Abstract
Objectives
Examine trends in aggressive behavior from 1991 to 2015, investigate whether these trends apply equally to all individuals, and explore the extent to which differences in trends over time cluster within families.
Methods
Our study included 69,465 measures from 40,400 individuals, from 15,437 Dutch families. Aggression was measured between 1 and 4 times by self-report. We fitted a mixed effects model, modeling the effect of time, age, and gender on aggression, and considering the three levels of nesting in the data, i.e. repeated measures, individuals, and families. To investigate if individual differences in trends in aggression over time cluster within families, variance in aggression and in time and age effects was partitioned into within- and between family variance components.
Results
We found a steady decline in aggression over time, between 1991 and 2015, as well as over the life course. Across time and age, women had slightly higher levels of aggression than men. There was clear evidence for clustering within, and variation between families, both in overall aggression levels and in time effects.
Conclusions
We confirm earlier findings of a decline in aggression over the past decades. Not all individuals follow the downward trend over time for aggression to the same extent. Trends over time cluster within families, demonstrating that family factors are not only important to explain variation in aggression levels, but also in understanding differences between individuals in time trends.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Aggression, behavior that intends to inflict harm on others (Berkowitz 1993; Lorenz 1966), can be encountered at home, at school, at the workplace, and elsewhere in the course of daily life. Aggression is a common type of human behavior (Tuvblad and Baker 2011), that comes in various forms, ranging from non-physical, verbal, and relational aggression, to physical aggression (Crick and Grotpeter 1995; Crick et al. 1999). Previous research has shown that males and females tend to differ in the form of aggression they portray. Physical aggression is more common in males, while indirect aggression seems to be more common in females (Hess and Hagen 2006; Card et al. 2008; Pickett et al. 2013; Beatton et al. 2018; Thomson et al. 2019). Aggression typically decreases across the life-course (Alink et al. 2006; Cairns et al. 1989; Cairns and Cairns 1994; Karriker-Jaffe et al. 2008; Loeber and Stouthamer-Loeber 1998; Tremblay et al. 2004; Tremblay 2010), while since the mid-nineties a declining trend in aggressive behavior at the population level has been observed (e.g., Pickett et al. 2013; Kann et al. 2016; Frøyland and von Soest 2018). It is well known that individual differences in aggression tend to cluster within families (Margolin et al. 2016, Repetti et al. 2002; Besemer et al. 2017; van de Weijer et al. 2014), but a novel question is if the change in aggressive behavior that is observed at the population level over time clusters within families. Here we address this question, after establishing that the general decline in aggression at the population level that is suggested in earlier studies replicates in Dutch society.
Trends in Aggression Over Time
Most studies on trends in aggression over time have found declining levels over the last few decades. In the United States, the prevalence of adolescents having been in a physical fight decreased from 42.5% in 1991, to 22.6% in 2015 (Kann et al. 2016), while violent offending in adults decreased from 1991 to 2019 (US Department of Justice 2019). In Norway, Frøyland and von Soest (2018) observed a decline in the prevalence of physical aggression in adolescence from 22.6% in 2007, to 12.8% in 2015. Pickett et al. (2013) found downward trends in physical fighting in adolescence from 2002 to 2010, in 19 out of 30 countries they investigated. Physical fighting in adolescents and violent crime in adults decreased in both males and females, but slightly faster in males, indicating that sex differences in physical aggression are decreasing (Beatton et al. 2018). Clear statistics on trends in broader measures of aggression in everyday interactions (including non-physical, relational or verbal aggression) are lacking.
The downward trend we see in most physical aggression and violent crime statistics can be the consequence of multiple influences. Broadly, these can be divided into societal and developmental influences. Societal influences include period and cohort effects. Most studies suggest period effects are the main driving force behind the downward trends in aggression and violence (e.g. Fabio et al. 2006). Period effects affect the entire population, i.e., people of all ages and birth cohorts. Several specific period effects have been suggested in past studies that could explain such trends, for example increased policing and incarceration rates, lead poisoning, declining hard drug markets, technological advances, and economic circumstances (Farrell et al. 2014).
In addition to potential period effects, the observed downward trend in aggressive behavior over the past decades could also be the consequence of cohort, or generational, effects. These are societal effects that affect only individuals from a certain birth-cohort. For example, Neugebauer et al. (1999) found an increased prevalence of antisocial personality disorder in a cohort of Dutch men prenatally exposed to severe maternal prenatal malnutrition during the harsh winter of 1944–1945 at the end of the Second World War. A sufficiently large birth cohort exposed to cohort-specific causes of aggressive behavior, could impact aggression trends on a populational level.
Trends in Aggression Over Age
Temporal changes in behavior at the population level may also be due to developmental influences, defined as age, or life-course, effects. Physical aggression tends to peak at age 2–4 years and then declines to a lower level during the school years (Alink et al. 2006; Cairns et al. 1989; Cairns and Cairns 1994; Karriker-Jaffe et al. 2008; Loeber and Stouthamer-Loeber 1998; Tremblay et al. 2004; Tremblay 2010). Social or relational aggression emerges in the preschool years, and continues through childhood and adolescence (Underwood 2003). Because there are highs and lows in a nation’s birthrate, the average age of a population will also change over time, which can be reflected in aggression trends at the population level. For example, most western societies are ageing, having more older, and thereby less aggressive, individuals.
