Abstract
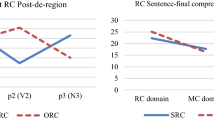
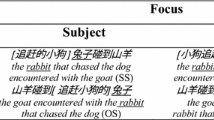
We investigated the role of number agreement on verb and of animacy in the comprehension of subject and object relative clauses in 51 monolingual Italian-speaking children, mean age 9:33, tested through a self-paced listening experiment with a final comprehension question. A digit span test and a listening span test were also administered to examine the role of memory in comprehension. Subject relative clauses were easier to comprehend than object relative clauses; animacy of the relative clause head improved comprehension of object relative clauses; memory, as measured by the digit span test, modulates comprehension of object relative clauses, both with animate and inanimate heads, as shown in response accuracy. Although all children process number agreement morphology on the verb, only some perform a correct reanalysis, as shown by the accuracy measures. We argue that number agreement disambiguation is particularly taxing for children, as it provides a negative symptom in the sense of Fodor and Inoue (J Psycholinguist Res 29(1):25–36, 2000) and reanalysis requires them to hold two dependencies in memory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adani, F. (2008). The role of features in relative clause comprehension: A study of typical and atypical development. PhD. Dissertation, University of Milano-Bicocca.
Arosio, F., Adani, F., & Guasti M. T. (2009) Grammatical features in the comprehension of Italian Relative Clauses by children. In A. Gavarrò, et al. (Eds.), Merging features: Computation, interpretation and acquisition. Oxford University Press
Baddeley A. D. (1986) Working memory. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Baddeley A. D., Eysenck M. W., Anderson M. C. (2009) Memory. Psychology Press, Hove
Baddeley A. D., Hitch G. J. (1974) Working memory. In: Bower G. A. (eds) The psychology of learning and motivation: Vol. 8 Advances in research and theory. Academic Press, San Diego
Bader M., Bayer J. (2006) Case and linking in language comprehension: Evidence from German. Springer, Berlin
Becker M. (2006) There began to be a learnability puzzle. Linguistic Inquiry 37: 441–456
Brainard D. H. (1997) The Psychophysics Toolbox. Spatial Vision 10: 433–436
Booth J. R., Mac Whinney B., Harasaki Y. (2000) Developmental differences in visual and Auditory processing of complex sentences. Child Development 71(4): 981–1003
Bornkessel I. D., Fiebach C. J., Friederici A. D. (2001) On the cost of syntactic ambiguity in human language comprehension: an individual differences approach. Cognitive Brain Research 21: 11–21
Ciccarelli, L. (1998). Comprensione del linguaggio, dei processi di elaborazione e memoria di lavoro: uno studio in età prescolare. PhD dissertation, University of Padua, Italy.
Daneman M., Carpenter P. A. (1980) Individual differences in working memory and reading. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behaviour 19: 450–466
De Villiers J., Tager-Flusberg H., Hakuta K., Cohen M. (1979) Children’s comprehension of relative clauses. Journal of Psycholinguistics Research 8: 499–518
De Vincenzi M. (1991) Syntactic parsing strategies in Italian. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Dixon, P. (2008). Models of accuracy in repeated-measures designs. Journal of Memory and Language. doi:10.1016/j.jml.2007.11.004.
Felser C., Marinis T., Clahsen H. (2003) Children’s processing of ambiguous sentences: A study of relative clause attachment. Language Acquisition 11: 127–163
Ferreira F., Anes M. (1994) Why study spoken language?. In: Gernsbacher M. A. (eds) Handbook of psycholinguistics. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 33–56
Ferreira F., Henderson J. M., Anes M. D., Weeks P. A. Jr., McFarlane D. K. (1996) Effects of lexical frequency and syntactic complexity in spoken language comprehension: Evidence from the auditory moving window technique. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 22: 324–335
Fodor D. J., Inoue A. (2000) Syntactic features in reanalysis: Positive and negative symptoms. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 29(1): 25–36
Frauenfelder U., Segui J., Mehler J. (1980) Monitoring around the relative clause. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behaviour 19: 328–337
Frazier L., Flores d’Arcais G. (1989) Filler-driven parsing: A study of gap-filling in Dutch. Journal of Memory and Language 28: 331–344
Friederici A. D. (1997) Diagnosis and reanalysis: Two processing steps the brain may differentiate. In: Fodor J., Ferreira F. (eds) Reanalysis in sentence processing. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Friederici A. D., Steinhauer K., Mecklinger A., Meyer M. (1998) Working memory constraints on syntactic ambiguity resolution as revealed by electrical brain responses. Biological Psychology 47: 193–221
