Abstract
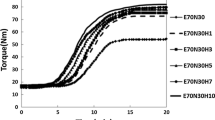
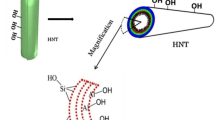
The halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) were modified using γ-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (γ-MPS), which interacts with the silanol and aluminol groups of the HNTs. Melt mixing technique was used to formulate the polymer composites using phenyl methyl silicone rubber (PVMQ) and various weight percentages of modified HNTs (mHNTs). The crosslinking density increases as a result of the HNTs modification by γ-MPS, increasing the interfacial and intertubular contacts as well as the degree of dispersion of the mHNTs within the PVMQ matrix. The influence of mHNTs on the cure and mechanical parameters, rebound resilience, abrasion resistance, hardness, heat buildup, and oil and solvent resistance of PVMQ is examined in this work. The amount of mHNTs in the PVMQ increased the maximum, minimum, and delta torque values as well as the optimum cure times and scorch, while decreasing the cure rate index (CRI) values. When the amount of mHNTs is increased, the tensile strength and modulus at 100% elongation of PVMQ rubber nanocomposites rises until 6 phr, after which they fall. The presence of mHNTs was found to improve the mechanical characteristics of nanocomposites, including tensile modulus, tensile strength, and tear strength. Due to the extensive intertubular connection, the PVMQ/mHNTs nanocomposites also showed improved oil and swelling resistance.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not Applicable.
References
Li Q, Zhao S, Pan Y (2010) Structure, morphology, and properties of HNBR filled with N550, SiO2, ZDMA, and two of three kinds of fillers. J Appl Polym Sci 117:421–427
Li H, Sun J, Song Y, Zheng Q (2009) The mechanical and viscoelastic properties of SSBR vulcanizates filled with organically modified montmorillonite and silica. J Mater Sci 44:1881–1888
Vishvanathperumal S, Gopalakannan S (2016) Reinforcement of ethylene vinyl acetate with carbon black/silica hybrid filler composites. In: Applied Mechanics and Materials (vol. 852, pp 16–22). Trans Tech Publications Ltd
Usuki A, Kojima Y, Kawasumi M, Okada A, Fukushima Y, Kurauchi T et al (1993) Synthesis of nylon 6-clay hybrid. J Mater Res 8:1179–1184
LeBaron PC, Pinnavaia TJ (2001) Clay nanolayer reinforcement of a silicone elastomer. Chem Mater 13:3760–3765
Vishvanathperumal S, Anand G (2021) Effect of Nanosilica and Crosslinking System on the Mechanical Properties and Swelling Resistance of EPDM/SBR Nanocomposites with and without TESPT. Silicon 13(10):3473–3497
Handge UA, Hedicke-Höchstötter K, Altstädt V (2010) Composites of polyamide 6 and silicate nanotubes of the mineral halloysite: influence of molecular weight on thermal, mechanical and rheological properties. Polymer 51(12):2690–2699
Vishvanathperumal S, Navaneethakrishnan V, Anand G, Gopalakannan S (2020) Evaluation of crosslink density using material constants of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer/styrene-butadiene rubber with different nanoclay loading: finite element analysis-simulation and experimental. Adv Sci Eng Med 12(5):632–642
Fakhru’l-Razi A, Atieh MA, Girun N, Chuah TG, El-Sadig M, Biak DRA (2006) Effect of multi-wall carbon nanotubes on the mechanical properties of natural rubber. Compos Struct 75(1–4):496–500
Yoon HJ, Shanker A, Wang Y, Kozminsky M, Jin Q, Palanisamy N, Burness ML, Azizi E, Simeone DM, Wicha MS, Kim J (2016) Tunable thermal-sensitive polymer–graphene oxide composite for efficient capture and release of viable circulating tumor cells. Adv Mater 28(24):4891–4897
Namasivayam M, Shapter J (2017) Factors affecting carbon nanotube fillers towards enhancement of thermal conductivity in polymer nanocomposites: a review. J Compos Mater 51(26):3657–3668
Badi N (2017) Non-linear PEG-based thermoresponsive polymer systems. Prog Polym Sci 66:54–79
Bag DS, Dubey R, Zhang N, Xie J, Varadan VK, Lal D, Mathur GN (2004) Chemical functionalization of carbon nanotubes with 3-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (3-MPTS). Smart Mater Struct 13(5):1263