Familial Clustering
Multiple studies have established that aggression, antisocial behavior, and violent crime cluster within families (Besemer et al. 2017; Margolin et al. 2016, Repetti et al. 2002; van de Weijer et al. 2014; Veroude et al. 2016; Yu and Gamble 2008). Such studies tend to rely on two approaches. One is to identify factors that vary between families, and assess their effects. This approach has the benefit that it provides information on specific family factors that are thought to play a role, which we then may target in interventions or policy. This approach has led to an extensive list of family factors related to psychosocial environment, social economic circumstances, and biological background, which can drive individual differences through a multitude of pathways (Tolan et al. 2013; Farrington et al. 2017; Jolliffe et al. 2017; Labella and Masten 2018). Many of these family influences are interrelated, and difficult to disentangle, adding to the complexity of the etiology of problem behavior. Guerra and Leidy (2008) provide an extensive overview of how individual characteristics, and contexts in which children are raised, can accumulate and interact, increasing or decreasing the risk of aggressive behavior. Dodge and Pettit (2003) illustrate the reciprocal nature of different influences on chronic conduct problems in a biopsychosocial model that includes a wide range of reciprocal influences situated in multiple domains: biological predisposition, parenting, peers, sociocultural context, and mental processes. When studying the effect of individual family factors, it is hard to account for their interdependency with other factors, and there is a risk of overestimating the causal effect of any single factor.
A second approach to study the role of family is to model family factors as one interrelated, but latent, construct. This approach does not require the identification and assessment of factors that vary between families, but does necessitate that outcome traits such as aggression are measured on multiple individuals from the same family. Using this design, family factors are defined as the combined total set of influences that lead to more similarities among individuals from within the same family than among individuals from different families.
Both approaches have their distinct advantages and disadvantages: the first approach requires measurement of the relevant family factors, while running the risk of not identifying important ones, but allows a design that does not require multiple individuals from the same family to take part in the study. The second approach does not require the identification of specific family factors, and allows us to get an understanding of the totality of influences that are specifically family based, without identifying these influences. If this second approach would offer little evidence for a significant ‘between families’ effect, the search to identify risk factors for aggression should be directed elsewhere.
Familial Clustering of Trends
Not only the levels or prevalence of violent and aggressive behavior is clustered within families, but developmental changes in these behaviors could also be more similar among family members than between families. Sampson and Laub, for example, argued that strong informal social bonds with family members lead to desistance from deviant behavior in adulthood (Sampson and Laub 1994; Laub and Sampson 2006). Persons from families with stronger social bonds between relatives might therefore all be more likely to desist, while those from families with weaker ties are more likely to persist in deviant behavior. In accordance with this line of reasoning, Van de Rakt et al. (2008) found intergenerational similarities in the developmental trajectories of criminal behavior among a large number of Dutch families and Eley et al. (2003) showed, in a twin study, that such similarities in developmental trajectories of aggressive antisocial behavior were largely mediated by genetic influences.
Although changes in criminal and aggressive behavior over the lifespan seem to cluster within families, this does not mean that time effects on aggression, reflecting changes in society, show similar clustering within families. We are not aware of any studies which investigated whether the beneficial downward trend in aggression over time that we see in the population also clusters within families. These trends in aggression over time may be explained by factors that affect all individuals in a population in a similar manner. In this case, individual differences in these time trends will be explained by the variation in initial aggression levels. However, time trends may also differ between individuals because changes in aggression over time reflect changes in underlying risk factors to which individuals are differently exposed, and which may be shared by family members. These changes can vary from economic circumstances, to changing role models or peers, to increased institutional control. If this is the case, time-trends are not a tide that raises or lowers all boats. Changes in society which may be beneficial to most, could harm others. Societal changes that affect families differently, may have a direct effect on aggression, or moderate the effect of other changes in society. A study by Odgers et al. (2015), for example, showed that living alongside more affluent neighbors predicts greater involvement in antisocial behavior among low-income boys. This suggests that non-conformity to beneficial economic change, may be one of the mechanisms that could lead to clustering of time effects on aggression within families. Regardless of the underlying mechanism, we expect time effects to differ between families. Consequently, we expect to see clustering of these effects within families.
The Current Study
In this study, we investigate the effect of time, age, and gender on a broad behavioral measure of aggression, in a large cohort of Dutch multi-generation families with longitudinal data collected between 1991 and 2015, with a focus on assessing whether time and age effects cluster within families, i.e. are more similar within than between families. We use a novel approach in aggression research, by fitting a mixed effects model (Snijders and Bosker 2012) to repeated measures of self-reported aggression of individuals within families, born between 1927 and 2001, aged 12–70 years. By specifying random effects in the model, the variance in overall aggression levels and in time and age effects is partitioned into within- and between family variance components. The random effects for families give an indication to what extent aggression levels and trends in aggression cluster within families. This informs us on the importance of family factors in explaining individual differences in trends in aggression over time and age.
Methods
Data Collection and Participants
We analyzed longitudinal data, collected in twins, their parents and siblings who registered with the Netherlands Twin Register (NTR). Adult twins and their family members enter the Adult Netherlands Twin Register (ANTR) at different ages and newborn and young twins enter the Young Netherlands Twin Register (YNTR). When twins from the YNTR turn 18, they and their entire family automatically joins the ANTR and the ANTR data collection.
