Abstract
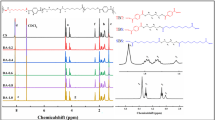
Suitable applications for a biodegradable polymer depend on its biodegradability (Bd), melting point (Tm) for thermal blending with biomass, tensile strength (σ) and tensile elongation (ε). A factorial experimental design was carried out in order to evaluate the targeted relationship among these properties, for synthesizing a novel biodegradable poly (butylene terephthalate-co-ε-caprolactone) (PBTCL). The results showed that the concentration of residual carboxyl end group ([COOH]) could inversely affect the number average molecular weight (Mn) and σ of PBTCL. Bd showed its loosely inversed relationship with crystallinity (Xc). The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis showed the increased ratio of aromatic/aliphatic segments in PBTCL increased its Tm, σ and Bd, but decreased ε and Xc. The regression models from the experimental design of Bd, Tm, σ and ε were plotted and overlaid; the targeted properties were achieved when the polycondensation temperature (Tp), the 1,4-butandiol/terephthalate (BDO/TPA), and the ε-caprolactone/terephthalate (CL/TPA) molar ratio were 255 °C, 1.39 mol/mol, and 1.48 mol/mol, respectively. Replicated PBTCL was synthesized under these optimal conditions, and the confirmed value of predicted Bd, Tm, σ, and ε were 58.9 ± 0.4%, 115 ± 2.5 °C, 17 ± 0.8 MPa, and 356 ± 22%, respectively. The targeted PBTCL showed comparable properties to a commercially available biodegradable plastic.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee LT, Hsu CY, Hung SP (2019) Promoted crystallization kinetics of biodegradable poly (butylene succinate) by a nucleation agent of green chemical. J Polym Res 26:255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1929-8
Ajioka M, Suizu H, Higuchi C, Kashima T (1998) Aliphatic polyesters and their copolymers synthesized through direct condensation polymerization. Polym Degrad Stab 59:137–143
Ahn BD, Kim SH, Kim YH, Yang JS (2001) Synthesis and characterization of the biodegradable copolymers from succinic acid and adipic acid with 1,4-butanediol. J Appl Polym Sci 82:2808–2826
Okada M (2002) Chemical syntheses of biodegradable polymers. Prog Polym Sci 27:87–133
Lai WC, Lee YC (2019) Effects of self-assembled sorbitol-derived compounds on the structures and properties of biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid) prepared by melt blending. J Polym Res 26:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1670-8
Martínez-Mercado E, Ruiz-Treviño FA, González-Montie A, Lugo-Uribe LE, Flores-Santos L (2019) Long chain branched structures of polylactic acid through reactive extrusion with styrene-acrylic copolymers bearing epoxy functional groups. J Polym Res 26:260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-019-1938-7
Ebrahimpour M, Safekordi AA, Mousavi SM, Heydarinasab A (2018) A miscibility study on biodegradable poly butylene succinate/polydioxanone blends. J Polym Res 25:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1411-4
Papadimitriou S, Bikiaris DN, Chrissafis K, Paraskevopoulos M, Mourtas SJ (2007) Synthesis, characterization, and thermal degradation mechanism of fast biodegradable PPSu/PCL copolymers. Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem 45:5076–5090
Endo M, Aida T, Onoue S (1987) ″immortal″ polymerization of ε-caprolactone initiated by aluminum porphyrin in the presence of alcohol. Macromolecules 20:2982–2988
Kricheldorf HR, Berl M, Scharnagl N (1988) Poly (lactones). 9. Polymerization mechanism of metal alkoxide initiated polymerizations of lactide and various lactones. Macromolecules 21:286–293
Righetti MC, Lorenzo MLD, Angiuli M, Tombari E, Pietra PL (2007) Poly(butylene terephthalate)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends: influence of PCL molecular mass on PBT melting and crystallization behavior. Eur Polym J 43:4726–4738
Lorenzo MLD, Pietra PL, Errico ME, Righetti MC, Angiuli M (2007) Poly(butylene terephthalate)/poly(ε-caprolactone) blends: miscibility and thermal and mechanical properties. Polym Eng Sci 47:323–329
Lim KY, Kim BC, Yoon KJ (2003) Structural and physical properties of biodegradable copolyesters from poly (ethylene terephthalate) and polycaprolactone blends. J Appl Polym Sci 88:131–138
Jun HS, Kim BO, Kim YC, Chang HN, Woo SI (1994) Synthesis of copolyesters containing poly (ethylene terephthalate) and poly(ε-caprolactone) units and their susceptibility to Pseudomonas. sp. lipase. J Environ Polym Degrad 2:9–18
Seretoudi G, Bikiaris DN, Panayiotous C (2002) Synthesis, characterization characterization and biodegradability of poly (ethylene succinate/poly(ε-caprolactone) block copolymers. Polymer 43:5405–5415