Ma PC, Kim JK, Tang BZ (2006) Functionalization of carbon nanotubes using a silane coupling agent. Carbon 44(15):3232–3238
Das A, Costa FR, Wagenknecht U, Heinrich G (2008) Nanocomposites based on chloroprene rubber: effect of chemical nature and organic modification of nanoclay on the vulcanizate properties. Eur Polymer J 44(11):3456–3465
Liu P (2007) Polymer modified clay minerals: a review. Appl Clay Sci 38(1–2):64–76
Yoon KB, Sung HD, Hwang YY, Noh SK, Lee DH (2007) Modification of montmorillonite with oligomeric amine derivatives for polymer nanocomposite preparation. Appl Clay Sci 38(1–2):1–8
Zhang Z, Wen L, Jiang L (2018) Bioinspired smart asymmetric nanochannel membranes. Chem Soc Rev 47(2):322–356
Kim M, Hong CK, Choe S, Shim SE (2007) Synthesis of polystyrene brush on multiwalled carbon nanotubes treated with KMnO4 in the presence of a phase-transfer catalyst. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 45(19):4413–4420
Kharchenko SB, Douglas JF, Obrzut J, Grulke EA, Migler KB (2004) Flow-induced properties of nanotube-filled polymer materials. Nat Mater 3(8):564–568
Lu HB, Shen HB, Song ZL, Shing KS, Tao W, Nutt S (2005) Rod-like silicate–epoxy nanocomposites. Macromol Rapid Commun 26(18):1445–1450
Habibi Y, Dufresne A (2008) Highly filled bionanocomposites from functionalized polysaccharide nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 9(7):1974–1980
An L, Pan YZ, Shen XW, Lu HB, Yang YL (2008) Rod-like attapulgite/polyimide nanocomposites with simultaneously improved strength, toughness, thermal stability and related mechanisms. J Mater Chem 18(41):4928–4941
Churchman GJ, Theng BKG (1984) Interactions of halloysites with amides: mineralogical factors affecting complex formation. Clay Miner 19(2):161–175
Deng S, Zhang J, Ye L, Wu J (2008) Toughening epoxies with halloysite nanotubes. Polymer 49(23):5119–5127
Marney DCO, Russell LJ, Wu DY, Nguyen T, Cramm D, Rigopoulos N et al (2008) The suitability of halloysite nanotubes as a fire retardant for nylon 6. Polym Degrad Stab 93(10):1971–1978
Liu M, Guo B, Du M, Cai X, Jia D (2007) Properties of halloysite nanotube–epoxy resin hybrids and the interfacial reactions in the systems. Nanotechnology 18(45):455703
Rooj S, Das A, Thakur V, Mahaling RN, Bhowmick AK, Heinrich G (2010) Preparation and properties of natural nanocomposites based on natural rubber and naturally occurring halloysite nanotubes. Mater Design 31(4):2151–2156
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, De Heer W (2002) Carbon nanotube – the route toward applications. Science 297(5582):787–792
Tjong SC, Liang GD, Bao SP (2007) Electrical behavior of polypropylene/multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposites with low percolation threshold. Scripta Mater 57(6):461–464
Shchukin DG, Sukhorukov GB, Price RR, Lvov YM (2005) Halloysite nanotubes as biomimetic nanoreactors. Small 1(5):510–513
Du M, Guo B, Jia D (2006) Thermal stability and flame retardant effects of halloysite nanotubes on poly (propylene). Eur Polymer J 42(6):1362–1369
Das RK, Ragupathy K, Kumar TS, Vishvanathperumal S (2023) Effect of Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs) on Mechanical Properties of EPDM/NBR blend-nanocomposites. Polym Korea 47(2):221–232
Du M, Guo B, Jia D (2010) Newly emerging applications of halloysite nanotubes: a review. Polym Int 59(5):574–582
Lvov Y, Abdullayev E (2013) Functional polymer–clay nanotube composites with sustained release of chemical agents. Prog Polym Sci 38(10–11):1690–1719
Bidsorkhi HC, Adelnia H, Pour H, R. and, Soheilmoghaddam M (2015) Preparation and characterization of ethylene-vinyl acetate/halloysite nanotube nanocomposites. J Mater Sci 50:3237–3245
Padhi S, Achary R, P.G. and, Nayak NC (2015) Molecular transport behaviour of organic solvents through halloysite nanotubes filled ethylene–vinyl acetate copolymer. Bull Mater Sci 38:925–933
Ke Y, Yao X, Yang H, Ma Y, Liu Y (2016) The compression and friction of tubular rubber seal under the curved surface loading. Proc Inst Mech Eng J J Eng Tribol 231:14–22