Survey data are collected in all participants every few years (Ligthart et al. 2019), in adolescent and adult participants by self-report, in children by parental and teacher report. From the ANTR databases, six waves of data collection were relevant for this study, as they contained the aggression scale from the Adult Self-Report (ASR, Achenbach and Rescorla 2003). From these six waves of data collection, we selected all participants aged 12–70 years. The data were collected around 1991, 1995, 1997, 2000, 2009, and 2013. Twins and their siblings were asked to participate from 1991 onwards, and a selected group of their spouses from 2000. Parents of twins were invited to complete the ASR in 2009 and 2014. With each wave of data collection new families could enter the ANTR.
In YNTR twin pairs, three waves of data collection between 2004 and 2015 included aggression data from the Youth Self-Report (YSR; Achenbach and Rescorla 2001). Twins were first approached when they were aged 12 to 18 and their siblings were invited to take part at the same time (see van Beijsterveldt et al. 2013). Thus, A family from the YNTR may have contributed YSR aggression data for the first time in 2006 from 16-year old twins and an additional sibling, and in 2009 through the ANTR survey 5, when the twins were 19-years old. Table 1 presents an overview of the surveys and sampling description (see also; Boomsma et al. 2002, 2006; Ligthart et al. 2019). Research ethics committee approval was received for each survey.
Our dataset consisted of 69,465 measures from 40,400 participants, from 15,437 families (see Tables 2, 3). Around 52% of the participants come from either monozygotic twin pairs (9228; 22.8%) or dizygotic pairs (11,760; 29.1%). The remainder of the participants are twins from incomplete pairs, siblings, parents, spouses or offspring of twins. Approximately 43% of all participants completed more than one survey, 18% completed more than two surveys. Because not all NTR participants were invited for all surveys, as described above, the composition of the sample differs over time.
Measurements
All participants completed Achenbach System of Empirically Based Assessment self-report questionnaires (ASEBA; Achenbach et al. 2017), either the Youth Self-Report (YSR; Achenbach and Rescorla 2001) or the Adult Self-Report (ASR; Achenbach and Rescorla 2003). In the early ANTR surveys, the YASR (Young Adult Self Report) was administered.
A score based on nine overlapping items that were present in all surveys was analyzed (see Table 4). All items were scored on a three-level scale: 0 = never, 1 = sometimes, 2 = often. Aggression scores were defined by Item-Response Theory (IRT; Embretson and Reise 2000) and calculated with the Generalized Partial Credit Model (GPCM) in R, with the mirt package (Chalmers 2012). GPCM is an Item Response Theory model, developed to analyze polytomous data. This IRT-aggression score has benefits over a simple sum-score, because it appropriately weights the relative contributions of individual items to a scale with a more favorable distribution.
Analyses
We fit a three-level mixed effects model (e.g. Snijders and Bosker 2012) to the longitudinal IRT data, with the package nlme (Pinheiro et al. 2017) in R (version 3.4.2; R Core Team 2017). We opted for a multilevel modeling approach because we are interested in the effects of age and time on aggression, and the within and between family variance of these trends. By modeling the within and between family variance we get an estimate of the extent to which family characteristics play a role in individual variance in aggression trends. The family characteristics are in this case a latent (i.e. not observed) construct that embodies all factors that lead to more similarities within- than between families. The mixed modeling approach allows for this, while also considering dependency between repeated measures.
Our model accounts for three levels of variance that are present in the data, namely variation between repeated measures, variation between individuals, and variation between families. The model is called a mixed effects model because both fixed and random effects are estimated. Fixed effects are population level effects that apply to each measure. Random effects are effects that allow for variation of effects at group level. Minică et al. (2015) showed that a similar approach generated correct standard errors in a design with varying levels of family resemblance. In both models we use z-scores of the continuous predictors (age and time). Gender is included as a fixed effect to assess gender differences in overall aggression levels and time and age trends. An autoregressive correlation structure is applied in the model at the individual level to account for dependence between measures. The autoregressive correlation structure assumes that measures in closer temporal proximity are more strongly related than more distant measures. A correlation between the random effects is calculated, giving an indication of the association between the estimated random intercept and random slope for time. Explained variance, R2, is calculated with the package MuMIn (Barton 2018) in R.
The outcome (aggression) is predicted by an intercept that can vary for each individual in each family, slopes for time and age that can vary for each family, a slope for gender, and non-linear slopes for age (age2) and time (time2). Parameter estimates with random effects are underscored:
In this notation, Ytij is the aggression outcome for measurement t in individual i in family j, β0ij is the intercept for each individual i in family j, β1j is the linear slope for age in family j, β2 is the non-linear slope for age, β3j is the linear slope for time in family j, β4 is the non-linear slope for time, β5 is the slope for gender, and εtij is an error term for each measurement t, for individual i, in family j. All first order interactions are included in the model. The random effect for the intercept for each individual is estimated by the global intercept and a random effect for individual i, and makes up Level 2 of our model:
This random term accounts for dependency of repeated measures within individuals. The random effect for the intercept for each family is estimated by the individual intercept and a random variable for family j. The random effects for the slopes of time and age for each family are estimated by the global slopes for time and age, and random effects for family j. These family-level effects form Level 3 of our model:
The random family effects, for the intercept and the slope of time and age, are the focus of our study. By specifying random effects in our model, variance is partitioned into within—and between family variance components. The model estimates of the random effects for families are a measure of between family variance. This informs us on how much individuals from different families differ in their intercept and slopes for time and age, compared to family members. Thus, the random intercept for families gives an indication to what extent aggression levels cluster within families. Similarly, the random effects for the slopes of time and age give an indication to what extent these effects cluster within families. No discrimination is made between different family relations when estimating random family effects. Thus, the family effects reflect overall resemblance between family members, including partners, siblings, parent–offspring or twins. The correlation between the random parameter estimates gives an indication of how aggression scores (high or low) are related to the increase or decrease of these scores over time and age. We tested the reliability of our model in estimating variation at the family level in both intercept and slopes with simulated data. The model was effective in estimating variation between families. Type I error rates for the random intercept and random slopes were investigated in a subset of 420 individuals from 100 families. Simulations were run 1000 times, both with a normally distributed outcome and with the empirical IRT distribution in the outcome. Type I error rates were similar for both outcomes, but slightly lower than expected, ranging from 1.2 to 1.5%.
