983-0_8
Xu T, Xin Y, Wang Y, Liao L, Li H, Ban J, Yang Y (2022) Simulation of β-dextranase from raw natural rubber to investigate structure and properties of natural rubber/halloysite composites. Polym Compos 43(2):798–810. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26411
Kouser S, Prabhu A, Prashantha K, Nagaraja GK, D’souza JN, Navada KM, Manasa DJ (2022) Modified halloysite nanotubes with Chitosan incorporated PVA/PVP bionanocomposite films: Thermal, mechanical properties and biocompatibility for tissue engineering. Colloids Surf A 634:127941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127941
Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Sun J, Wang Z (2017) Thermal behavior analysis of halloysite–dimethylsulfoxide intercalation complex. J Therm Anal Calorim 129(2):985–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6258-8
Zhang A, Zhang Y, Zhu Z (2019) Thermal properties of Halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) intercalation complexes-A review. E3S Web Conf 131:01055. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/201913101055
Mahrez N, Bendenia S, Marouf-Khelifa K, Batonneau-Gener I, Khelifa A (2015) Improving of the adsorption capacity of halloysite nanotubes intercalated with dimethyl sulfoxide. Compos Interfaces 22(6):403–417. https://doi.org/10.1080/09276440.2015.1036581
Wiewióra A (1969) Potassium acetate intercalation in kaolinite and its removal; effect of material characteristics. Proc Int Clay Conf 1:723–733
Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhang Y (2020) Preparation and intercalation structure model of halloysite-stearic acid intercalation compound. Appl Clay Sci 187:105451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2020.105451
Cheng H, Zhang S, Liu Q, Li X, Frost RL (2015) The molecular structure of kaolinite–potassium acetate intercalation complexes: a combined experimental and molecular dynamic simulation study. Appl Clay Sci 116:273–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.04.008
Fujii K, Nakagaito AN, Takagi H, Yonekura D (2014) Sulfuric acid treatment of halloysite nanoclay to improve the mechanical properties of PVA/halloysite transparent composite films. Compos Interfaces 21(4):319–327. https://doi.org/10.1080/15685543.2014.876307
Gârea SA, Ghebaur A, Constantin F, Iovu H (2011) New hybrid materials based on modified halloysite and unsaturated polyester resin. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 50(11):1096–1102. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2011.557818
Deng S, Zhang J, Ye L (2009) Halloysite–epoxy nanocomposites with improved particle dispersion through ball mill homogenisation and chemical treatments. Compos Sci Technol 69(14):2497–2505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2009.07.001
Djomgoue P, Njopwouo D (2013) FT-IR spectroscopy applied for surface clays characterization. J Surf Eng Mater Adv Technol 3(04):275–282. https://doi.org/10.4236/jsemat.2013.34037
Zich D, Zacher T, Darmo J, Szöcs V, Lorenc D, Janek M (2013) Far-infrared investigation of kaolinite and halloysite intercalates using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Vib Spectrosc 69:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2013.09.003
Zhang R, Li Y, He Y, Qin D (2020) Preparation of iodopropynyl butycarbamate loaded halloysite and its anti-mildew activity. J Mater Res Technol 9(5):10148–10156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.07.019
Martens WN, Ding Z, Frost RL, Kristof J, Kloprogge JT (2002) Raman spectroscopy of hydrazine-intercalated kaolinite at 77, 298, 323, 343 and 358 k. J Raman Spectrosc 33(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.812
Caglar B, Afsin B, Eren E, Tabak A, Cirak C, Cubuk O (2010) The spectral, structural and thermal characterizations of dimethyl sulphoxide, pyridine, Ethanol-amine and N-methyl formamide intercalated kaolinites. Z Naturforsch A 65(11):1009
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Wu Z, Zheng Q, Cheng H (2012) Thermal behavior analysis of kaolinite–dimethylsulfoxide intercalation complex. J Therm Anal Calorim 110(3):1167–1172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-011-2038-z
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Zhang Q, Frost RL (2010) Thermal behavior and decomposition of kaolinite–potassium acetate intercalation composite. Thermochim Acta 503:16–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2010.02.014
Costanzo PM, Giese RF (1986) Ordered halloysite: dimethylsulfoxide intercalate. Clays Clay Miner 34(1):105–107. https://doi.org/10.1346/ccmn.1986.0340115
Joussein E, Petit S, Fialips CI, Vieillard P, Righi D (2006) Differences in the dehydration-rehydration behavior of halloysites: New evidence and interpretations. Clays Clay Miner 54(4):473–484. https://doi.org/10.1346/ccmn.2006.0540408
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Frost RL (2010) Thermogravimetric analysis of selected coal-bearing strata kaolinite. Thermochim Acta 507:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2010.05.004
Mei D, Zhang B, Liu R, Zhang H, Liu J (2011) Preparation of stearic acid/halloysite nanotube composite as form-stable PCM for thermal energy storage. Int J Energy Res 35(9):828–834. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.1874
Frost RL, Kristof J, Horvath E, Kloprogge JT (1999) Deintercalation of dimethylsulphoxide intercalated kaolinites–a DTA/TGA and Raman spectroscopic study. Thermochim Acta 327(1–2):155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-6031(98)00605-4
Wang Y, Zhang H, Wu Y, Yang J, Zhang L (2005) Preparation and properties of natural rubber/rectorite nanocomposites. Eur Polym J 41(11):2776–2783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2005.05.019
Malas A, Pal P, Giri S, Mandal A, Das CK (2014) Synthesis and characterizations of modified expanded graphite/emulsion styrene butadiene rubber nanocomposites: Mechanical, dynamic mechanical and morphological properties. Compos B 58:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.10.028
Mahrez N, Bessaha F, Marouf-Khelifa K, Coruh A, Khelifa A (2020) Performance and mechanism of interaction of crystal violet with organohalloysite. Desalin Water Treat 207:410–419. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.26447
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Zhang S, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Liang P (2016) Characterization of kaolinite/styrene butadiene rubber composite: Mechanical properties and thermal stability. Appl Clay Sci 124:167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.02.002
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Natural Science Foundation Project of China (52064040), the National Natural Science Foundation Project of China (11562015), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (2018MS05061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing, Visualization: Kaiyuan Xiao; Supervision, Funding acquisition: Yinmin Zhang; Software, Formal analysis: Yongfeng Zhang; Resources, Conceptualization: Yanbing Gong.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, K., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Preparation of stearic acid/halloysite intercalation compound and their reinforcement for styrene butadiene rubber composite. J Polym Res 29, 451 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03275-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-03275-0