Friedmann N., Novogrodsky R. (2004) The acquisition of relative clause comprehension in Hebrew: A study of SLI and normal development. Journal of Child Language 31: 661–681
Gaulin C., Campbell T. (1994) Procedure for assessing verbal working memory in normal school-age children: Some preliminary data. Perceptual and Motor Skills 79: 55–64
Gibson E. (1998) Linguistic complexity: Locality of syntactic dependencies. Cognition 68: 1–76
Gordon P. C., Hendrick R., Johnson M. (2001) Memory interference during language processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 27: 1411–1423
Guasti M. T., Cardinaletti A. (2003) Relative clause formation in romance child production. Probus 15: 47–88
Guasti M. T., Stavrakaki S., Arosio F. (2007) Number and Case in the comprehension of relative clauses: Evidence from Italian and Greek. In: Gavarrò A., Freitas M. J. (eds) Language acquisition and development: Proceedings of GALA 2007. Cambridge Scholar Press, Newcastle
Harris A. C. (1981) Georgian syntax. A study in relational grammar. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
King J., Just M. A. (1991) Individual differences in syntactic processing: The role of working memory. Journal of Memory and Language 30: 580–602
King J. W., Kutas M. (1995) Who did what and when? Using word- and causal- level ERPs to monitor working memory usage in reading. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 7(3): 376–395
Little R. C., Milliken G. A., Stroup W. W., Wolfinger R. D. (1996) SAS system for mixed models. SAS Publishing, North Carolina
Love T. E. (2007) The processing of non-canonically ordered constituents in long distance dependencies by pre-school children: A real-time investigation. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 36: 191–206
Luce R. D. (1986) Response times: Their role in inferring elementary mental organization. Oxford University Press, New York
MacWhinney B., Pléh C. (1988) The processing of restrictive relative clauses in Hungarian. Cognition 29: 95–141
Mak W. M., Vonk W., Schriefers H. J. (2002) The influence of animacy on relative clause processing. Journal of Memory and Language 47(1): 50–68
Mak, W. M., Vonk, W., & Schriefers, H. J. (2008) Discourse structure and relative clause processing. Memory & Cognition (Vol. 36, pp. 170–181). Utrecht: Ms. University of Utrecht
McKee C., Nicol J., McDaniel D. (1993) Children’s application of binding during sentence processing. Language and Cognitive Processes 8(3): 265–290
Meng M., Bader M. (2000) Mode of disambiguation and garden path strength: An investigation of subject–object ambiguities in German. Language and Speech 43: 43–74
Palladino P. (2005) Uno strumento per esaminare la memoria di lavoro verbale in bambini di scuola elementare: taratura e validità. Psicologia clinica dello sviluppo 1: 129–150
Papagno C., Cecchetto C., Reati F., Bello L. (2007) Processing of syntactically complex sentences relies on verbal short-term memory. Evidence from a STM patient. Cognitive Neuropsychology 24: 292–311
Pelli D. G. (1997) The VideoToolbox software for visual psychophysics: Transforming numbers into movies. Spatial Vision 10: 437–442
Rizzi L. (1982) Issues in Italian syntax. Foris Publications, Dordrecht
Roberts L., Marinis T., Felser C., Clahsen H. (2007) Antecedent priming at trace positions in children’s sentence processing. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 36: 175–188
Schriefers H., Friederici A. D., Kühn K. (1995) The processing of locally ambiguous relative clauses in German. Journal of Memory and Language 8: 499–520
Sekerina I., Stromswold K., Hestvik A. (2004) How do adults and children process referentially ambiguous pronouns?. Journal of Child Language 31: 123–152
Traxler M. J., Morris R. K., Seely R. E. (2002) Processing subject and object relative clauses: Evidence from eye-movements. Journal of Memory and Language 47: 69–90
Vos S. H., Gunter T. C., Schriefers H., Friederici A. D. (2001) Syntactic parsing and working memory: The effects of syntactic complexity, reading span, and concurrent load. Language and Cognitive Processes 16: 65–103
Waters G. S., Caplan D. (1996) Processing resource capacity and the comprehension of garden path sentences. Memory and Cognition 24: 342–355
Waters G. S., Caplan D. (1996) The measurement of verbal working memory capacity and its relation to reading comprehension. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 49: 51–79
Wittek A., Tomasello M. (2005) German-speaking children’s productivity with syntactic constructions and case morphology: Local cues help locally. First Language 25: 103–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arosio, F., Guasti, M.T. & Stucchi, N. Disambiguating Information and Memory Resources in Children’s Processing of Italian Relative Clauses. J Psycholinguist Res 40, 137–154 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-010-9160-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-010-9160-0