The effect of time reflects both period and cohort effects. To get an idea of the relative importance of period and cohort effects, we investigate linear trends within four age categories: 12–25 years, 26–40 years, 41–55 years, and 56–70 years. These four age ranges represent four birth cohorts in our data. If change in aggression in our data would be due to changes in specific birth cohorts, we would see clear differences in aggression trends over time between the four cohorts. With this simple method we aim to establish whether change is cohort-specific or due to period effects. We fitted the linear relation between time and aggression within the four groups with the lm method in ggplot2 (Wickham 2009).
Results
Our dataset consisted of 69,465 aggression measures collected between 1991 and 2015 from 40,400 participants (58% female), who were part of 15,437 families (see Tables 2, 3). On average, aggression declined between 1991 and 2015, by 0.87 SD (Fig. 1). The downward trend was found for both sexes, with women scoring on average 0.08 SD higher than men, which can be explained by higher scores on items related to non-physical aggression (Table 4). Figure 2 shows that aggression decreased over the beginning of the life course, from age 12 to age 34, by 0.94 SD. From age 34 to age 70, only a slight increase in aggression, of 0.06 SD, was visible in males. We are reluctant to interpret this slight increase, as this could be due to overfitting because of smaller sample size at old ages.
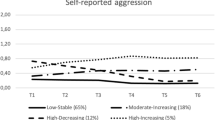
Because the model does not allow for simultaneous analysis of time and cohort effects, the results did not inform us on which of these effects drove the effect of time. To get an idea of the relative importance of period and cohort effects, we plotted the linear effect of time on aggression within four age categories; 12–25 years, 26–40 years, 41–55 years, and 56–70 years (Fig. 3). A clear downward trend was visible within each age category. This suggested that period effects predominantly drove the downward trend, across ages and birth-cohorts.
The fixed and random effects together explained 52% of the variance in aggression, with the fixed effects alone explaining 14% of the variance in aggression, i.e. random effects accounted for the largest part of the variance in aggression measures. The random effects included a random intercept for individuals to account for dependence between repeated measures, and a random intercept and random slopes for time and age to investigate variation between, and clustering within families. Table 5 shows the estimates for the fixed and random effects.
By including random effects for families, variance was partitioned into within and between family variance. The random intercept for families is a measure of between family variance: SD = 0.302, Δχ2(3) = 1333.739, p < 0.001. This indicated that variance in aggression levels between individuals from different families was larger than the variance between individuals within the same family, or stated otherwise, that aggression levels clustered within families.
Our main interest is in the variance of the effects of time and age, which were also partitioned into within- and between family variance components. Between family variance of the effect of time on aggression was estimated by a random slope for time: SD = 0.116, Δχ2(3) = 96.825, p < 0.001, indicating that variance in the effect of time on aggression between individuals from different families was larger than the variance between individuals within the same family. Thus, members of the same family resembled each other in the magnitude and direction of the effect of time. Moreover, the model with a random slope for time for families fit significantly better than the same model with a random slope for time for individuals, Δχ2(1) = 30.592, p < 0.001. The estimate of the random effect of time was not related to the estimate of the random intercept for families, r = 0.039, meaning that these estimates are interpretable separately.
Between family variance of the effect of age on aggression was estimated by a random slope for age: SD = 0.102, Δχ2(3) = 416.744, p < 0.001, indicating family resemblance in age effects. We could not compare the fit of the model with a random age effect for family with a model with a random age effect for individuals, as the model with a random age effect for individuals did not converge. Contrary to the random effect of time, the estimate of the random effect of age was negatively associated with the estimate of the random intercept for families: r = −0.912, making an interpretation of the random effect of age separate from the random intercept impossible. This is a result of a strong relationship between age and aggression. Families with higher aggression scores are more likely to have a stronger decrease over age.
Discussion
We investigated whether trends in aggression cluster within families, making this the first study that combines the analyses of trends and family clustering of aggressive behavior. We investigated whether the effects of time and age on aggression cluster within families, after first establishing that a downward trend in aggressive behavior is replicated in the Netherlands between 1991 and 2015.