Cheng XM, Luo XL, Li ZB, Ma DZ (1999) Synthesis and structure of butylene terethphalate-ε-caprolactone copolyesters. Chin Chem Lett 10:593–596
Tripathy AR, MacKnight WJ, Kukureka SN (2004) In-situ copolymerization of cyclic poly (butylenes terephthalate) oligomers and ε-caprolactone. Macromolecules 37:6793–6800
Witt U, Müller RJ, Deckwer DW (1997) Biodegradation behavior and material of aliphatic/aromatic polyesters of commercial importance. J Envirom Polym Degrad 5:81–89
Lee SH, Lim SW, Lee KH (1999) Properties of potentially biodegradable copolyesters of (succinic acid−1,4-butylenediol)/(dimethyl terephthalate−1,4-butylenediol). Polym Int 48:861–867
Kondratowicz FŁ, Ukielski R (2009) Synthesis and hydrolytic degradation of poly(ethylene succinate) and poly(ethylene terephthalate) copolymers. Polym Degrad Stab 94:375–382
Papageorgiou GZ, Nanaki SG, Bikiaris DN (2010) Synthesis and characterization of novel poly(propylene terephthalate-co-adipate) biodegradable random copolyesters. Polym Degrad Stab 95:627–637
Park SS, Jun HW, Im SS (1998) Kinetics of forming poly (butylene succinate) (PBS) oligomer in the presence of MBTO catalyst. Polym Eng Sci 38:905–913
Bikiaris DN, Achilias DS (2006) Synthesis of poly (alkylene succinate) biodegradable polyesters I. Mathematical modeling of the esterification reaction. Polymer 47:4851–4860
Bikiaris DN, Achilias DS (2008) Synthesis of poly (alkylene succinate) biodegradable polyesters, part II: mathematical modeling of the esterification reaction. Polymer 49:3677–3685
Tripathy AR, Elmoumni A, Winter HH, MacKnight WJ (2005) Effects of catalysts and polymerization temperature on the in-situ polymerization of cyclic poly (butylene terethphalate) oligomers for composite applications. Macromolecules 38:709–716
Endah YK, Han SH, Kim JH, Kim NK, Kim WN, Lee HS, Lee HJ (2016) Solid-state polymerization and characterization of a copolyamide based on adipic acid, 1,4-butanediamine, and 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid. J Appl Polym Sci https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43391
Aust N, Gahleitner M, Reichelt K, Raninger B (2006) Optimization of run parameters of temperature-rising elution fractionation with aid of a factorial design experiment. Polym Test 25:896–903
Ramos DV, da Costa HM, Rocha MCG, de Gomes SA (2006) Study of different peroxide types on the modification of LLDPE. Part 1. Factorial experimental design and thermal properties. Polym Test 25:306–312
Oprea S, Vlad S, Stanciu A (2000) Optimization of the synthesis of polyurethane acrylates with polyester compounds. Eur Polym J 36:2409–2416
Solomon OF, Ciutǎ IZ (1962) Détermination de la viscosité intrinsèque de solutions de polymères par une simple détermination de la viscosité. Appl Polym Sci 6:683–686
Wang CH, Tsai PH, Kan LS, Chen CW (2013) Synthesis and characterization of copolymeric aliphatic–aromatic esters derived from terephthalic acid, 1,4-butanediol, and ε-caprolactone by physical, thermal, and mechanical properties and NMR measurements. J Appl Polym Sci 127:4385–4394
Tsai PH, Wang CH, Kan LS, Chen CW (2012) Studies on the optimal conditions for synthesizing poly (butylene succinate-co-terephthalate) copolyesters with targeted properties. Asia Pac J Chem Eng 7(Suppl. 1):S88–S94
Askeland DR (1984) The science and engineering of materials. Wadsworth, Belmont, California
Montgomery DC (2004) Design and analysis of experiments. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Storey RF, Sherman JW (2002) Kinetics and mechanism of the stannous octoate-catalyzed bulk polymerization of ε-caprolactone. Macromolecules 35:1504–1512
Rosa DS, Lopes DR, Calil MR (2005) Thermal properties and enzymatic degradation of blends of poly(ε-caprolactone) with starches. Polym Test 24:756–761
Xu YX, Xu J, Liu DH, Guo BH, Xie XM (2008) Synthesis and characterization of biodegradable poly(butylene succinate-co-propylene succinate)s. J Appl Polym Sci 109:1881–1889
Li FX, Xu XJ, Hao QG, Li QB, Yu JY, Cao A (2006) Effects of comonomer sequential structure on thermal and crystallization behaviors of biodegradable poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene terephthalate)s. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 44:1635–1644
Acknowledgments
Technical support from both the Institute of Chemistry and the Core Facility for Protein Structural Analysis, supported by National Core Facility Program for Biotechnology, is gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, PH., Wang, CH., Kan, LS. et al. Targeted biodegradability and physical properties of poly(butylene terephthalate-co-ε-caprolactone). J Polym Res 27, 121 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02096-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-020-02096-3