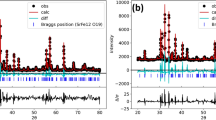
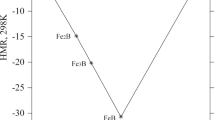
Abstract
In previous literatures, the influence of doping atoms in some suitable positions of Fe on the magnetic properties of iron-based alloys was briefly introduced, but the variation trend of the effects with doping atom content is not reported in detail. In the present work, Fe–V alloys were studied, and the effect of occupied state of V atom on the magnetic properties and charge transfer was investigated by the first-principles calculations and Mössbauer spectroscopy. The results show that the average magnetic moment of Fe atom increases with the increase of Fe–V bond. V atom has a great magnetic effect on the first (1NN-Fe) and second (2NN-Fe) nearest neighbors Fe. With the increase of V content, the magnetic effect of V atom on 1NN-Fe decreases gradually which is due to the hybridizations between Fe3d and V3d spin-down electrons, but that on 2NN-Fe is weaker when V content is low. As V content continues to increase, the strengthening of the interaction between 1NN-Fe and 2NN-Fe can lead to the enhancement of the ferromagnetism of 2NN-Fe. However, the magnetic properties of 2NN-Fe continue to decrease under the influence of V3d spin-down electrons when V content is too high. In addition, the results of charge transfer and magnetic properties of Fe–V alloys studied by Mössbauer spectroscopy are in good agreement with those by first-principles calculation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandran, M., Iorio, L.E., Subramanian, P.R.: Effect of nitrogen on the magnetic moment of a-Fe and FeCo alloys from first-principle calculations. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 033912 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2435814
Yin, Z.P., Pickett, W.E.: Antiphase magnetic boundaries in iron-based superconductors: a first-principle density-functional theory study. Phys. Rev. B. 80, 144522 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevb.80.144522
Yang, Z.-h., Wang, X., Liu, L., Xu-ping, S.: Structural, magnetic and electronic properties of FeF2 by first-principle calculation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 22(386-390), 386 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1003-6923(11)61188-6
Jacob, B.J., Chapman, S.L., Dudarev, P., Ma, W.: The dynamic of magnetism in Fe-Cr alloys with Cr clustering. Phys. Rev. B. 99, 184413 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.99.184413
Sundararajan, V., Sahu, B.R., Kanhere, D.G., Panat, P.V., Das, G.P.: Cohesive, electronic and magnetic properties of the transition metal aluminides FeAl CoAl and NiAl. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 7, 6019–6034 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/7/30/007
Ren, J., Zhang, H., Cheng, X.-L.: Electronic and magnetic properties of all 3d transition-metal-doped ZnO monolayers. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 113, 2243–2250 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/qua.24442
Shirai, M.: Electronic and magnetic properties of 3d transition-metal-doped GaAs. Phys. E. 10, 143–147 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1386-9477(01)00070-4
Mahadevan, P., Solovyev, I.V., Terakura, K.: Low-temperature spin dynamics of doped manganites: roles of Mn t2g, Mn eg, and O 2p states. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter. 60, 11439 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.60.11439
Wang, S., Yu, J.: Magnetic behaviors of 3d transition metal-doped silicane: a first-principle study. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31, 2789–2795 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4532-4
Li, J.-B., Liu, H.-X.: Theoretical research of diluted magnetic semiconductors: GaN monolayer doped with transition metal atoms. Superlattice. Microst. 120, 382–388 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2018.06.008
Cranshaw, E.: The disturbance produced in an iron lattice by Cr atoms and some other solutes (Mössbauer effect). J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 2, 615–624 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1088/0305-4608/2/3/028
Wertheim, G.K., Buchanan, D.N.E., Wernick, J.H.: 57Fe hyperfine fields in iron-co alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 1602–1603 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1660356
Rubinstein, M.: Hyperfine field spectra of binary Fe-co alloys: nuclear magnetic resonance of 57Fe and 59Co. Phys. Rev. 172, 277–283 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.172.277
Marcus, H., Fine, M.E., Schwartz, L.H.: Mössbauer-effect study of solid-solution and precipitated Fe-rich Fe-Mo alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 36, 4750–4758 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1709214
Sauer, W.E., Reynik, R.J.: Electronic and magnetic structure of dilute iron-base alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 42, 1604–1606 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1660357
Môri, N., Mitsui, T.: Magnetic properties on σ-phase of Fe-V alloys. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 22, 931 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1143/JPSJ.22.931
Nunes, C.B., Paduani, C., dos Santos, C.T., Izario, H.J., Coelho, A.A., Ghivelder, L.: Magnetostriction of Fe100-xVx alloys for 5.2<x<40.7. J. Alloys Compd. 553, 233–238 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.11.034
Cieslak, J., Tobola, J., Dubiel, S.M.: Theoretical study of magnetic properties and hyperfine interactions in σ-phase Fe-V alloys. Intermetallics. 22, 7–12 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2011.10.015
Liu, H.-Y., Wang, J.-J., Jin, J.-F., Liu, C.-M., Zhang, H.-Y.: A first-principles investigation on the effect of the divacancy defect on magnetic properties of Fe94V6 alloy. J. Appl. Phys. 124, 163904 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5042012
Shi, H., Huang, Z.B., Tse, J.S., Lin, H.Q.: Magnetic behavior of Fe(se,Te) systems: first-principles calculations. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 3296 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3624759
Gorbunova, M.A., Sein, I.R., Makurin, Y.N., Kiiko, V.S., Ivanovskii, A.L.: Electronic and magnetic properties of beryllium oxide with 3d impurities from first-principles calculations. Physica B. 400, 47–52 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2007.06.017
Zhang, H., Punkkinen, M.P.J., Johansson, B., Vitos, L.: Elastic parameters of paramagnetic iron-based alloys from first-principles calculations. Phys. Rev. B. 85, 054107 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.85.054107
Zhang, D., Shangguan, Q., Liu, F., Zhang, M.: Site preference of alloying elements in DO22-Ni3V phase: phase-field and first-principles study. Met. Mater. Int. 21, 623–627 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-015-5027-0
Qin, G., Wang, X., Zheng, J., Kong, C., Zeng, B.: First-principles investigation of the electronic and magnetic properties of ZnO nanosheet with intrinsic defects. Comput. Mater. Sci. 81, 259–263 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.08.018
Idczak, R., Kaśków, B., Konieczny, R., Chojcan, J.: Mössbauer study of vacancy-solute pairs in iron-based binary alloys. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 577, 411794 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411794
Chojcan, J.: Interactions between impurity atoms of 3d transition metals dissolved in iron. J. Alloys. Comp. 264, 50–53 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(97)00264-8
Idczak, R., Konieczny, R., Chojcan, J.: An enthalpy of solution of chromium in iron studied with 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy. Physica B. 407, 2078–2081 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2012.02.009
Das, T.P.: Calculation of magnetic and electric hyperfine fields in metals. Phys. Scr. 11, 121 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/11/3-4/003
Dubiel, S.M., Zukrowski, J.: Mossbauer effect study of charge and spin transfer in Fe-Cr. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 23, 214–228 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(81)90137-2
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully appreciate the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51471048), the Basic Research Program of Key Laboratory of Liaoning Province (Grant No. LZ2015035), and 111Project (Grant No. B20029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HY., Wang, JJ., Jin, JF. et al. Magnetic Effect of the Occupied State of V Atom in Fe–V Alloy: First-Principles Calculation and Mössbauer Spectroscopy. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 1425–1433 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05860-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-05860-8