Levels of self-reported aggression were calculated by IRT (Embretson and Reise 2000). Overall, IRT aggression scores decreased by 0.87 SD from 1991 to 2015. Our model did not allow for simultaneous estimates of period and cohort effects, but aggression also decreased within separate age categories, suggesting that mainly period effects play an important role: changes in society that affects the entire population across ages and birth-cohorts. If cohort effects were more important, we would not expect a similar decrease within different age categories. Identifying which specific period effects drive the trend we see is not an easy feat. It is likely that a large number of diverse factors play a role. Farrell et al. (2014) reviewed 17 hypotheses to identify the cause for the observed drop in criminal and violent behavior. They included hypotheses related to increased policing and incarceration rates, lead poisoning, declining hard drug markets, technological advances, increased security and economic circumstances, but did not find much proof to either debunk or corroborate the hypotheses. It was beyond the scope of the current study to directly test specific factors that may drive the observed time effects, but this remains an important topic for criminological research.
In the mixed-effects model, variance in aggression levels was partitioned into within- and between family variance. We found that aggression levels cluster within families: family members are more alike in aggressive behavior than individuals from different families. This is in line with multiple studies on aggressive, criminal and antisocial behavior (Besemer et al. 2017; Margolin et al. 2016; Repetti et al. 2002; van de Weijer et al. 2014; Veroude et al. 2016). Factors shared by family members thus may help in explaining individual differences in aggression, and previous research has identified several of those factors that likely play a role in driving individual differences in aggression, including genetic risk, low income, harsh parenting, and family violence (Margolin et al. 2016; Odintsova et al. 2019; Repetti et al. 2002; Labella and Masten 2018). We added a new element to family analyses, namely the analyses of trends and family clustering. We investigated whether the effects of time and age on aggression also cluster within families. Variance in slopes was partitioned into within—and between family variance. We found that for the effect of time, family members are more alike in trends over time compared to unrelated individuals. So, even though at the population level, average scores are declining, not everyone in society is benefitting from this trend. There are two ways to interpret these results. Risk factors shared by family members could change over time, leading to a similar effect on family members. Alternatively, societal effects may be moderated by family factors, leading to different outcomes in different families. Under both scenarios and interpretations, family factors are not only important in understanding differences in aggression levels, but also in understanding change over time. The overall downward trend is, thus, not necessarily beneficial for everyone. The familial resemblance in how far individuals diverge from the overall trend, indicates that certain families or groups are differentially affected by changes in society. One possible mechanism could be variation in the benefits of economic progress. Not only is poverty a well-established risk factor for aggression, but also differences in ‘relative poverty’: a poor family, living in close proximity to a more wealthy family, has a further increased risk (Odgers et al. 2015; Nieuwenhuis et al. 2017). Thus, if other families in the neighborhood benefit from economic progress, the effect of poverty on aggression may increase.
Regardless of the mechanisms behind the clustering of trends, our study provides strong indications that even with beneficial changes in society, we should not lose focus on families when trying to understand or change aggressive behavior. Families are important in understanding the mechanisms that drive aggressive behavior now, and in the future. Because the estimate of the random slope for time was not related to the estimate of the random intercept, factors that lead to clustering of aggression levels within families may not be the same factors that lead to clustering of time trends. Risk factors for aggression that reside in the family system, may not be static but dynamic, changing over time as society as a whole changes. Policymakers should be aware that theories on aggression might not translate over time, and that the importance of specific factors may change as society changes.
The age-aggression curve observed in the present study resembles previous results, with a decrease in aggression over age that gradually levels off from early adulthood onwards (Alink et al. 2006; Cairns et al. 1989; Cairns and Cairns 1994; Tremblay 2010; Tremblay et al. 2004). We also found that variance between non-related individuals was larger than variance between family members for the effect of age, indicating clustering of age effects within families. Liu et al. (2013) discuss risk factors for aggression pertaining to several developmental stages. They conclude that different risk factors, of which several may be shared within families, have unique influences at specific ages. Thus, familial risk factors not only contribute to overall levels of aggression, but also to the development of aggression over age. In line with this finding, Eley et al. (2003) also showed that continuity of aggressive and non-aggressive antisocial behavior in childhood was mediated by genetic and shared environmental factors. Our results indicated that the estimate of the random slope for age, reflecting clustering of age effects in families, was dependent on the estimate of the random intercept, reflecting clustering of aggression levels in families. This indicates that we cannot interpret the clustering of age effects separately from the overall aggression levels. In other words, high levels of aggression are related to a large age effect, presumably because starting levels are higher, and lower levels are related to a smaller age effect.
Results further indicate slightly higher overall aggression in females than in males. A close inspection of the aggression scores in males and females revealed that this difference was mainly because females scored higher on items related to non-physical or relational aggression. Previous research is inconsistent on gender differences in indirect aggression. For example, Crick and Grotpeter (1995) found that relational aggression was more prevalent among adolescent girls than boys, and Thomson and colleagues found similar higher levels of indirect aggression in adult females compared to males. However, in a large meta-analysis on 148 studies on child and adolescent aggression, Card et al. (2008) found trivial gender differences in what they call ‘indirect’ aggression. Several factors may cause gender differences in aggression, including biological factors, for example differences in physical strength (Björkqvist 1994) and hormonal differences (Björkqvist 2018); and socio-cultural factors, for example different role models (Underwood et al. 2008), differences in the number and closeness of social relationships (Maccoby 1990) and differences in the social acceptance of aggression (Underwood 2003). We did not find clear gender differences in trends in aggression over time and age, indicating that the factors driving the overall downward trend we see over time, affects males and females similarly.
