Abstract
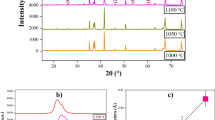
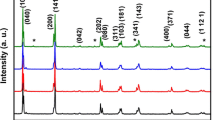
Polycrystalline Bi 0.85Eu 0.15FeO 3 ceramics were synthesized by solid-state reaction method with rapid liquid phase sintering process at various sintering temperatures. The dependence of structural, microstructural, electrical, and magnetic properties on sintering temperature was systematically investigated. X-ray diffraction measurements reveal that single perovskite phase is developed in Bi 0.85Eu 0.15FeO 3 ceramics sintered at 850 and 870∘ C, while secondary phases can be detected in the samples sintered at 890∘ C due to the volatilization of Bi 3+ ions, and the crystallinity increases with increasing sintering temperature from 850 to 890 °C. The scanning electron microscopy investigation has suggested that the grain size increases with increasing sintering temperature from 855 t o 890∘ C; while the pore size decreases with increasing sintering temperature from 850 to 870∘ C and then increases with a further increase of sintering temperature. The electrical and magnetic measurements show that the leakage current, dielectric constant, dielectric loss, and magnetic properties are strongly dependent on the sintering temperature. The Bi 0.85Eu 0.15FeO 3 ceramics sintered at 870∘ C have the lower leakage current, higher dielectric constant, and lower dielectric loss. The room temperature magnetization increases with increasing sintering temperature from 850 to 890 °C. The possible reason for all the above observations was discussed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar, A., Varshney, D.: Ceram. Int. 38, 3935 (2012)
Arora, M., Sati, P.C., Chauhan, S., Chhoker, S., Panwar, A.K., Kumar, M.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26, 443 (2013)
Kumar, A., Yadav, K.L.: J. Alloy. Compd. 554, 138 (2013)
Singh, V., Sharma, S., Dwivedi, R.K., Kumar, M., Kotnala, R.K., Mehra, N.C., Tandon, R.P.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26, 657 (2013)
Jha, P.A., Jha, P.K., Jha, A.K., Dwivedi, R.K.: Mater. Res. Bull 48, 101 (2013)
Chauhan, S., Kumar, M., Chhoker, S., Katyal, S.C., Singh, H., Jewariya, M., Yadav, K.L.: Solid State Commun. 152, 525 (2012)
Liu, J., Li, M.Y., Hu, Z.Q., Pei, L., Wang, J., Liu, X.L., Zhao, X.Z.: Appl. Phys. A 102, 713 (2011)
Durga Rao, T., Karthik, T., Asthana, S.: J. Rare Earth 31, 370 (2013)
Liu, J., Fang, L., Zheng, F.G., Ju, S., Shen, M.R.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 022511, 95 (2009)
Uniyal, P., Yadav, K.L.: Vol. 105, p 07D914 (2009)
Zhang, X.Q., Sui, Y., Wang, X.J., Wang, Y., Wang, Z.: J. Alloy. Compd. 507, 157 (2010)
Zhang, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, X.G., Ma, T., Yuan, Z.B.: Ceram. Int. 38, 4765 (2012)
Lee, Y.J., Kim, J.S., Han, S.H., Kang, H.W., Lee, H.G., Cheon, C.: J. Korean Phys. Soc. 61, 947 (2012)
Yasin Shami, M., Awan, M.S., Anis-Ur-Rehman, M.: J. Electron. Mater 41, 2216 (2012)
Fu, C.L., Long, X.L., Cai, W., Chen, G., Deng, X.L.: Ferroelectrics 445, 114 (2013)
Zhang, S.X., Luo, W.J., Wang, D.L., Ma, Y.W.: Mater. Lett. 63, 1820 (2009)
Liu, J., Li, M.Y., Hu, Z.Q., Pei, L., Wang, J., Liu, X.L., Zhao, X.Z.: Appl. Phys. A 102, 713 (2011)
Jha, P.A., Jha, A.K.: J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 1511 (2013)
Mishra, P., Sonia, Kumar: P.: J. Alloy. Compd 545, 210 (2012)
Huang, F.Z., Lu, X.M., Wang, Z., Lin, W.W., Kan, Y., Bo, H.F., Cai, W., Zhu, J.S.: Appl. Phys. A 97, 699 (2009)
Yang, H.B., Lin, Y., Wang, F., Luo, H.J.: Mater. Manuf. Process 23, 489 (2008)
Singh, V.R., Dixit, A., Garg, A., Agrawal, D.C.: Appl. Phys. A 90, 197 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 11305142, 11175159, and 51302250), Zhengzhou Administration of Science and Technology of Henan Province of China (131PPTGG411-10), and Key Members of the Outstanding Young Teacher of Zhengzhou University of Light Industry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, H.Y., Liu, H.Z., Du, J.F. et al. Effect of Sintering Temperature on the Microstructure, Electrical, and Magnetic Properties of Bi 0 . 8 5 Eu 0 . 1 5 FeO 3 Ceramics. J Supercond Nov Magn 27, 2105–2110 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2558-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2558-4