Tan J, Chao YJ, Li X, Van Zee JW (2007) Degradation of silicone rubber under compression in a simulated PEM fuel cell environment. J Power Sources 172:782–789
Yao XF, Lei YM, Xiong C, Wang XQ, Wang YQ (2010) Experimental study on damage-induced Helium Leakage in Flexible Composites. J Reinforced Plast Compos 29:2936–2945
Stieghorst J, Majaura D, Wevering H, Doll T (2016). Toward 3D printing of medical implants: reduced lateral droplet spreading of silicone rubber under intense IR curing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 8(12):8239–8246
Yang H, Yao X, Yan H, Yuan Y, Dong Y, Liu Y (2018) Anisotropic hyper-viscoelastic behaviors of fabric reinforced rubber composites. Compos Struct 187:116–121
Yang H, Yao X, Ke Y, Ma Y, Liu Y (2016) Constitutive behaviors and mechanical characterizations of fabric reinforced rubber composites. Compos Struct 152:117–123
Ke Y, Yao X, Yang H, Liu X (2014) Kinetic friction characterizations of the tubular rubber seals. Tribol Int 72:35–41
Yang H, Xue FY, Shen W, Ke YC, Huang SH, Liu Y (2018) Analysis and inversion of contact stress for the Finite Thickness Neo-Hookean Layer. J Appl Mech 85:101008
Magennis EP, Hook AL, Williams P, Alexander MR (2016) Making silicone rubber highly resistant to bacterial attachment using thiol-ene grafting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:30780–30787
Yang H, Yao X, Zheng Z, Gong L, Yuan L, Yuan Y, Liu Y (2018) Highly sensitive and stretchable graphene-silicone rubber composites for strain sensing. Compos Sci Technol 167:371–378
Jie Z, Feng S, Ma Q (2010) Kinetics of the thermal degradation and thermal stability of conductive silicone rubber filled with conductive carbon black. J Appl Polym Sci 89:1548–1554
Dong Y, Ke Y, Zheng Z, Yang H, Yao X (2017) Effect of stress relaxation on sealing performance of the fabric rubber seal. Compos Sci Technol 151:291–301
Kim ES, Kim EJ, Shim JH, Yoon JS (2010) Thermal stability and ablation properties of silicone rubber composites. J Appl Polym Sci 110:1263–1270
Liu Y, Imae I, Kawakami Y (2010) Novel thermally resistant polysilphenylenesiloxanes with a high content of vinyl substituents. Polym Int 53:1259–1265
Chinn S, Deteresa S, Sawvel A, Shields A, Balazs B, Maxwell RS (2006) Chemical origins of permanent set in a peroxide cured filled silicone elastomer – tensile and 1H NMR analysis. Polym Degrad Stab 91:555–564
Camino G, Lomakin SM (2001) Lazzari. Polydimethylsiloxane thermal degradation part 1. Kinetic aspects. Polymer 42:2395–2402
Pasbakhsh P, Ismail H, Fauzi MA, Bakar AA (2010) EPDM/modified halloysite nanocomposites. Appl Clay Sci 48(3):405–413
Manoj KC, Kumari P, Rajesh C, Unnikrishnan G (2010) Aromatic liquid transport through filled EPDM/NBR blends. J Polym Res 17:1–9
Thomas PC, Tomlal JE, Selvin TP, Thomas S, Joseph K (2010) High-performance nanocomposites based on acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber with fillers of different particle size: mechanical and morphological studies. Polym Compos 31:1515–1524
Barton FM (1990) Handbook of polymer-liquid interaction parameters and solubility parameters. CRC Press, Inc, Boca Raton, Florida
Gonzalez-Perez G, Burillo G, Ogawa T, Avalos-Borja M (2012) Grafting of styrene and 2-vinylnaphthalene onto silicone rubber to improve radiation resistance. Polym Degrad Stab 97(8):1495–1503
Rabiei S, Shojaei A (2016) Vulcanization kinetics and reversion behavior of natural rubberr/styrene- butadiene rubber blend filled with nanodiamond – the role of sulfur curing system. Eur Polym J 81:98–113
Vishvanathperumal S, Anand G (2022) Effect of nanosilica on the mechanical properties, compression set, morphology, abrasion and swelling resistance of sulphur cured EPDM/SBR composites. Silicon 14(7):3523–3534
Vishvanathperumal S, Anand G (2020) Effect of nanoclay/nanosilica on the mechanical properties, abrasion and swelling resistance of EPDM/SBR composites. Silicon 12(8):1925–1941
Arrighi V, Gagliardi S, Higgins JS, Triolo A, Zanotti J-M (2002) Quasielastic neutron scattering as a probe of molecular motion in polymer-filler systems. E-MRS Spring Meeting. Strasbourg (France). N-15