Although our study provides important new insights on the development of aggressive behavior over time, it also has several limitations. Our longitudinal study design is inevitably accompanied by drop-out, both ‘by design’, because not all participants were asked to take part in all surveys, and due to nonresponse. Nonresponse may partly explain the negative aggression trend that we found, if more aggressive respondents are more likely to drop out than less aggressive respondents. Additional analyses showed the effect of drop-out to be small, if not absent. Participants with multiple measures scored slightly lower on aggression in most age categories, however, our study allows for new inflow of participants at each wave, so that the effects of non-response are not limited to later surveys. Analyses with only the first measure of each participant yielded similar results to those reported, indicating that the downward trend is not driven by repeated measures of less aggressive individuals.
A second limitation is that the adult self-report (ASR) surveys slightly differ from the youth self-report (YSR) surveys. To ensure comparability of measures, we included the nine aggression items that are the same in both surveys.
Finally, family environments may increase the likelihood of displaying aggressive behavior, because of close proximity and more interaction between individuals compared to people living alone. Since we analyzed family data, this may have slightly biased the results. To assess this possible bias, we tested for differences in aggression levels between twins and their non-twin siblings, and found no significant differences within 10-year age groups. Moreover, twin pairs may interact more closely with each other than siblings. However, there is no evidence for an increase in similarity between twins compared to non-twin siblings when using self-report measures (Plomin and Daniels 2011; Mark et al. 2017). We also reran the analyses without monozygotic twins, and found similar results, indicating that the relatively small number of monozygotic twin pairs did not drive the effects we see.
In summary, we replicated that aggression decreases in the period between 1991 and 2015, with an average decline in aggression scores of 0.87 SD. The decrease over time was present across all ages in the sample. Aggression clustered within families. Thus, factors shared by family members can help explain individual differences in aggression. The effect of time on aggression also cluster within families. This indicates that not all individuals follow the beneficial trend we see in the population, and demonstrates that family factors are important in understanding and explaining differences between individuals in their aggression development over time.
Data Availability
Data and analysis code are available upon request (please contact the first author).
References
Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA (2001) Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms & profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth & Families, Burlington
Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA (2003) Manual for the ASEBA adult forms & profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth & Families, Burlington
Achenbach TM, Ivanova MY, Rescorla LA (2017) Empirically based assessment and taxonomy of psychopathology for ages 1½-90+ years: developmental, multi-informant, and multicultural findings. Compr Psychiatry 9:4–18
Alink LR, Mesman J, Van Zeijl J, Stolk M, Juffer F, Koot H, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, Van Ijzendoorn M (2006) The early childhood aggression curve: development of physical aggression in 10- to 50-month-old children. Child Dev 77(4):954–966
Barton K (2018) MuMIn: multi-model inference. R package version 1.40.4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn. Accessed 15 Aug 2021
Beatton T, Kidd MP, Machin S (2018) Gender crime convergence over twenty years: evidence from Australia. Eur Econ Rev 109:275–288
Berkowitz L (1993) Aggression: its causes, consequences, and control. McGraw-Hill, New York
Besemer S, Ahmad S, Hinshaw S, Farrington D (2017) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the intergenerational transmission of criminal behavior. Aggress Violent Beh 37:161–178
Björkqvist K (1994) Sex differences in physical, verbal, and indirect aggression: a review of recent research. Sex Roles 30(3–4):177–188
Björkqvist K (2018) Gender differences in aggression. Curr Opin Psychol 19:39–42
Boomsma DI, Vink JM, van Beijsterveldt CEM, de Geus EJC, Beem AL, Mulder EJCM, Derks EM, Riese H, Willemsen GA, Bartels M, van Baal GCM (2002) Netherlands Twin Register: a focus on longitudinal research. Twin Res 5:401–406
Boomsma DI, de Geus EJC, Vink JM, Stubbe JH, Distel MA, Hottenga JJ, Posthuma D, Van Beijsterveldt TC, Hudziak JJ, Bartels M, Willemsen G (2006) Netherlands Twin Register: from twins to twin families. Twin Res Hum Genet 9:849–857
Cairns RB, Cairns BD (1994) Life Lines and risks: pathways of youth in our time. Cambridge University Press, New York
Cairns R, Cairns B, Neckerman H, Ferguson L, Gariépy J (1989) Growth and aggression: I. Childhood to early adolescence. Dev Psychol 25(2):320–330
Card NA, Stucky BD, Sawalani GM, Little TD (2008) Direct and indirect aggression during childhood and adolescence: a meta-analytic review of gender differences, intercorrelations, and relations to maladjustment. Child Dev 79(5):1185–1229
Chalmers RP (2012) mirt: a multidimensional item response theory package for the R environment. J Stat Softw 48(6):1–29
Crick NR, Grotpeter JK (1995) Relational aggression, gender, and social-psychological adjustment. Child Dev 66:710–722
Crick NR, Werner NE, Casas JF, O’Brien KM, Nelson DA, Grotpeter JK, Markon K (1999) Childhood aggression and gender: a new look at an old problem. In: Bernstein D (ed) Nebraska symposium on motivation. Gender and motivation, vol 45. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, pp 75–141
Dodge KA, Pettit GS (2003) A biopsychosocial model of the development of chronic conduct problems in adolescence. Dev Psychol 39(2):349
Eley T, Lichtenstein P, Moffitt T (2003) A longitudinal behavioral genetic analysis of the etiology of aggressive and nonaggressive antisocial behavior. Dev Psychopathol 15(2):383–402
Embretson SE, Reise SP (2000) Item response theory for psychologists. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah
Fabio A, Loeber R, Balasubramani G, Roth J, Fu W, Farrington D (2006) Why some generations are more violent than others: assessment of age, period, and cohort effects. Am J Epidemiol 164(2):151–160
Farrell G, Tilley N, Tseloni A (2014) Why the crime drop? Crime Justice 43(1):421–490
Farrington DP, Gaffney H, Ttofi MM (2017) Systematic reviews of explanatory risk factors for violence, offending, and delinquency. Aggress Violent Behav 33:24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2016.11.004
Frøyland LR, von Soest T (2018) Trends in the perpetration of physical aggression among Norwegian adolescents 2007–2015. J Youth Adolesc 47(9):1938–1951
Guerra NG, Leidy MS (2008) Lessons learned: recent advances in understanding and preventing childhood aggression. Adv Child Dev Behav 36:287–330
Hess NH, Hagen EH (2006) Sex differences in indirect aggression: psychological evidence from young adults. Evol Hum Behav 27(3):231–245
Jolliffe D, Farrington DP, Piquero AR, MacLeod JF, van de Weijer S (2017) Prevalence of life-course-persistent, adolescence-limited, and late-onset offenders: a systematic review of prospective longitudinal studies. Aggress Violent Behav 33:4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2017.01.002
Kann L, McManus T, Harris WA, Shanklin SL, Flint KH, Hawkins JL, Queen B, Lowry R, Olsen EOM, Chyen D, Zaza S (2016) Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States, 2015. MMWR Surveill Summ 65(6):1–174
Karriker-Jaffe K, Foshee V, Ennett S, Suchindran C (2008) The development of aggression during adolescence: sex differences in trajectories of physical and social aggression among youth in rural areas. J Abnorm Child Psychol 36(8):1227–1236
Labella M, Masten A (2018) Family influences on the development of aggression and violence. Curr Opin Psychol 19:11–16
Laub JH, Sampson RJ (2006) Shared beginnings, divergent lives: delinquent boys to age 70. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Ligthart L, van Beijsterveldt CEM, Kevenaar ST, de Zeeuw E, van Bergen E, Bruins S, Pool R, Helmer Q, van Dongen J, Hottenga JJ, Boomsma DI (2019) The Netherlands Twin Register: longitudinal research based on twin research and twin-family designs. Twin Res Hum Genet 22(6):623–636
Liu J, Lewis G, Evans L (2013) Understanding aggressive behaviour across the lifespan. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs 20(2):156–168
Loeber R, Stouthamer-Loeber M (1998) Development of juvenile aggression and violence. Some common misconceptions and controversies. Am Psychol 53(2):242–259
Lorenz K (1966) Das sogenannte böse: Zur naturgeschichte der aggression. Borotha-Schoeler, Vienna
Maccoby EE (1990) Gender and relationships: a developmental account. Am Psychol 45:513–520
Margolin G, Ramos M, Timmons A, Miller K, Han S (2016) Intergenerational transmission of aggression: physiological regulatory processes. Child Dev Perspectives 10(1):15–21
Mark KM, Pike A, Latham RM, Oliver BR (2017) Using twins to better understand sibling relationships. Behav Genet 47(2):202–214
Minică CC, Dolan CV, Kampert MM, Boomsma DI, Vink JM (2015) Sandwich corrected standard errors in family-based genome-wide association studies. Eur J Hum Genet 23(3):388–394
Neugebauer R, Hoek HW, Susser E (1999) Prenatal exposure to wartime famine and development of antisocial personality disorder in early adulthood. JAMA 282(5):455–462
Nieuwenhuis J, van Ham M, Yu R, Branje SJT, Meeus WHJ, Hooimeijer P (2017) Being poorer than the rest of the neighbourhood: relative deprivation and problem behaviour of youth. J Youth Adolesc 46(9):1891–1904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-017-0668-6
Odgers CL, Donley S, Caspi A, Bates CJ, Moffitt TE (2015) Living alongside more affluent neighbors predicts greater involvement in antisocial behavior among low-income boys. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 56(10):1055–1064
Odintsova V, Roetman P, Ip HF, Pool R, Van D, Tona K, Vermeiren RR, Boomsma DI (2019) Genomics of human aggression: current state of genome-wide studies and an automated systematic review tool. Psychiatr Genet 29(5):170–190
Pickett W, Molcho M, Elgar F, Brooks F, De L, Rathmann K, Ter Bogt TF, Gabhainn SN, Sigmundová D, de Matos MG, Craig W, Currie C (2013) Trends and socioeconomic correlates of adolescent physical fighting in 30 countries. Pediatrics 131(1):18–26
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, R Core Team (2017) nlme: linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R package version 3.1–131. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nlme
Plomin R, Daniels D (2011) Why are children in the same family so different from one another? Int J Epidemiol 40(3):563–582