Senthilvel K, Vishvanathperumal S, Prabu B, Baruch J, L (2016) Studies on the morphology, cure characteristics and mechanical properties of acrylonitrile butadiene rubber with hybrid filler (carbon black/silica) composite. Polym Polym Compos 24(7):473–480
Persello J Designing nanostructured particular fillers for elastomers. Role of nanostructure and polymer filler interactions in rubber reinforcement. E-MRS Spring Meeting 2002. Strasbourg (France). N-8
Zaborski M, Donnet JB (2003) Activity of fillers in elastomer networks of different structure. Macromol Symp 194:87–100
Vishvanathperumal S, Gopalakannan S (2017) Swelling properties, compression set behavior and abrasion resistance of ethylene-propylene-diene rubber/styrene butadiene rubber blend nanocomposites. Polym Korea 41(3):433–442
Vishvanathperumal S, Navaneethakrishnan V, Gopalakannan S (2018) The effect of Nanoclay and hybrid filler on curing characteristics, mechanical properties and swelling resistance of ethylene-vinyl acetate/styrene butadiene rubber blend composite. J Adv Microsc Res 13(4):469–476
Theja R, Kilari N, Vishvanathperumal S, Navaneethakrishnan V (2021) Modeling tensile modulus of nanoclay-filled ethylene–propylene–diene monomer/styrene–butadiene rubber using composite theories. J Rubber Res 24(5):847–856
Sundar R, Mohan SK, Vishvanathperumal S (2022) Effect of surface modified halloysite nanotubes (mHNTs) on the mechanical properties and swelling resistance of EPDM/NBR nanocomposites. Polym Korea 46(6):728–743
Ganeche PS, Balasubramanian P, Vishvanathperumal S (2022) Halloysite Nanotubes (HNTs)-Filled Ethylene-Propylene-diene Monomer/Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (EPDM/SBR) Composites: mechanical, swelling, and Morphological Properties. Silicon 14:6611–6620
Osabohien E, Egboh SHO (2008) Utilization of bowstring hemp fiber as a filler in natural rubber compounds. J Appl Polym Sci 107:210–214
Vishvanathperumal S, Gopalakannan S (2019) Effects of the nanoclay and crosslinking systems on the mechanical properties of ethylene-propylene-diene monomer/styrene butadiene rubber blends nanocomposite. Silicon 11(1):117–135
Ismail H, Ishiaku US, Lu ES, Mohd Ishak ZA (1997) The fatigue behaviour of filled Epoxidized Natural Rubber Compounds. Int J Polym Mater 38(3–4):275–289
Ismail H, Osman H, Ariffin A (2007) Curing characteristics, fatigue and hysteresis behavior of feldspar filled natural rubber vulcanizates. Polym -Plast Tech Eng 46:579–584
Brouzi AE, Vergnaud JM (2009) Diffusion of curing agent through the thickness of a bilayer EPDM system during the cure. Polym Test 28:392–401
Ragupathy K, Prabaharan G, Pragadish N, Vishvanathperumal S (2023) Effect of silica nanoparticles and modified silica nanoparticles on the mechanical and swelling properties of EPDM/SBR blend nanocomposites. Silicon pp 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-023-02497-1
Acknowledgements
This work was experimentally supported by the Maeon Laboratories, Chennai, the Head of the Mechanical Department of SA Engineering College, Chennai, and the Special thanks for Principal of SA Engineering College, Chennai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Govindan K - Research scholar and done a experimental work. Ramabalan S - Supervisor and supervise the overall work. Vishvanathperumal S - Wrote the main manuscript. Chockalingam S – Removal of the plagiarism. *All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Department of Mechanical Engineering, SA Engineering College, Chennai.
Consent to participate
No human subjects or animals were used in this study.
Consent for publication
This manuscript’s contents have not been previously published or subject to copyright. This manuscript’s material is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Govindan, K., Ramabalan, S., Vishvanathperumal, S. et al. Influence of halloysite nanotubes on mechanical and swelling properties of silicone rubber compound. J Polym Res 30, 310 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03632-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03632-7