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Repetti R, Taylor S, Seeman T (2002) Risky families: Family social environments and the mental and physical health of offspring. Psychol Bull 128(2):330–366
Sampson RJ, Laub JH (1994) Urban poverty and the family context of delinquency: a new look at structure and process in a classic study. Child Dev 65(2):523–540
Snijders TAB, Bosker RJ (2012) Multilevel analysis: an introduction to basic and advanced multilevel modeling, 2nd edn. SAGE, London
Thomson ND, Bozgunov K, Psederska E, Vassileva J (2019) Sex differences on the four-facet model of psychopathy predict physical, verbal, and indirect aggression. Aggress Behav 45(3):265–274. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21816
Tolan PH, Dodge K, Rutter M (2013) Tracking the multiple pathways of parent and family influence on disruptive behavior disorders. In: Tolan PH, Leventhal B (eds) Disruptive behavior disorders. Springer, New York, pp 161–191
Tremblay RE (2010) Developmental origins of disruptive behaviour problems: the ‘original sin’ hypothesis, epigenetics and their consequences for prevention. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 51(4):341–367
Tremblay RE, Nagin DS, Séguin JR, Zoccolillo M, Zelazo PD, Boivin M, Perusse D, Japel C (2004) Physical aggression during early childhood: trajectories and predictors. Pediatrics 114(1):43–50
Tuvblad C, Baker LA (2011) Human aggression across the lifespan: genetic propensities and environmental moderators. Adv Genet 75:171–214
Underwood MK (2003) Social aggression among girls. Guilford, New York
Underwood MK, Beron KJ, Gentsch JK, Galperin MB, Risser SD (2008) Family correlates of children’s social and physical aggression with peers: negative interparental conflict strategies and parenting styles. Int J Behav Dev 32(6):549–562
United States Department of Justice, Federal Bureau of Investigation (2019) Crime in the United States, 2019. Retrieved 22 March 2021, from https://ucr.fbi.gov/crime-in-the-u.s/2019/crime-in-the-u.s.-2019
van Beijsterveldt CE, Groen-Blokhuis M, Hottenga JJ, Franić S, Hudziak JJ, Lamb D, Huppertz C, De Zeeuw E, Nivard M, Schutte N, Boomsma DI (2013) The Young Netherlands Twin Register (YNTR): longitudinal twin and family studies in over 70,000 children. Twin Res Hum Genet 16(1):252–267
van de Rakt M, Nieuwbeerta P, De Graaf ND (2008) Like father, like son: the relationships between conviction trajectories of fathers and their sons and daughters. Br J Criminol 48(4):538–556
van de Weijer SGA, Bijleveld CCJH, Blokland AAJ (2014) The intergenerational transmission of violent offending. J Fam Violence 29(2):109–118
Veroude K, Zhang-James Y, Fernàndez-Castillo N, Bakker M, Cormand B, Faraone S (2016) Genetics of aggressive behavior: an overview. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 171(1):3–43
Wickham H (2009) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer, New York
Yu JJ, Gamble WC (2008) Familial correlates of overt and relational aggression between young adolescent siblings. J Youth Adolesc 37(6):655–673
Acknowledgements
We thank all the twin families registered with the Netherlands Twin Register for their participation. CvdL was supported by the Amsterdam Law and Behavior Institute (A-LAB; Vrije Universtiteit, Amsterdam). SvdW was supported by NWO-Grant 451-16-014. Data collection was made possible by multiple grants from the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO): 575-25-006, 480-04-004, 904-61-090, 904-61-193, 400-05-717, 311-60008, SPI 56-464-14192 and the Avera Institute for Human Genetics. We gratefully acknowledge Grant NWO 480-15-001/674: Netherlands Twin Registry Repository: researching the interplay between genome and environment. M.G.N. is supported by ZonMw grant: ‘Genetics as a research tool: a natural experiment to elucidate the causal effects of social mobility on health’ (pnr: 531003014) and ZonMw project: ‘Can sex- and gender-specific gene expression and epigenetics explain sex-differences in disease prevalence and etiology?’ (pnr: 849200011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
The procedures used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics committee approval was obtained separately for each survey: ANTR Survey 1: Health, lifestyle and personality: A study of adolescent twins and their parents. Netherlands Heart Foundation and NWO-900-562-137; PI Boomsma; METC: 91/156. ANTR Survey 2/3: Genetics of alcohol and nicotine use. VU-USF 96/22; PI Boomsma; METC 96/164. ANTR Survey 4: The genetic basis of anxiety and depression: mapping quantitative trait loci in humans. NWO 904-61-090; PI Boomsma; METC 96/164. ANTR Survey 5: Genetics of individual differences in smoking initiation and persistence. NWO 985-10-002; PI Boomsma; METC 98/222. ANTR Survey 8: Genetic determinants of risk behavior in relation to alcohol use and alcohol use disorder: a developmental perspective. ZonMW (Addiction) Project nr: 31160008; PI Boomsma; METC: 2008/244. ANTR Survey 10: Beyond the Genetics of Addiction. ERC Starting grant 284167 JM Vink; METC 2012/433. YSR: adolescent survey: Genetic and Family influences on Adolescent Psychopathology and Wellness (Bartels, Boomsma). NWO-463-06-001; METC: NTR25-05-2007.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
van der Laan, C.M., van de Weijer, S.G.A., Nivard, M.G. et al. Familial Clustering of Trends in Aggression. J Quant Criminol 39, 1–19 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10940-021-09523-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10940-021-09523-8